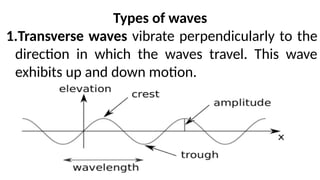
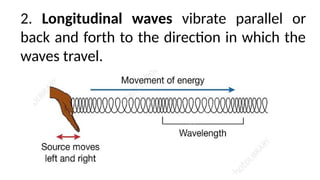
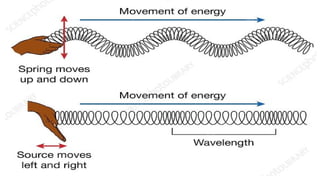
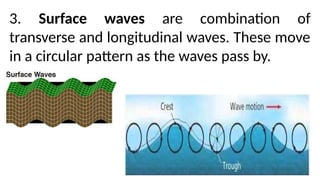
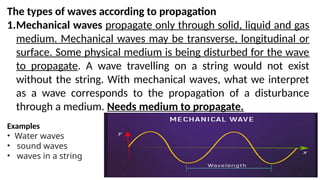
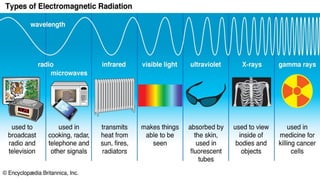
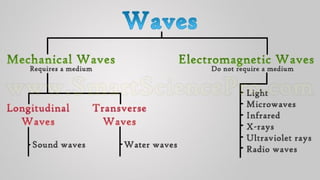
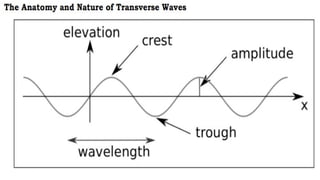
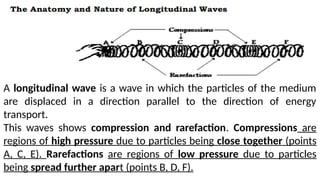
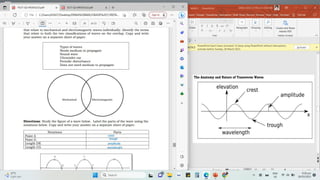
Waves can be classified by the direction of motion of vibrating particles, which can be transverse, longitudinal, or surface waves. They can also be categorized by propagation as mechanical waves, which require a medium to travel, or electromagnetic waves, which do not. Key properties of waves include amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and speed, with relationships defined by equations such as wave speed = frequency x wavelength.