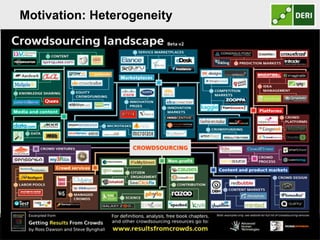
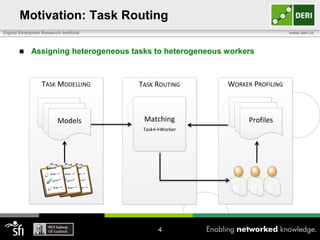
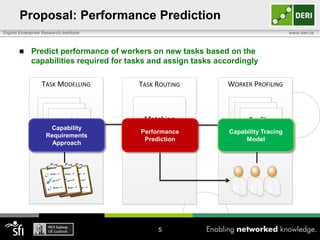
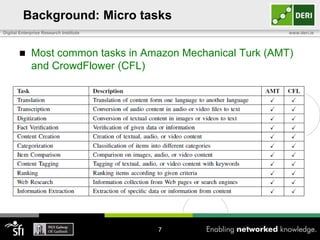
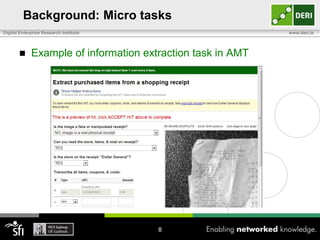
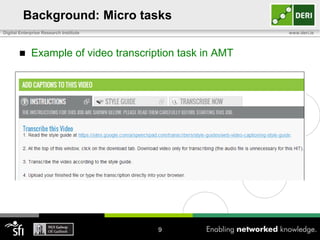
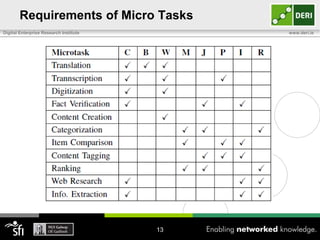
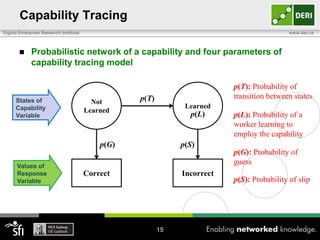
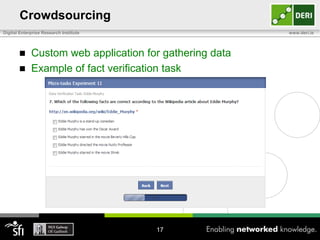
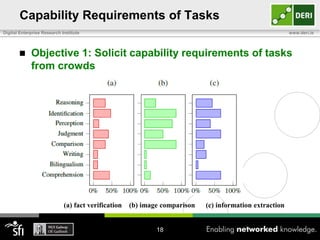
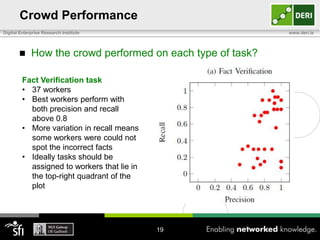
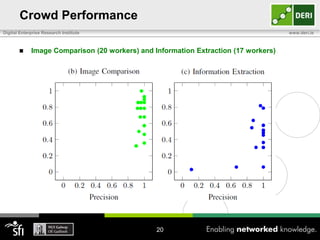
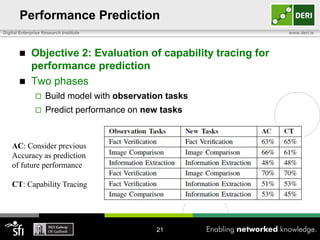
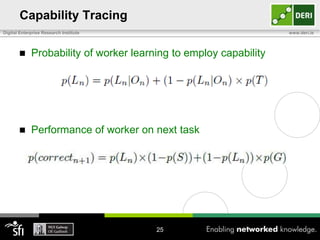
The document discusses a capability requirements approach for predicting worker performance in crowdsourcing, emphasizing the importance of effectively assigning tasks to workers based on their capabilities. It introduces a capabilities taxonomy and capability tracing model to evaluate and predict worker performance on various micro-tasks. Future work aims to expand evaluations across more task types and develop standard tests for measuring worker capabilities.