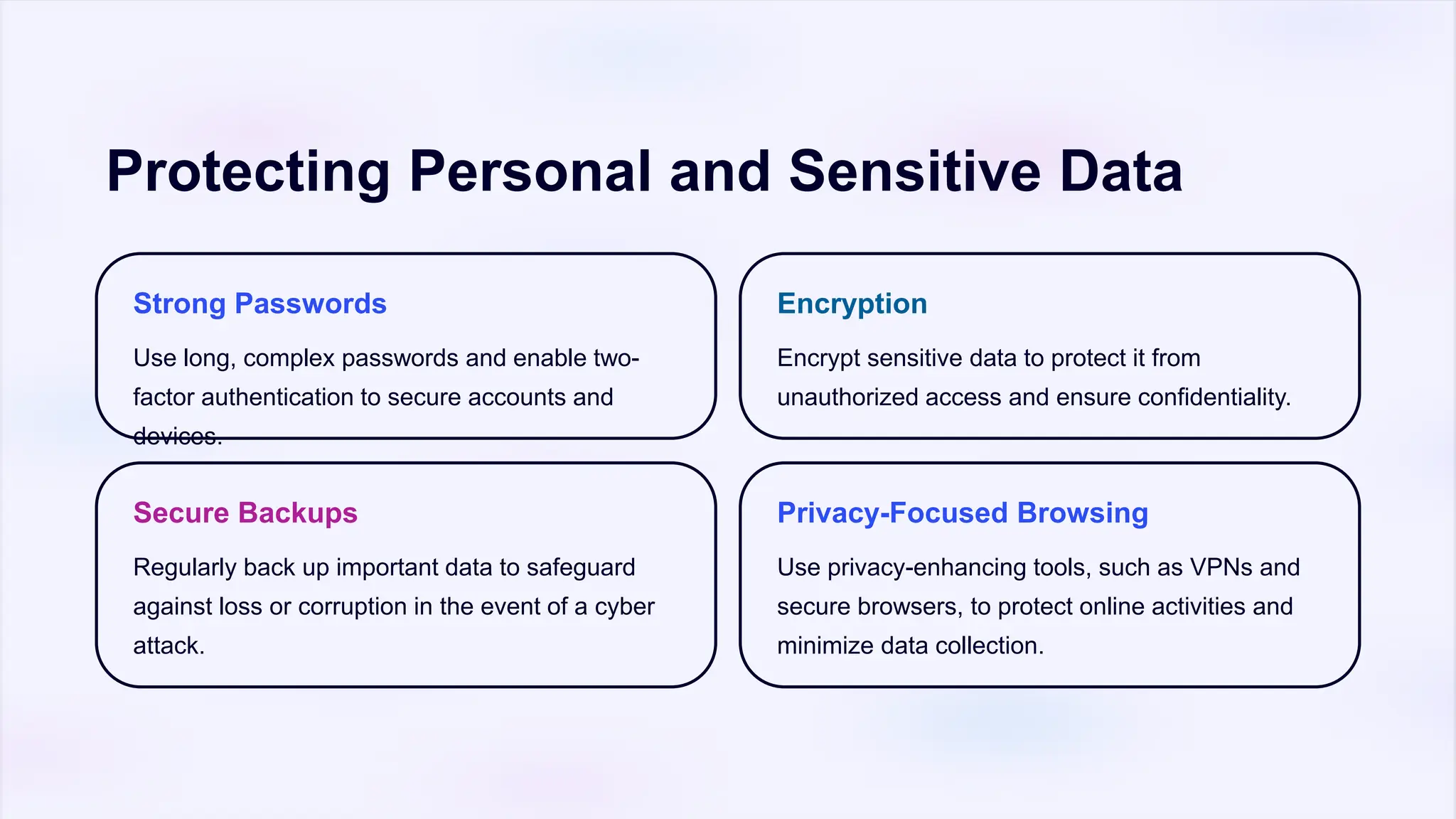
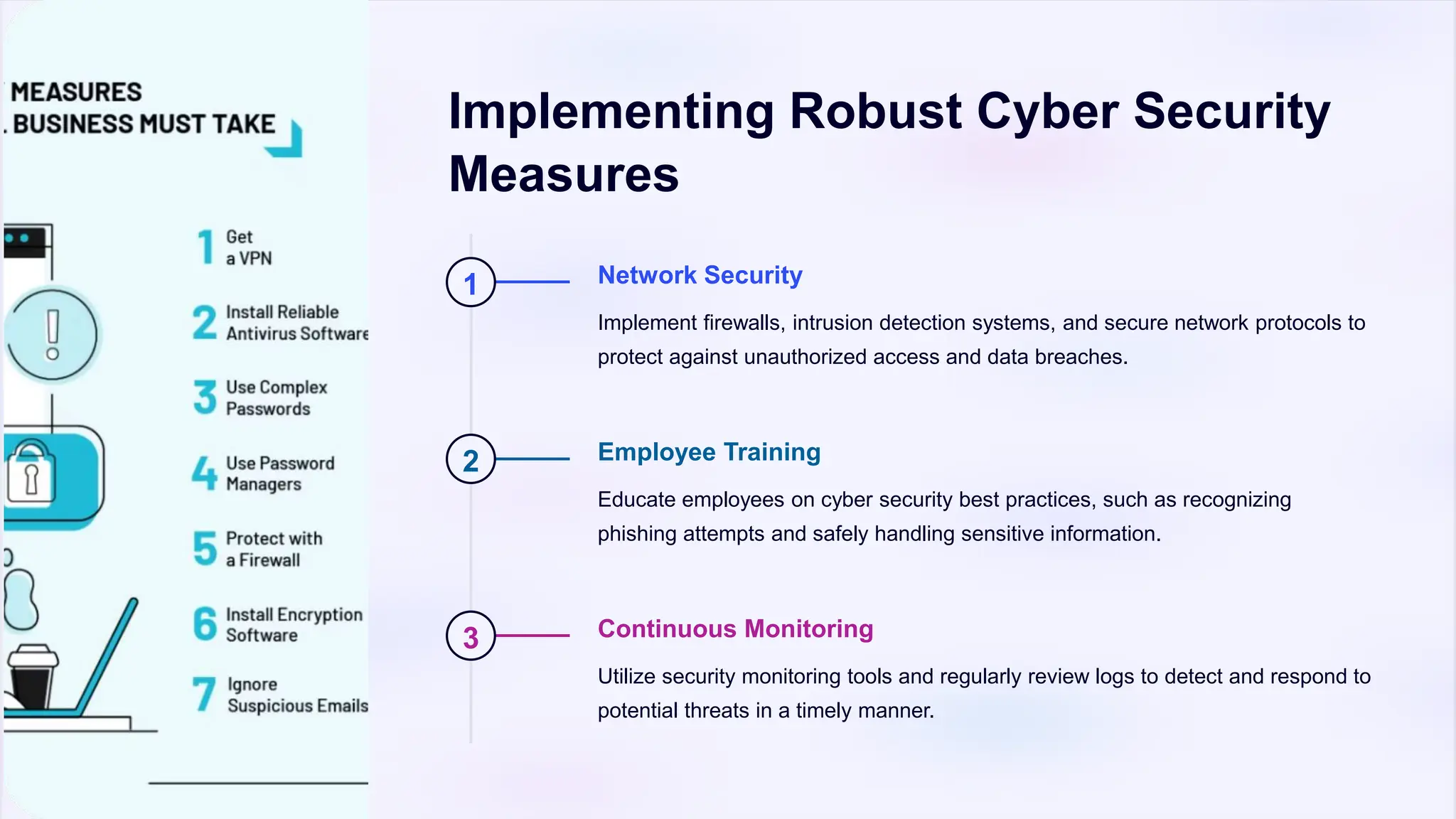
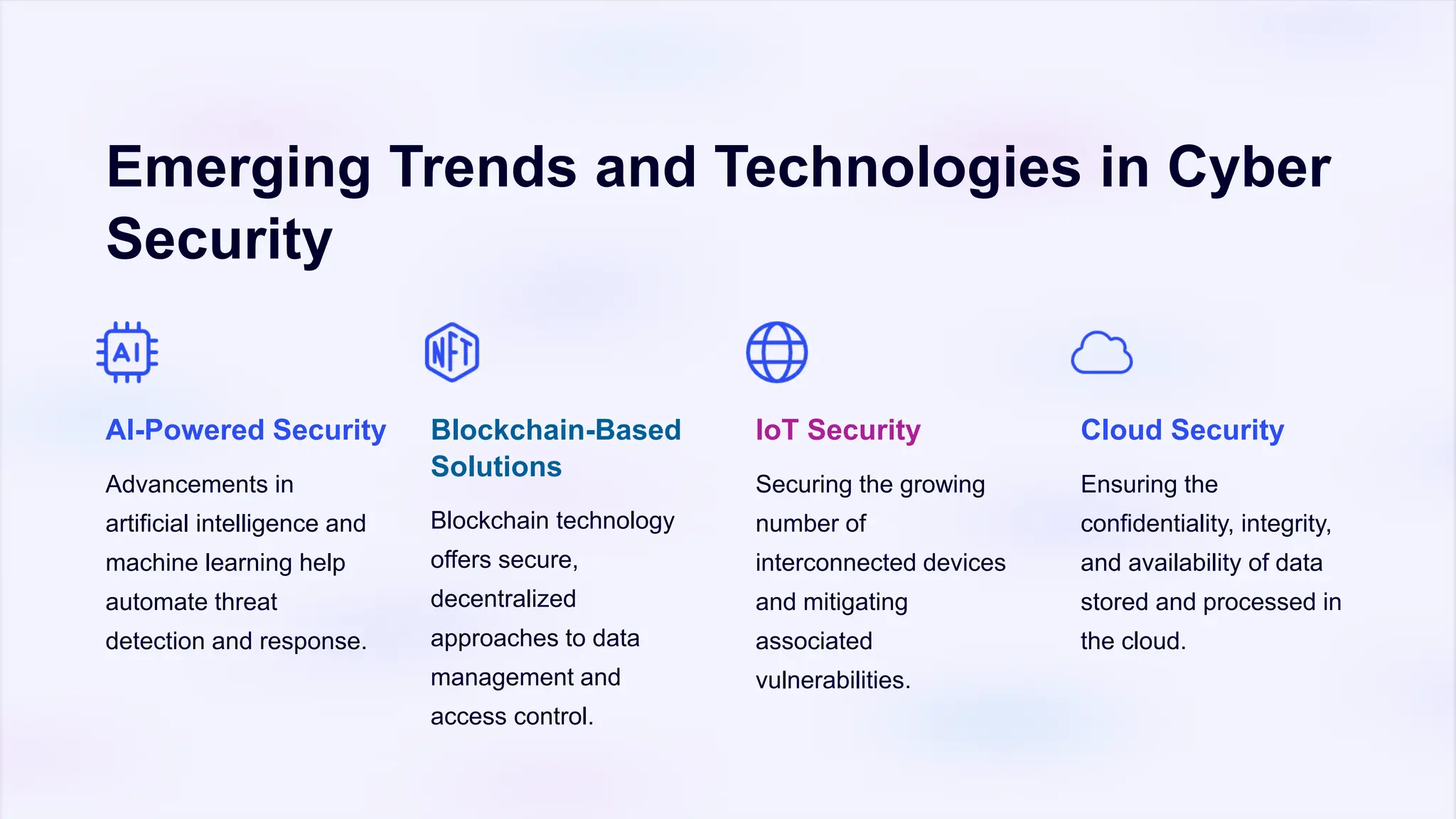
The document emphasizes the critical importance of cyber security and data privacy in today's digital landscape, highlighting the need to protect against cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and unsecured devices. It outlines effective measures for safeguarding personal information, including strong passwords, encryption, secure backups, and employee training. Additionally, it discusses emerging trends like AI and blockchain in cyber security, urging individuals and organizations to remain vigilant and advocate for stronger policies.