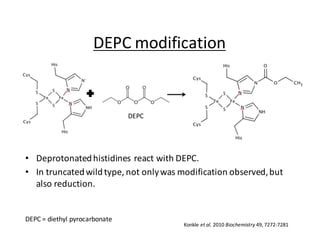
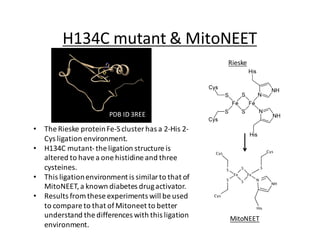
The document summarizes research on the H134C mutant of the Thermus thermophilus Rieske protein, which substitutes one of the ligating histidines with a cysteine, altering the ligation structure of the iron-sulfur cluster. Spectroscopic analysis showed the mutant has a different pH dependence and stability compared to the wild type. Crystals of the mutant confirmed the 3-cysteine, 1-histidine ligation structure. Modification experiments with DEPC showed the mutant is modified but not reduced, and the modification may reverse over longer times. The results provide insights into proteins containing this type of iron-sulfur cluster ligation.

![Abstract
The Rieske protein is found in the bc1 complex (complex III)
and plays an important role in transporting electrons and
protons through the electron transport chain. The Rieske
protein contains a [2Fe-2S] cluster ligated by a 2-cystines and
2- histidines. The reduction potential of this cluster is pH-
dependent and varies across species. An H134C mutant of
the Thermus thermophilus Rieskesubstitutes one of the
ligating histidines for a cysteine, changing the ligation
structure of the cluster from a 2Cys-2His to a 3Cys-1His
environment. To study the effects of this mutation, the protein
is subjected to modification with diethyl pyrocarbonate
(DEPC) and to pH changes. The behavior of this protein is
compared to the wild type protein as observed through
circular dichroism and UV visible spectroscopy. Because of the
similarity in the iron-sulfur cluster ligands, H134C will also be
compared to another mitochondrial protein, mitoNEET, which
contains a 3Cys-1His environment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dd868e6a-e46c-4929-9bc3-24792810e168-151112151343-lva1-app6892/85/ACS-poster-final-2-320.jpg)


![H134C Crystals
• Crystals for H134C Rieske
mutant were isolated under
the following conditions:
30% PEG 4000, 0.2 M
MgCl2, 0.1 M Tris-HCl pH
8.5 or 20% PEG 2000 MME,
0.01 M NiCl2· 6H2O, 0.1 M
Tris pH 8.5.
• Best data collected to 1.66
Å resolution!
• Space group P2221
Preliminary electron density map (2Fo-Fc)
showing 3 Cys, 1 His [2Fe2S] cluster
His 154
Cys 134
Cys 132 Cys 151](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dd868e6a-e46c-4929-9bc3-24792810e168-151112151343-lva1-app6892/85/ACS-poster-final-6-320.jpg)