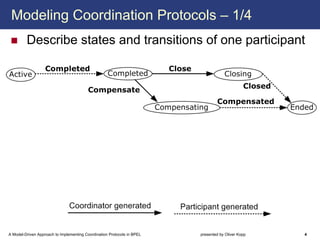
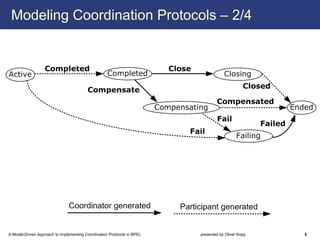
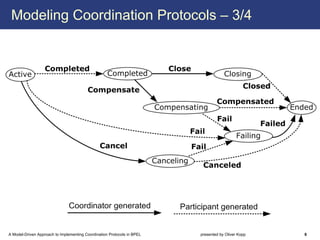
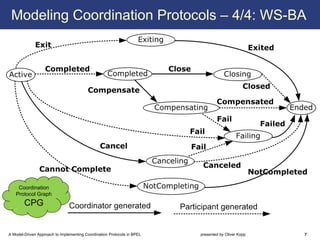
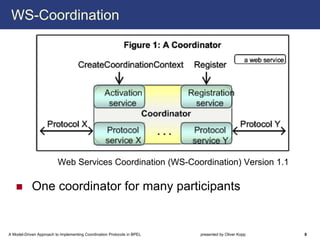
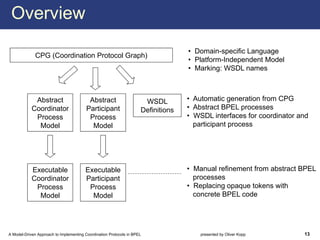
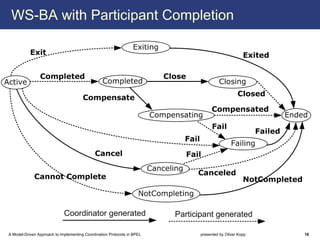
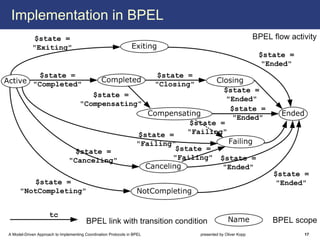
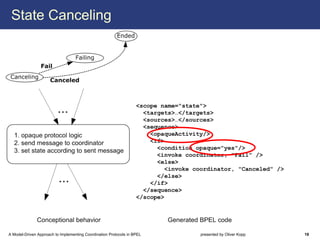
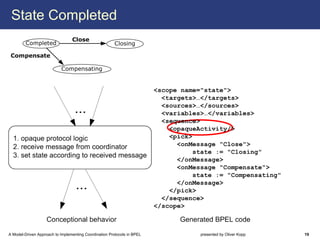
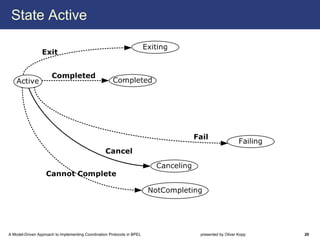
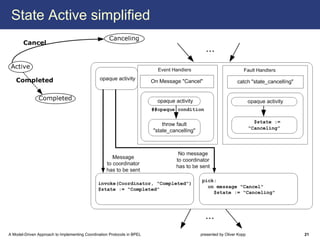
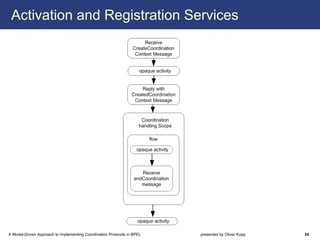
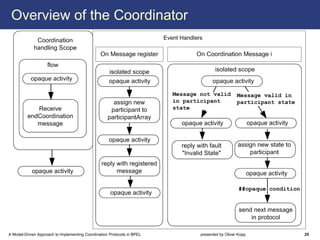
The document describes a model-driven approach to implementing coordination protocols in BPEL. It presents a method to model coordination protocols as Coordination Protocol Graphs (CPGs) and then automatically generate abstract BPEL processes for the coordinator and participants. These abstract processes are then manually refined into executable BPEL code. The approach represents states and transitions for participants as BPEL processes and uses events and conditions to model the coordinator's management of registrations, activations, and protocol completion. The conclusion discusses future work on supporting loops, coordinator hierarchies, and mixed protocols.