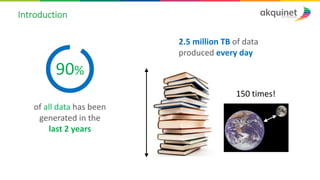
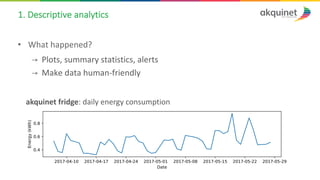
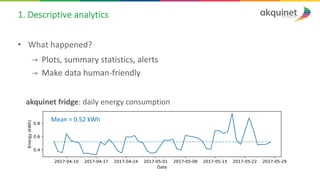
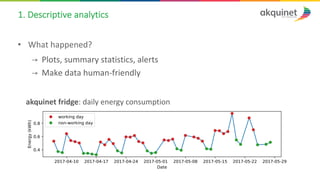
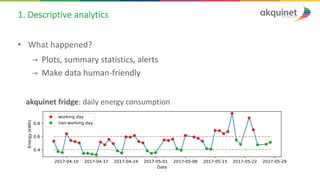
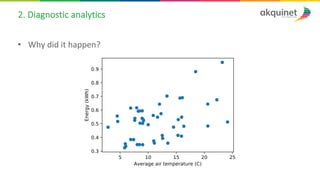
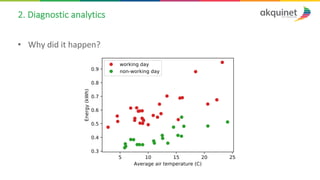
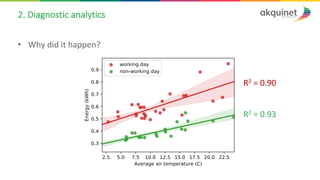
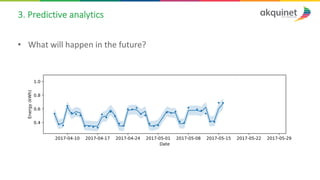
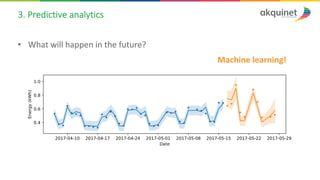
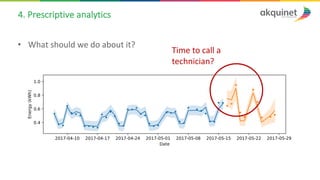
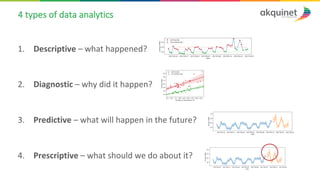
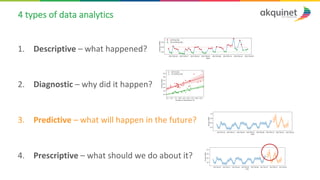
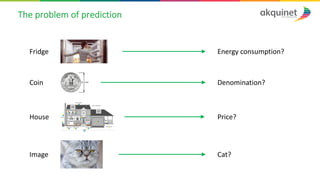
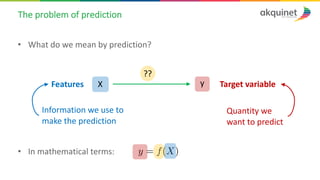
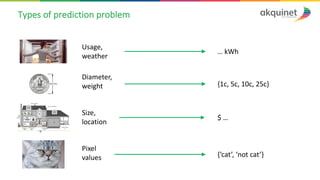
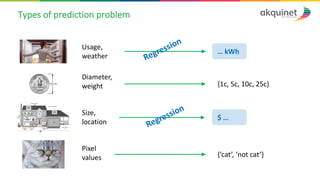
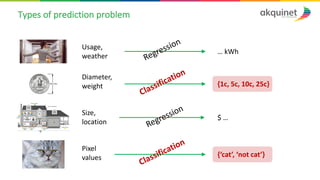
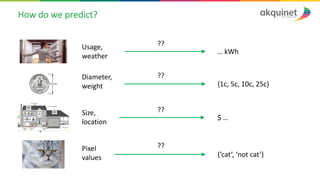
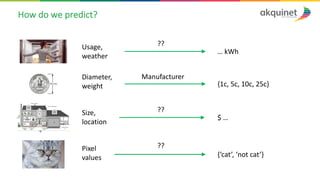
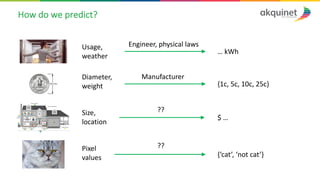
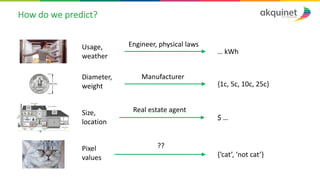
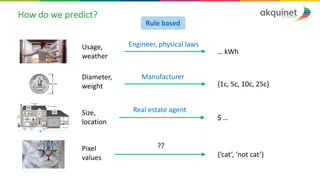
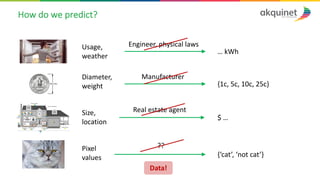
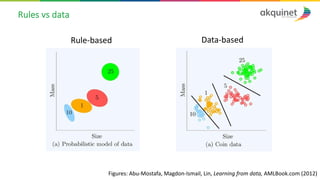
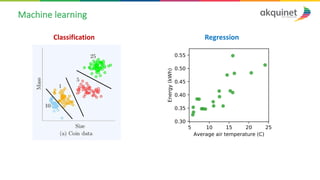
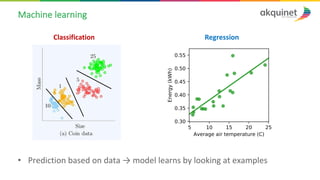
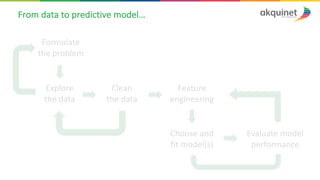
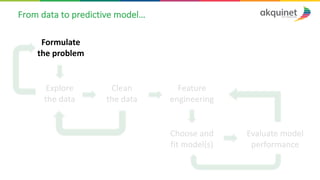
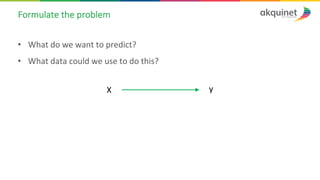
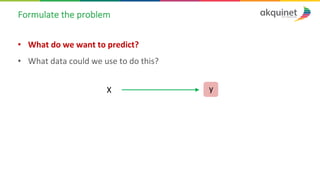
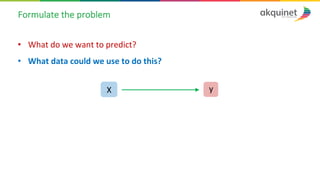
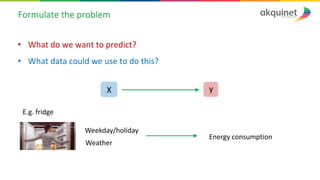
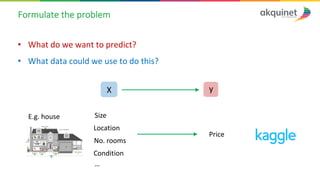
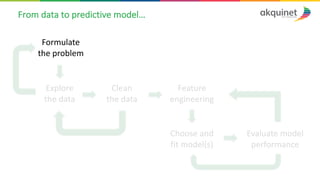
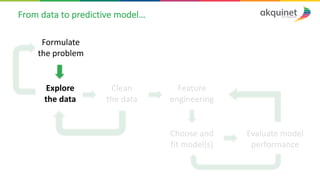
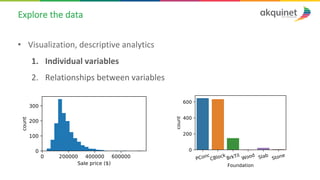
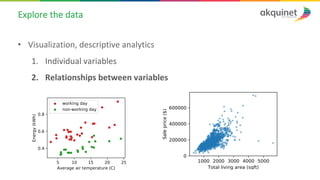
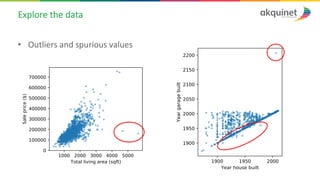
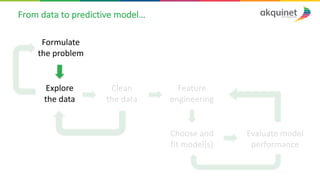
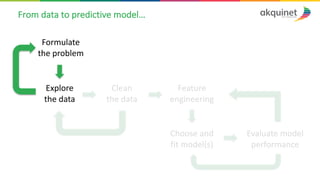
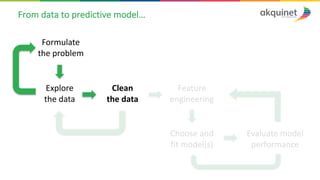
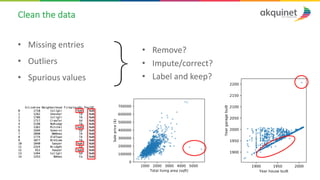
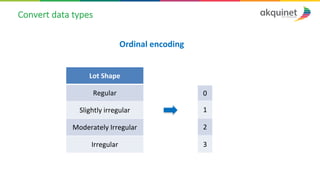
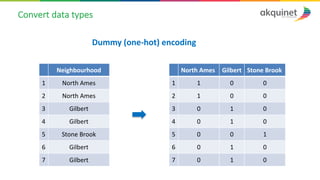
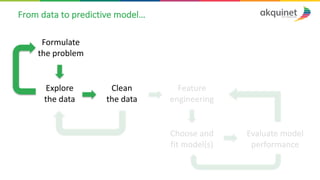
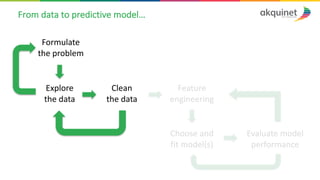
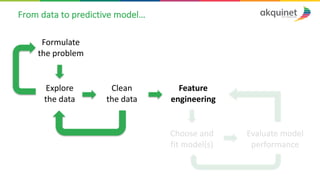
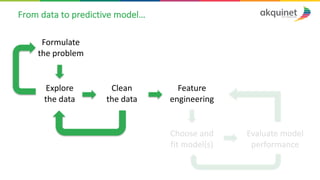
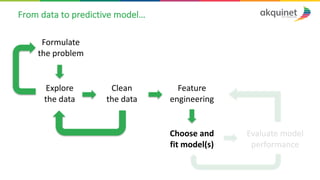
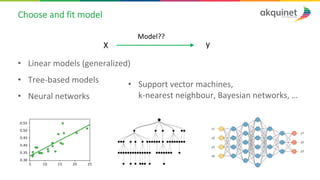
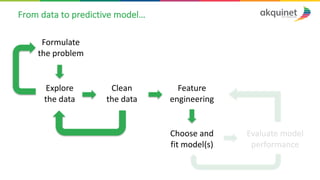
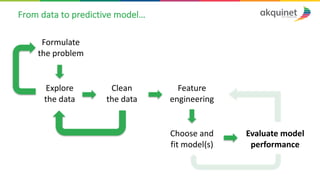
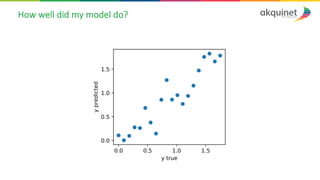
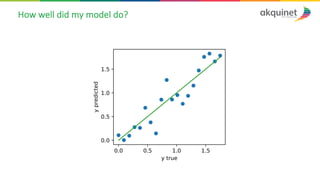
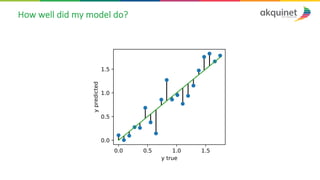
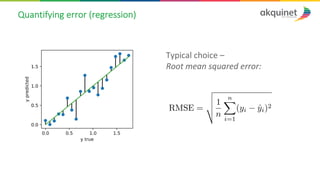
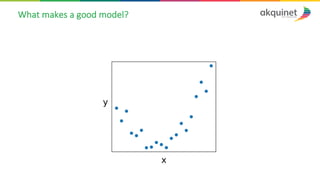
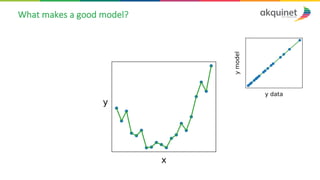
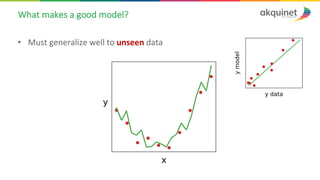
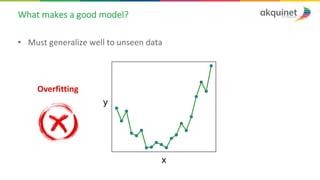
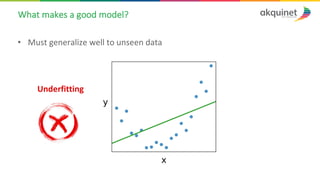
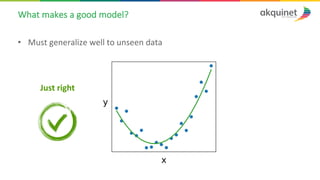
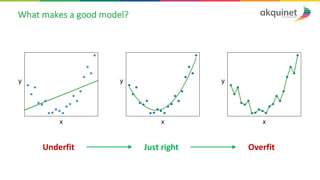
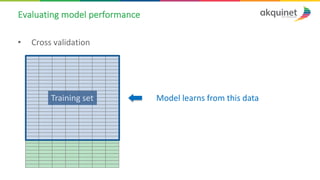
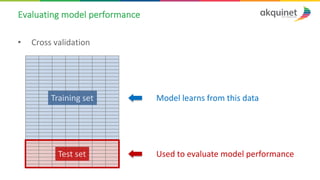
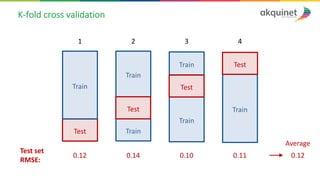
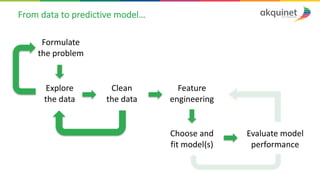
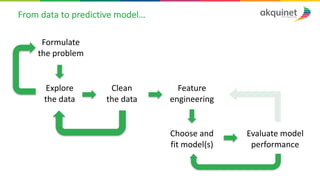
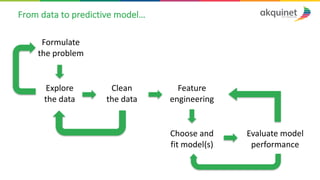
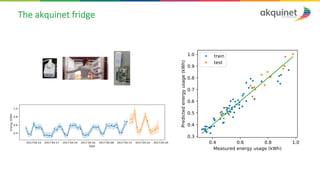
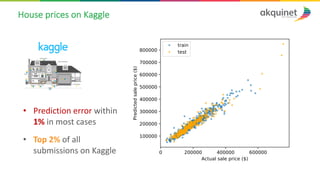
The document provides a practical introduction to data science and machine learning, detailing types of data analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. It outlines the process of creating predictive models, including problem formulation, data exploration, cleaning, feature engineering, and model evaluation. The summary emphasizes the importance of data preparation and model performance assessment in achieving accurate predictions.