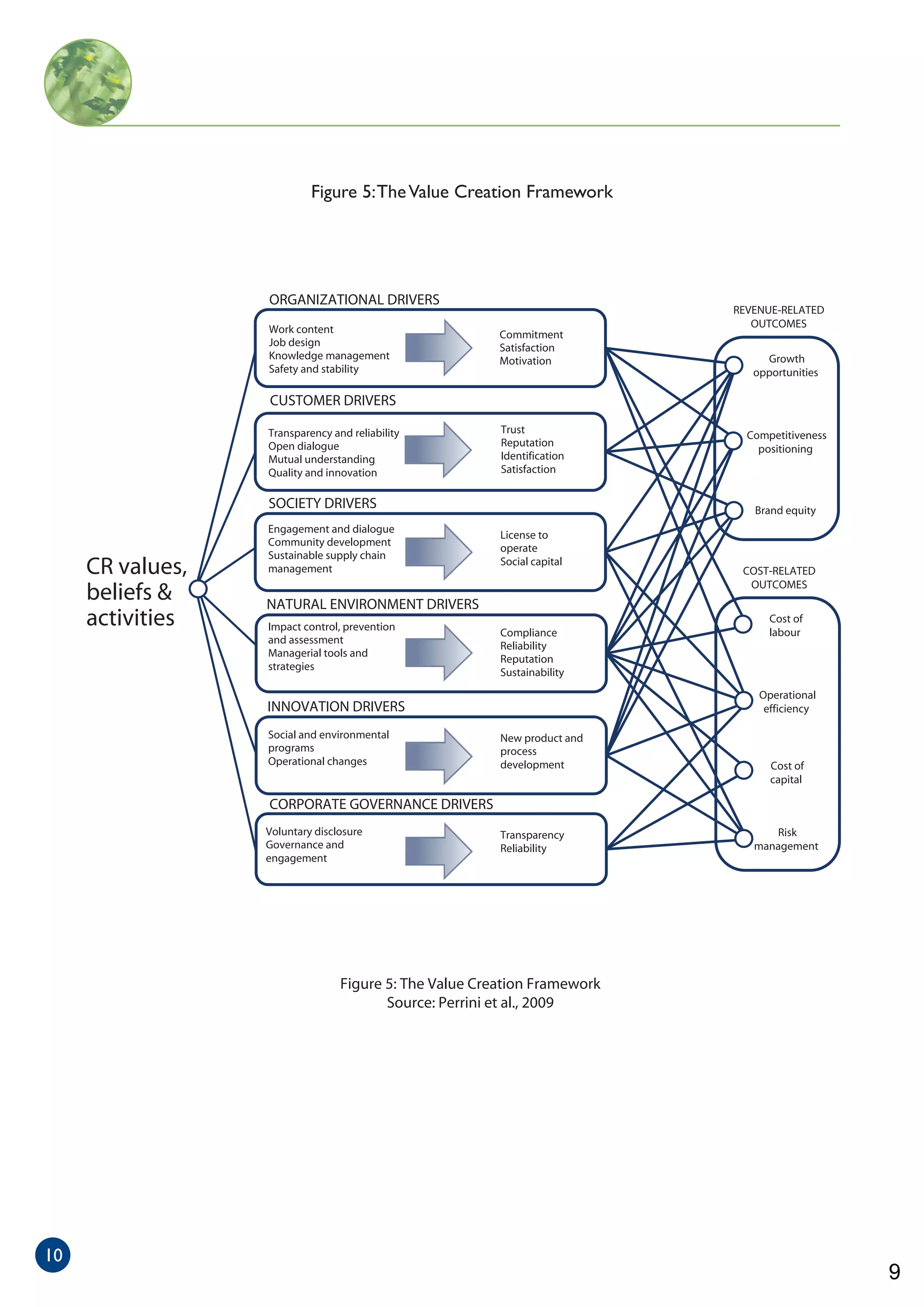
The document outlines the forma initiative, which promotes agent-based thinking across various disciplines, aiming to enhance participants' expertise in modeling complex systems through workshops and case studies. It includes a value creation framework designed to help companies understand the impact of stakeholder-oriented governance on corporate performance using a simplified model to analyze employee satisfaction and retention. Overall, the workshop facilitates collaboration between researchers and skilled programmers, fostering networking and continued development of modeling skills.