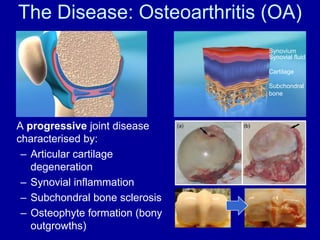
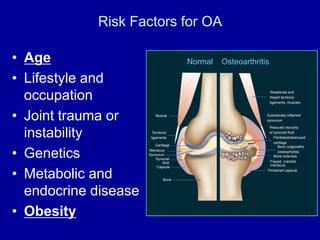
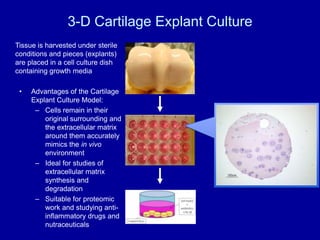
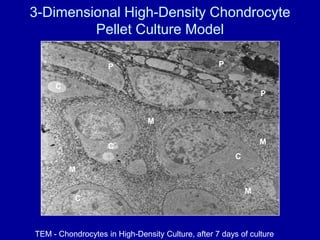
The document discusses the challenges and opportunities in studying osteoarthritis (OA), a prevalent joint disease affecting millions. It highlights the limitations of current treatments and the need for new biomarkers and therapeutic approaches, emphasizing the use of in vitro models, such as cartilage cultures, to advance research. These models aim to identify early indicators of OA and predict its progression in both humans and animals.