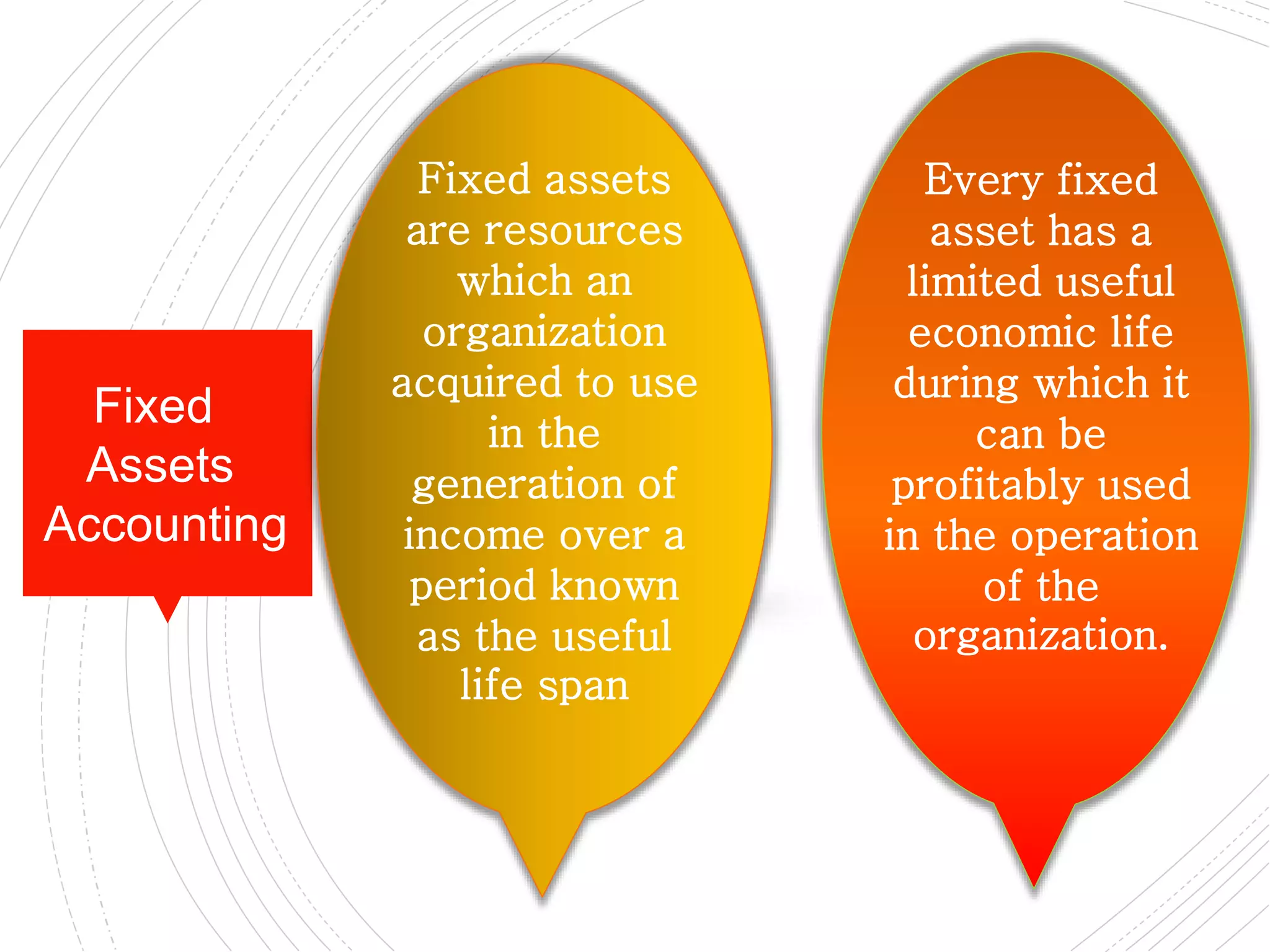
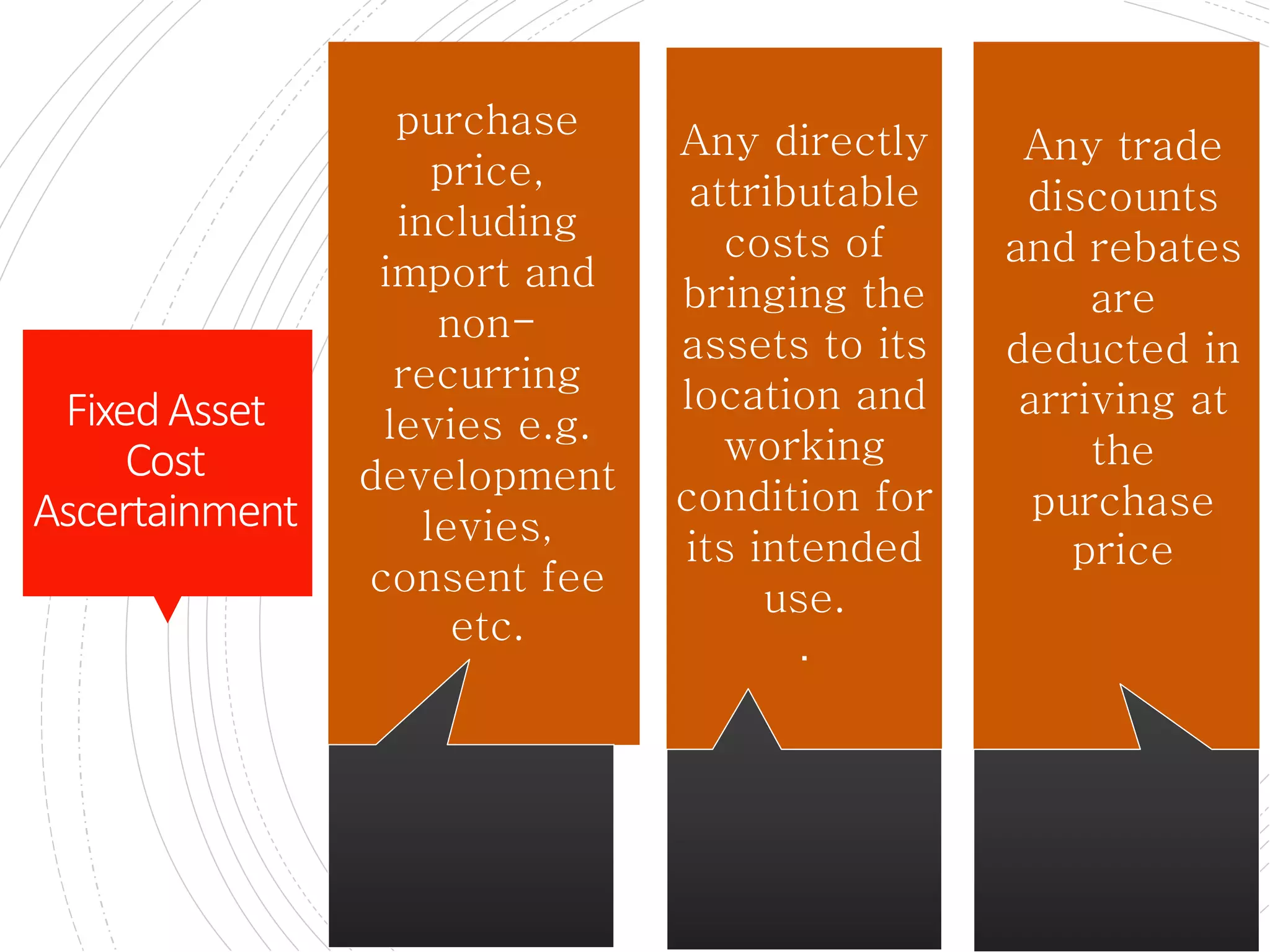
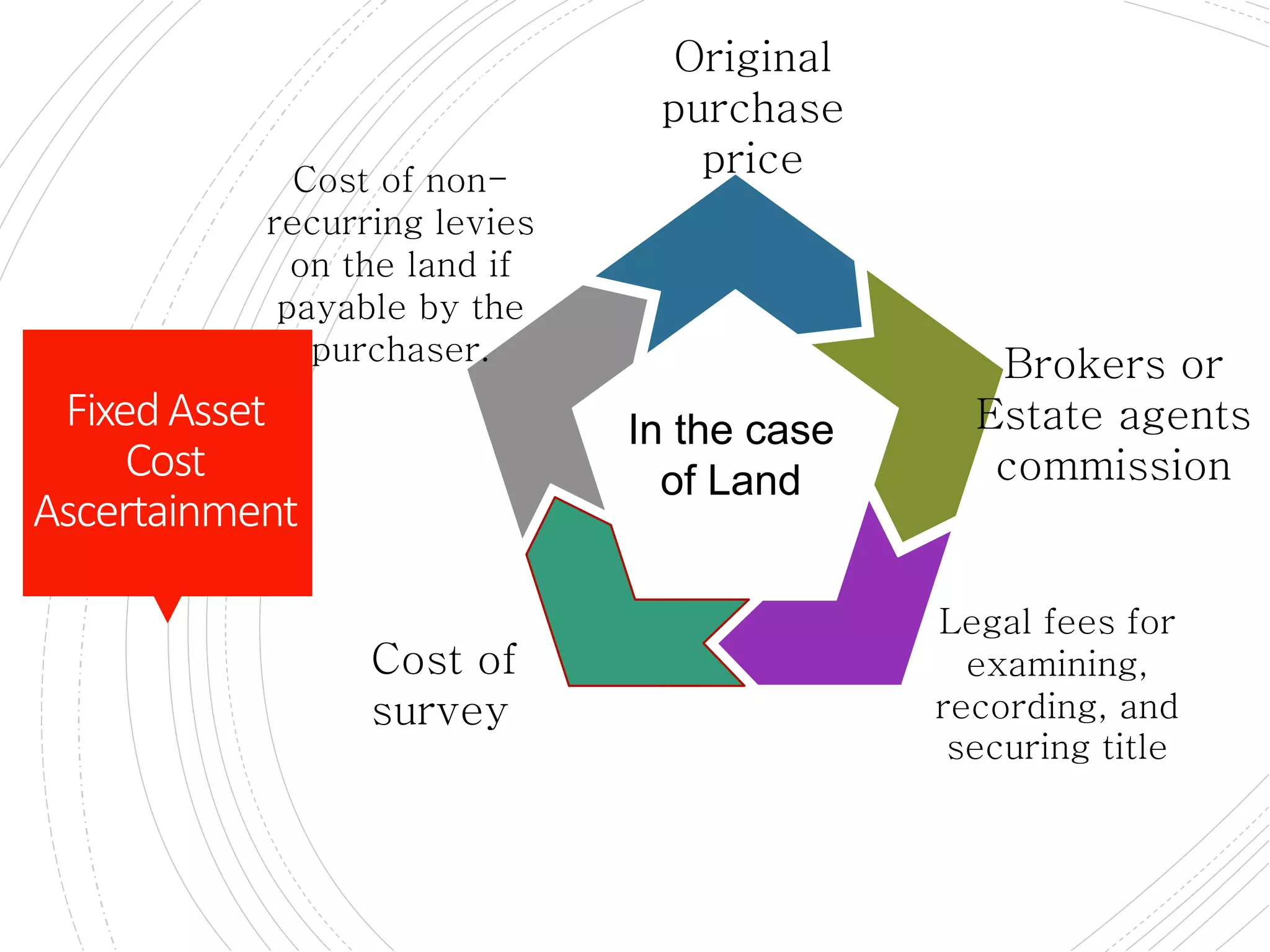
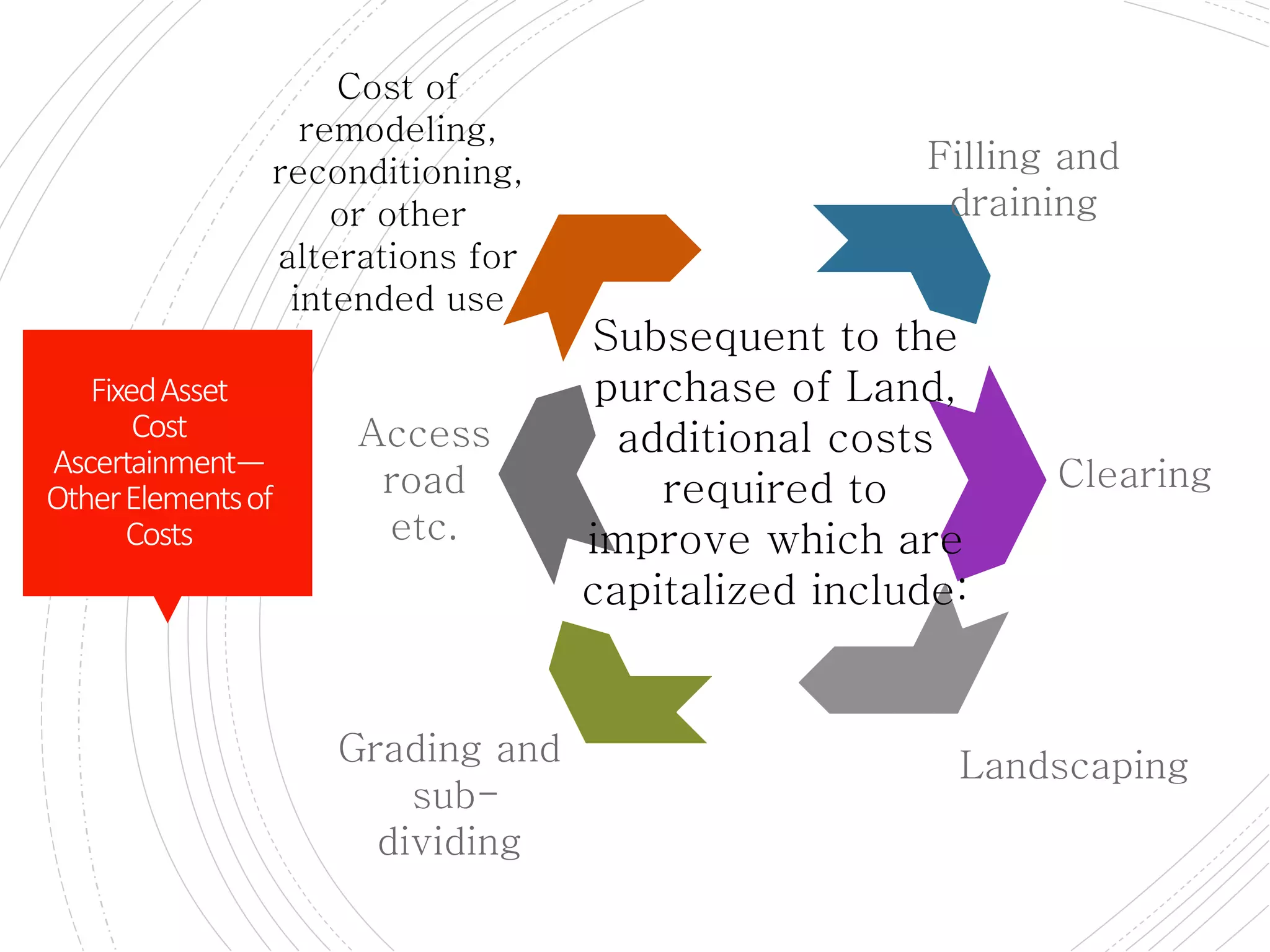
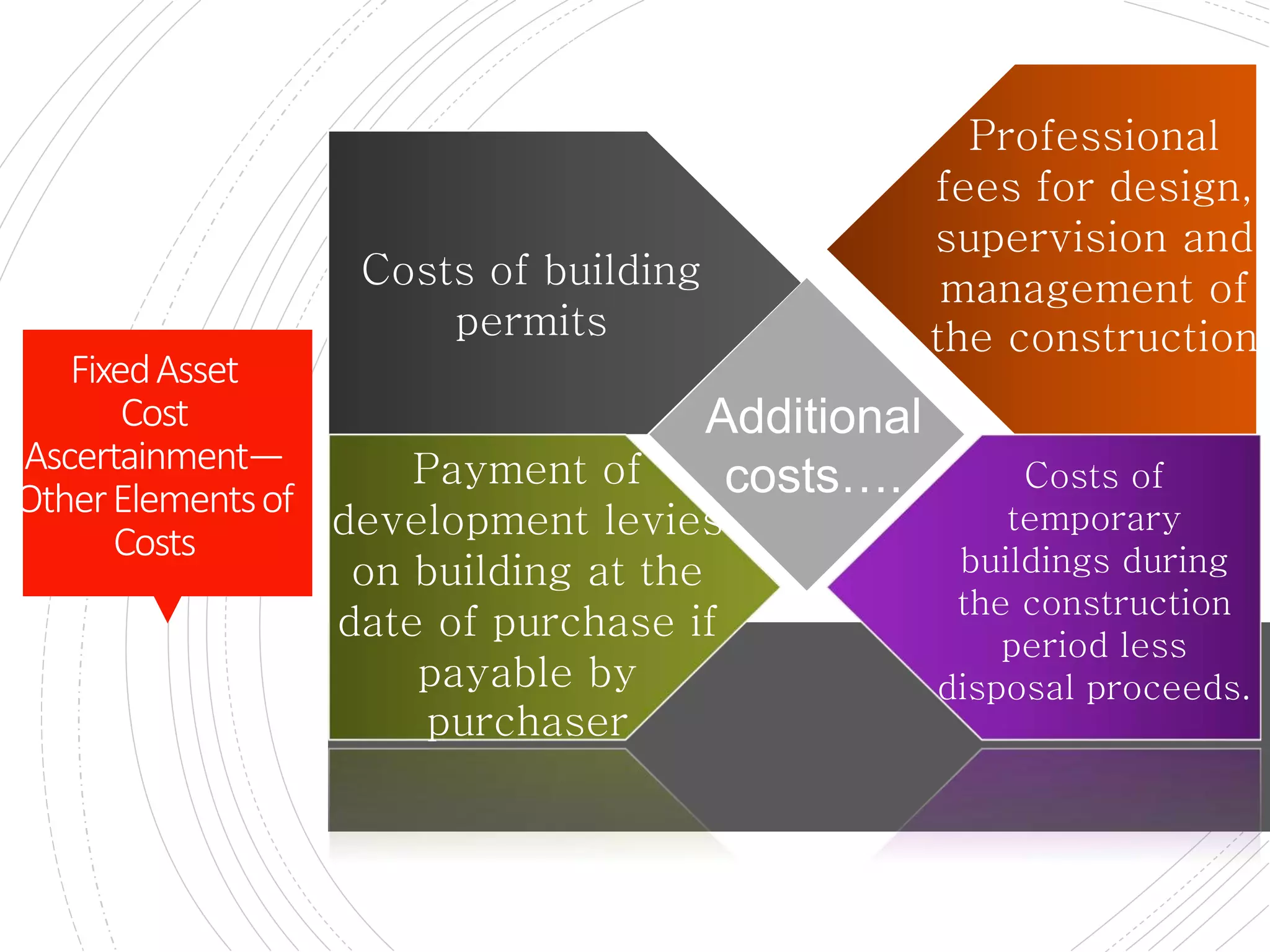
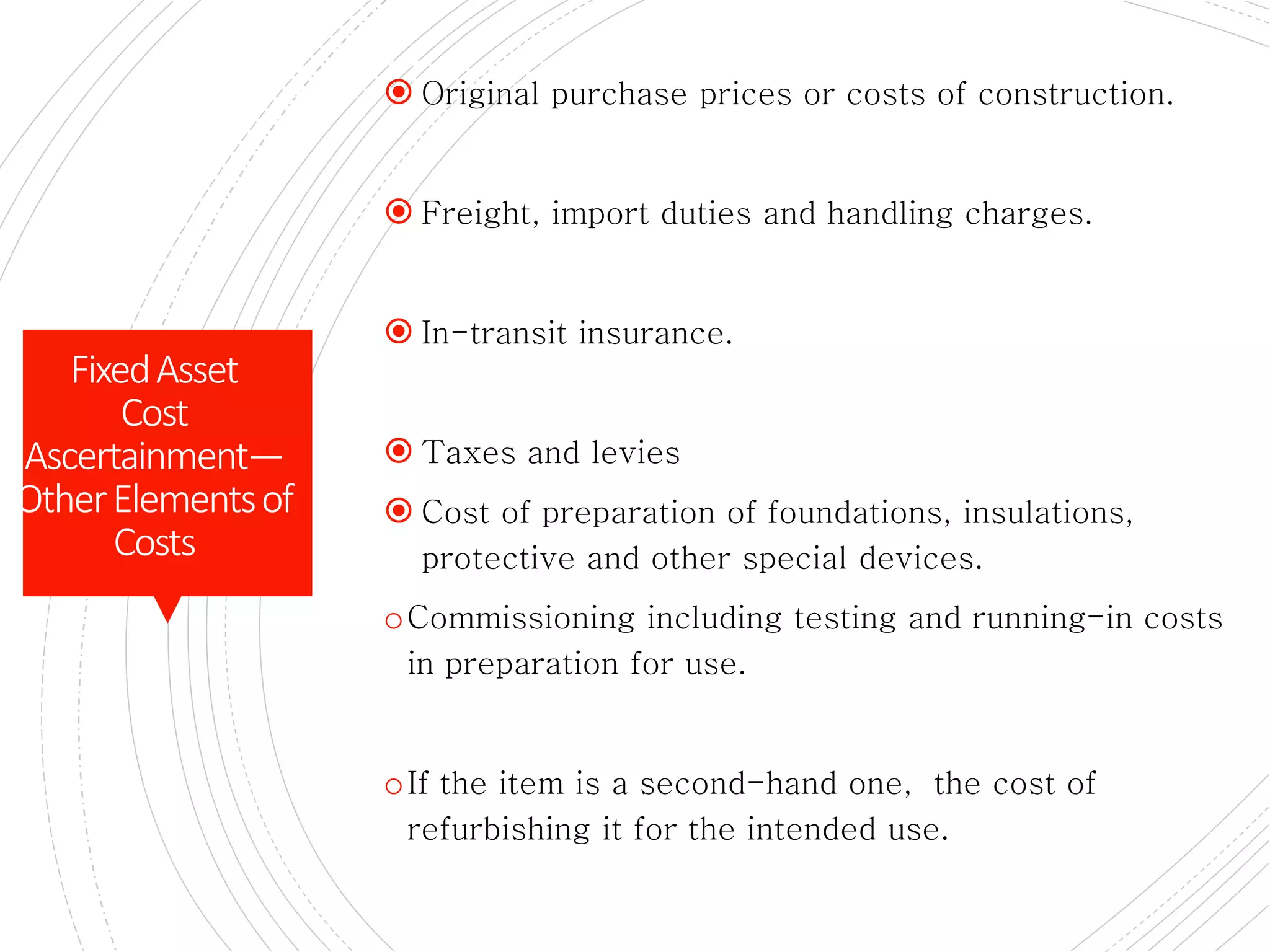
The document provides a comprehensive overview of accounting for fixed assets, detailing their definition, classification, and the processes involved in cost accumulation, appraisal, and disposal. It outlines the basis for determining asset costs, including purchase price, legal fees, and construction-related expenses, as well as the financial treatment of disposals and revaluation. Additionally, it highlights necessary disclosures regarding the valuation methods and movements in fixed assets.