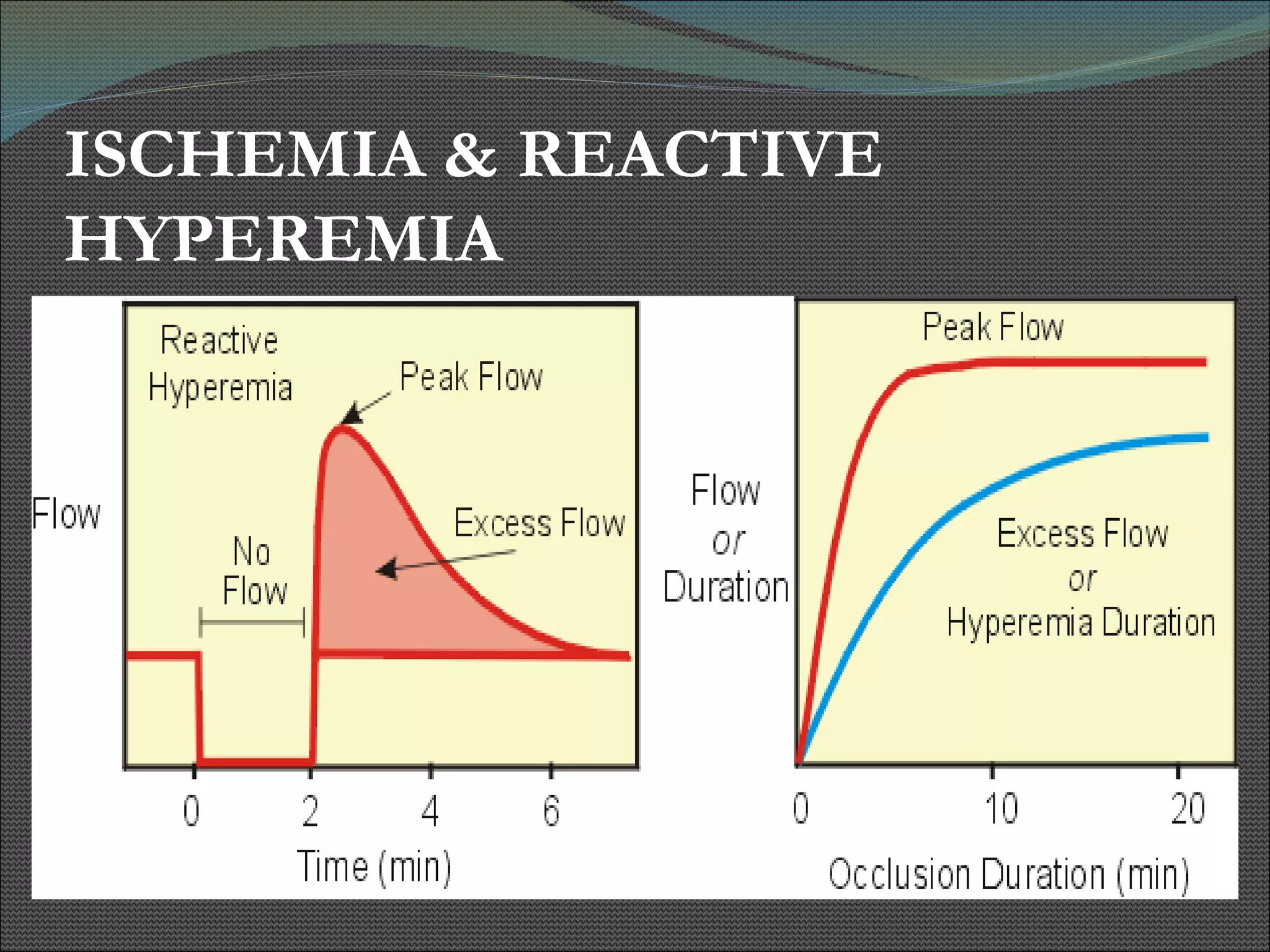
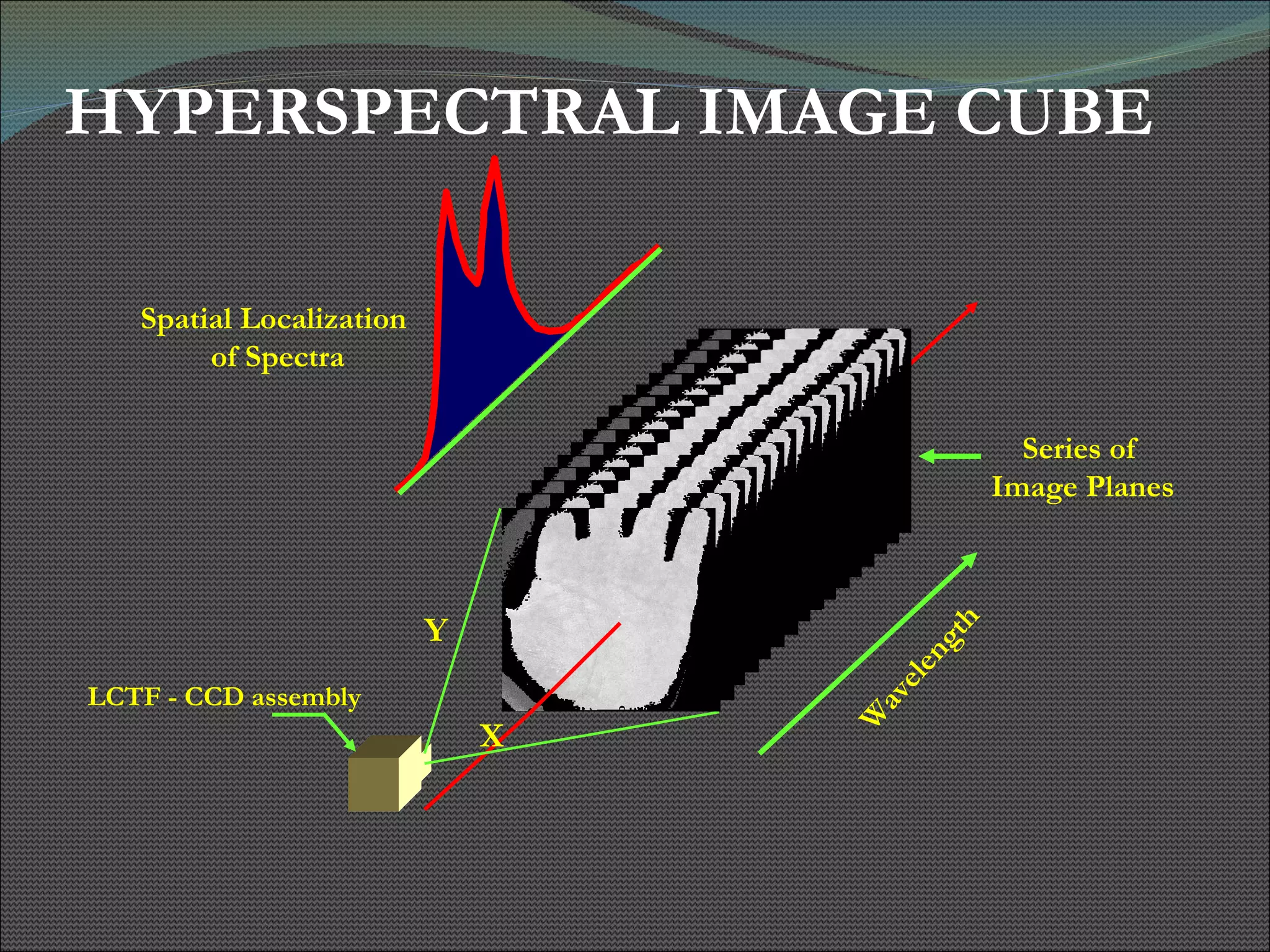
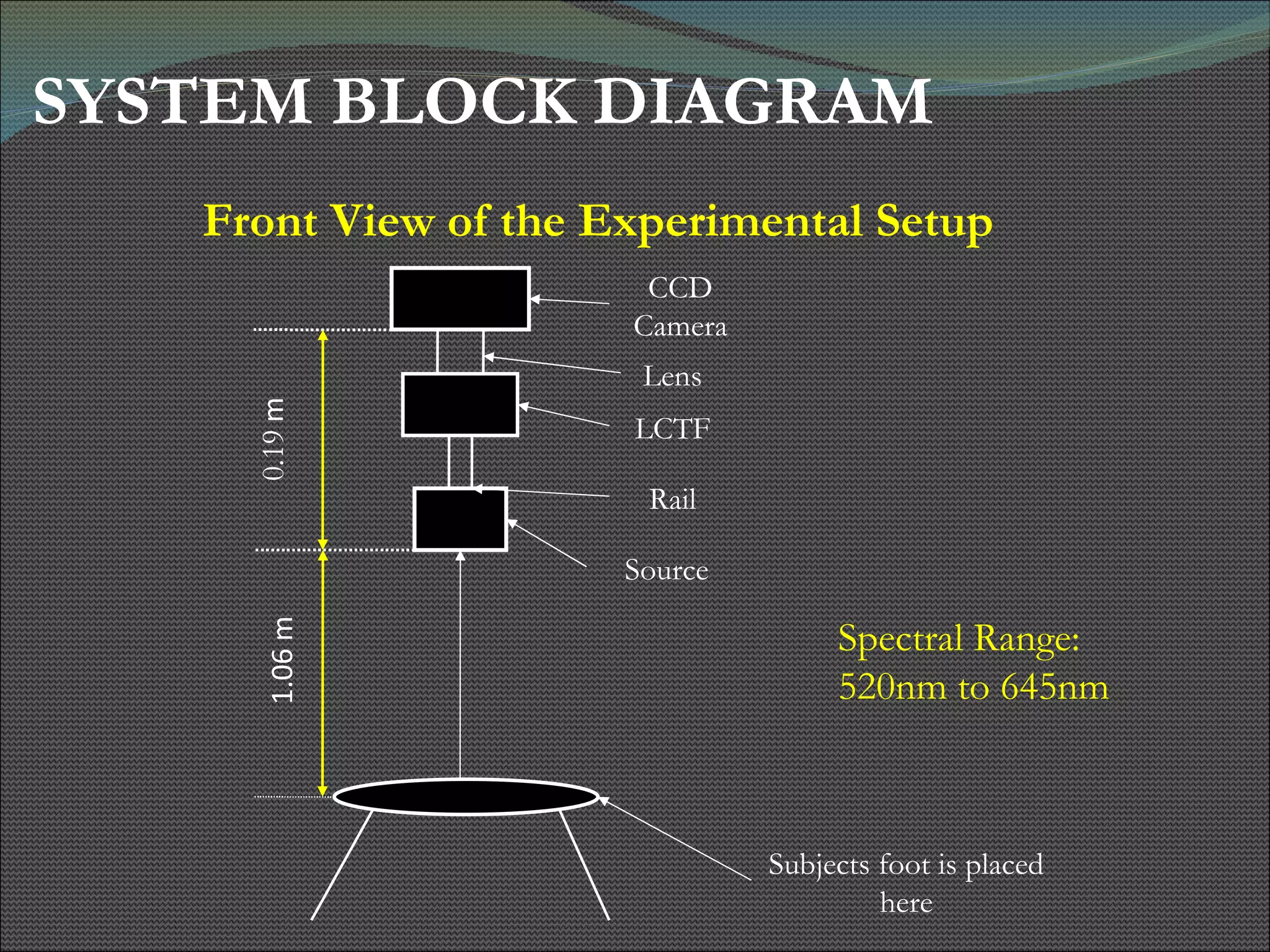
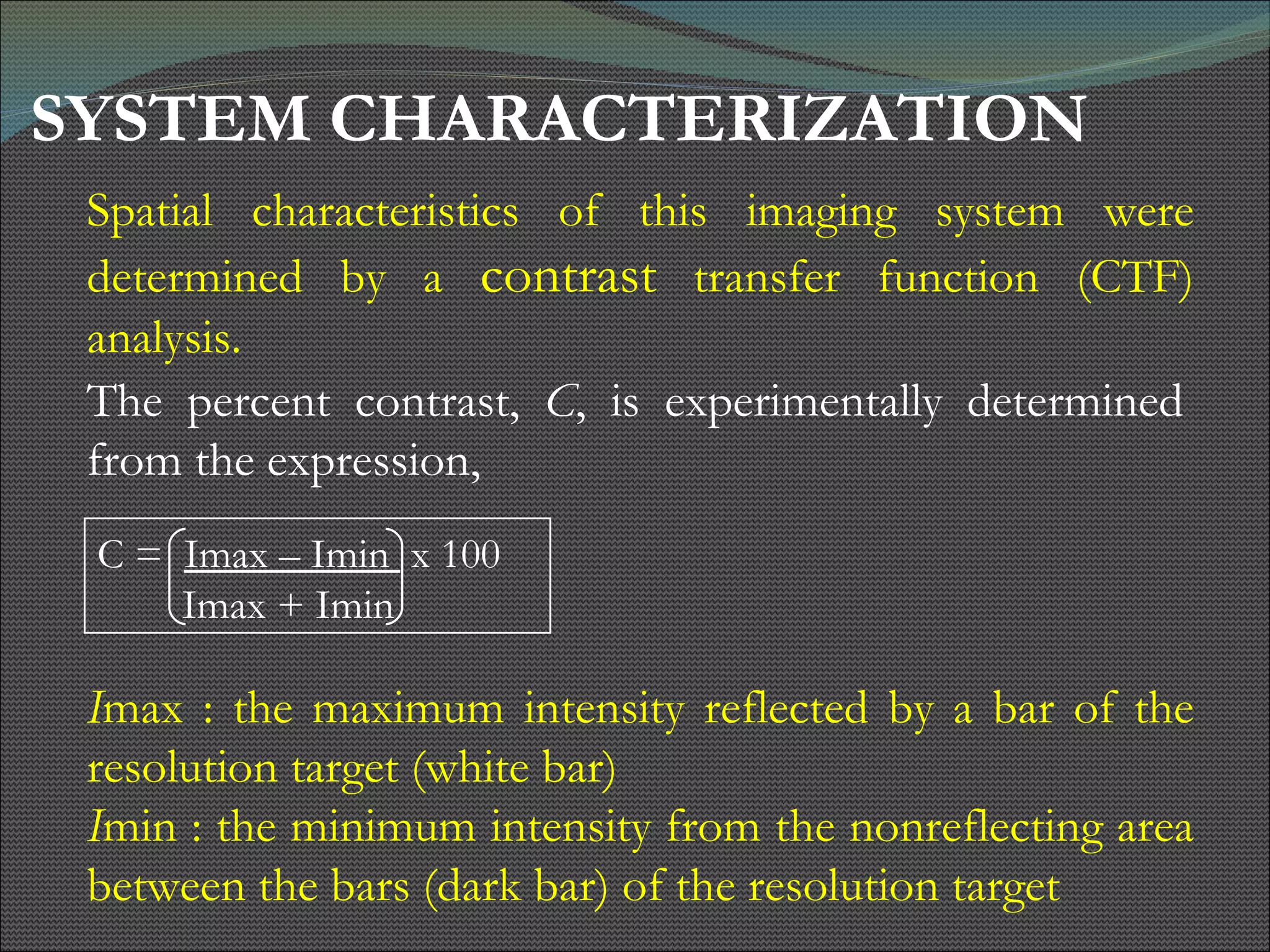
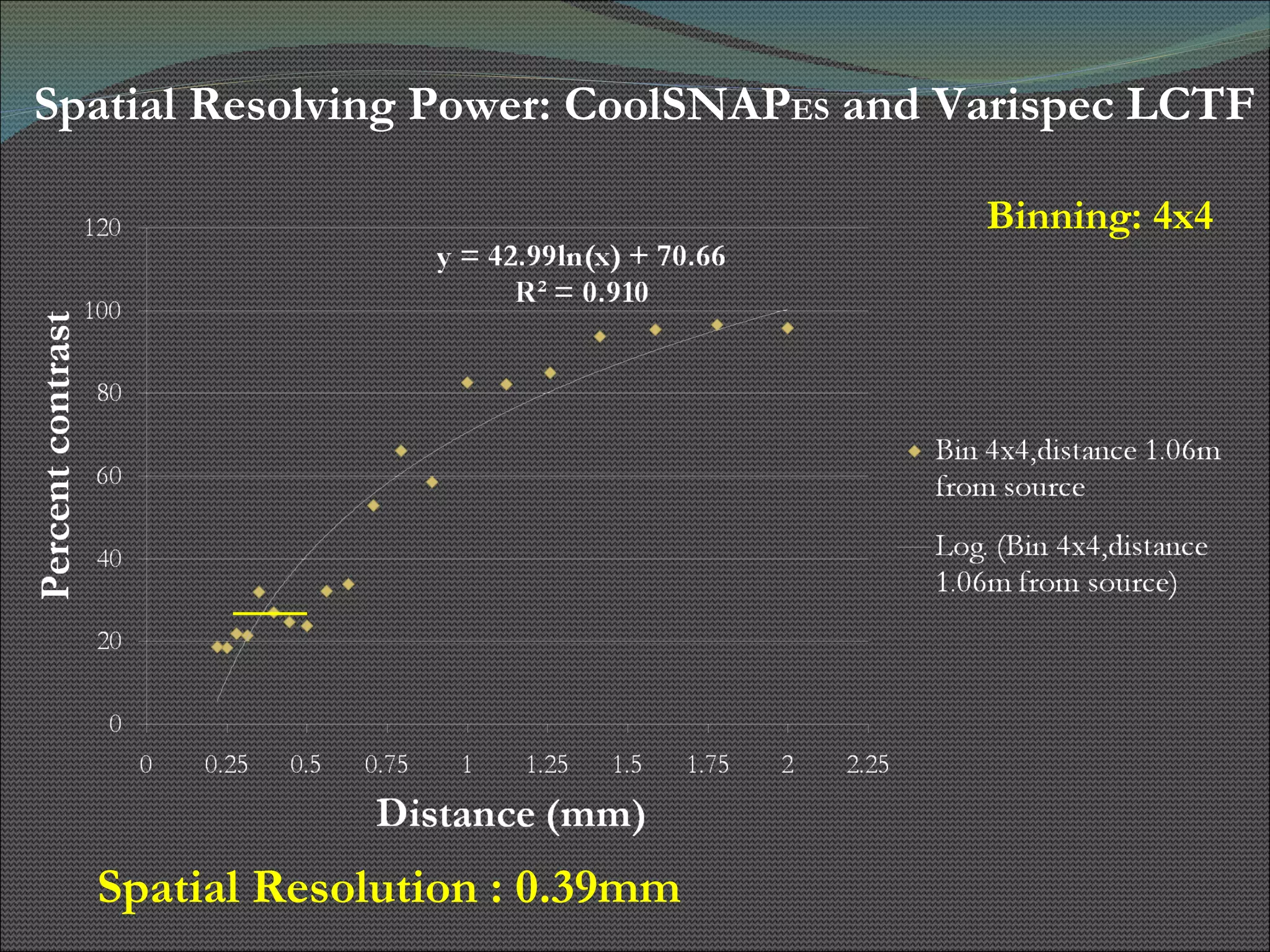
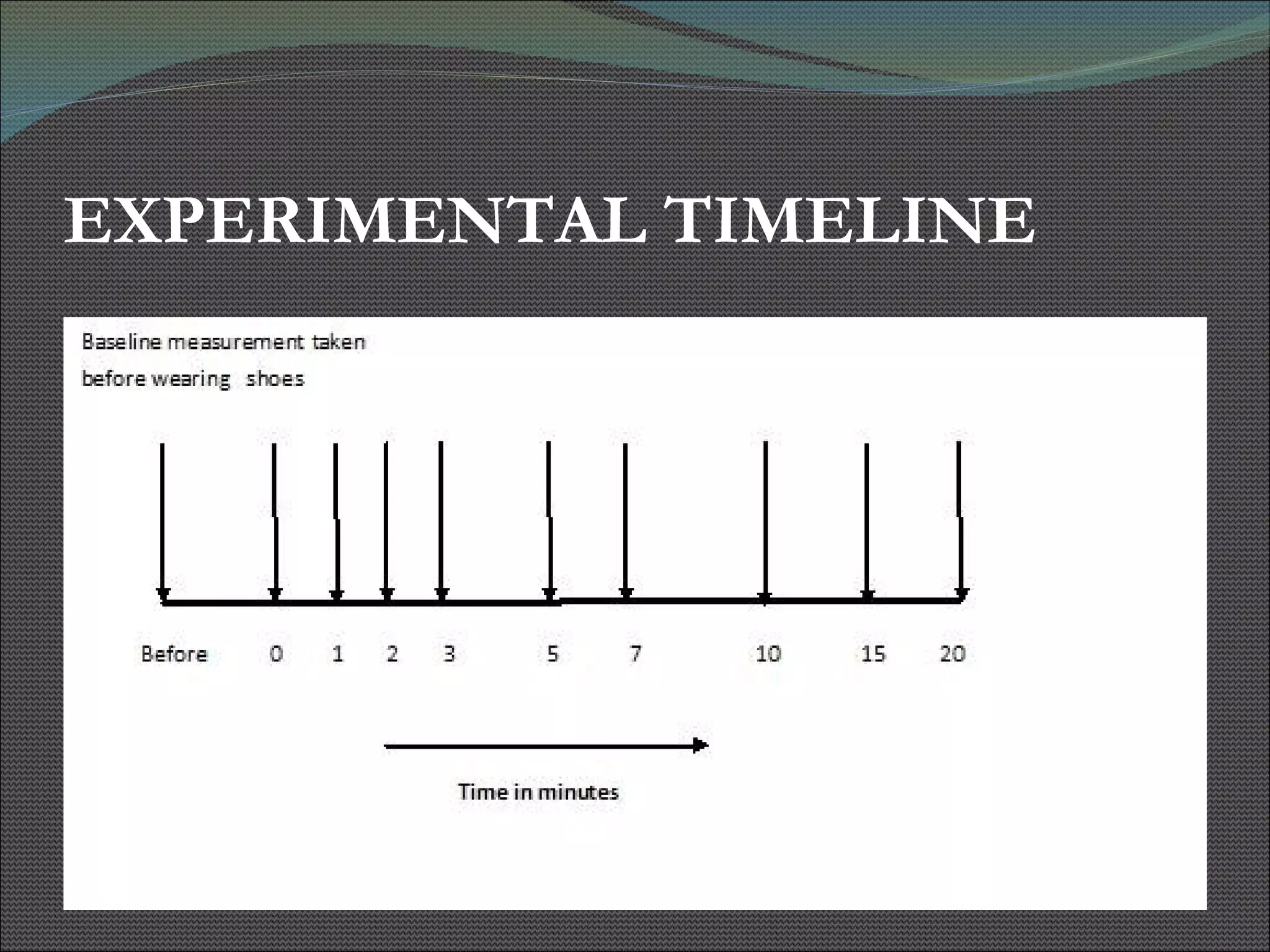
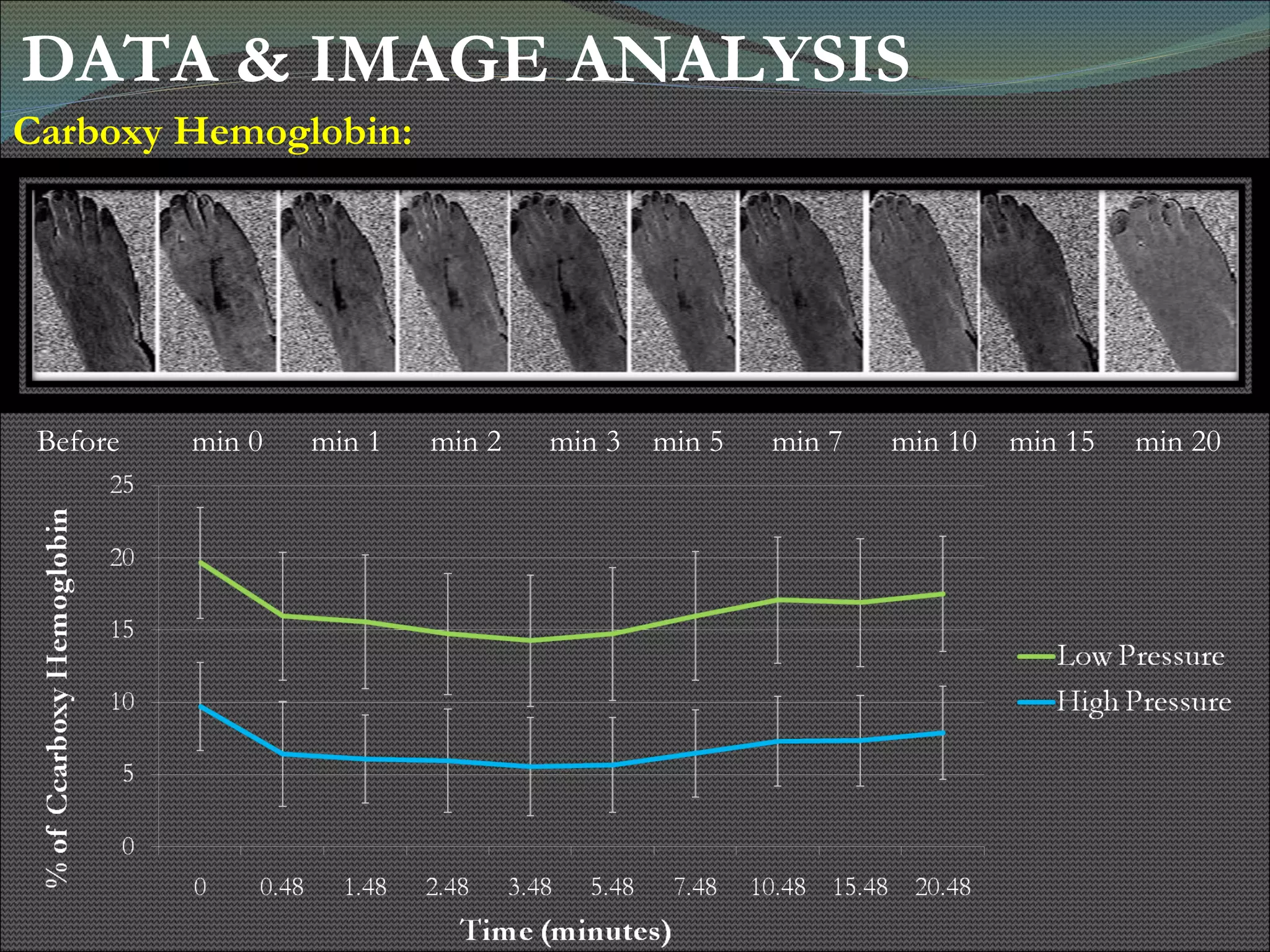
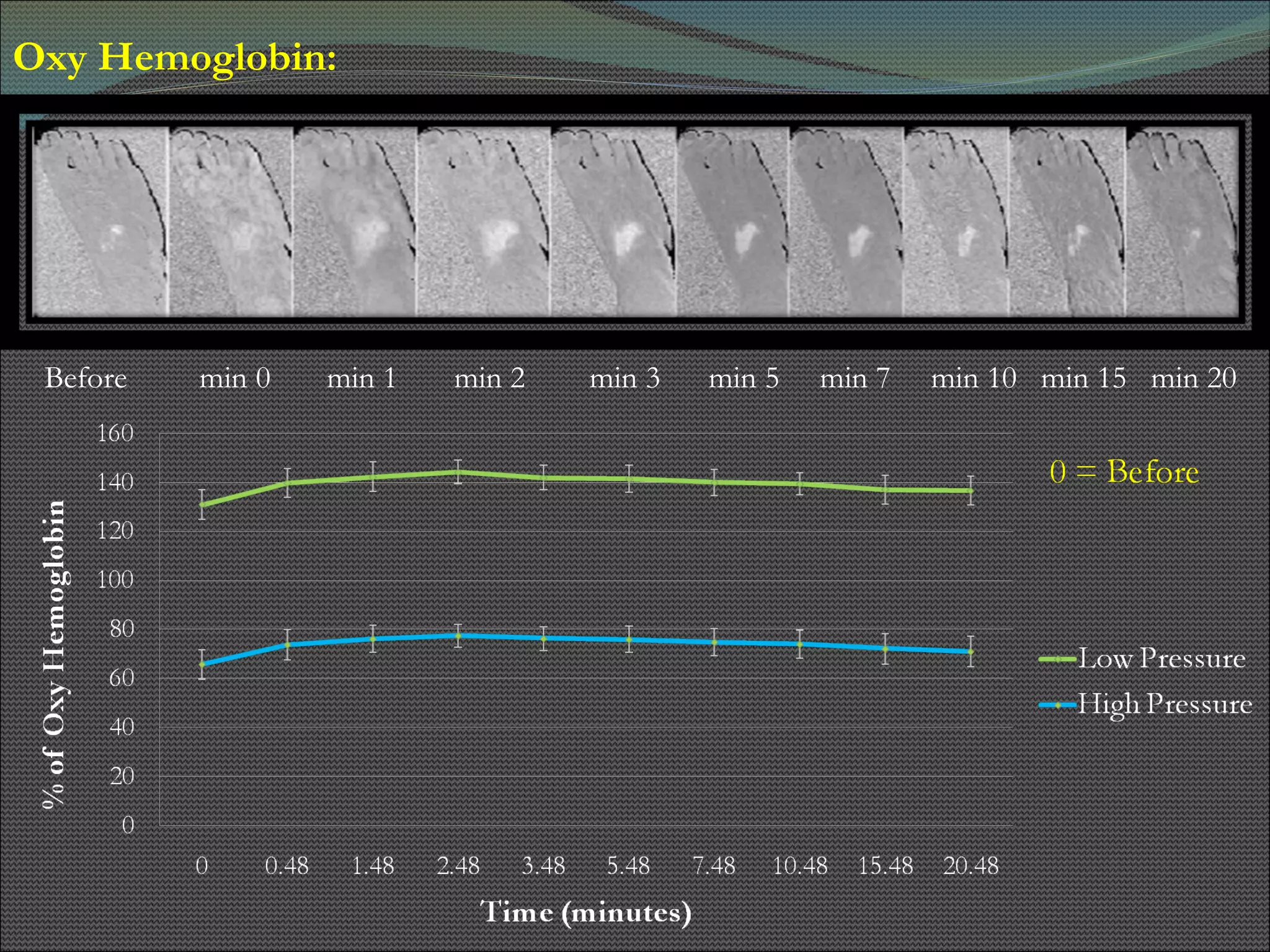
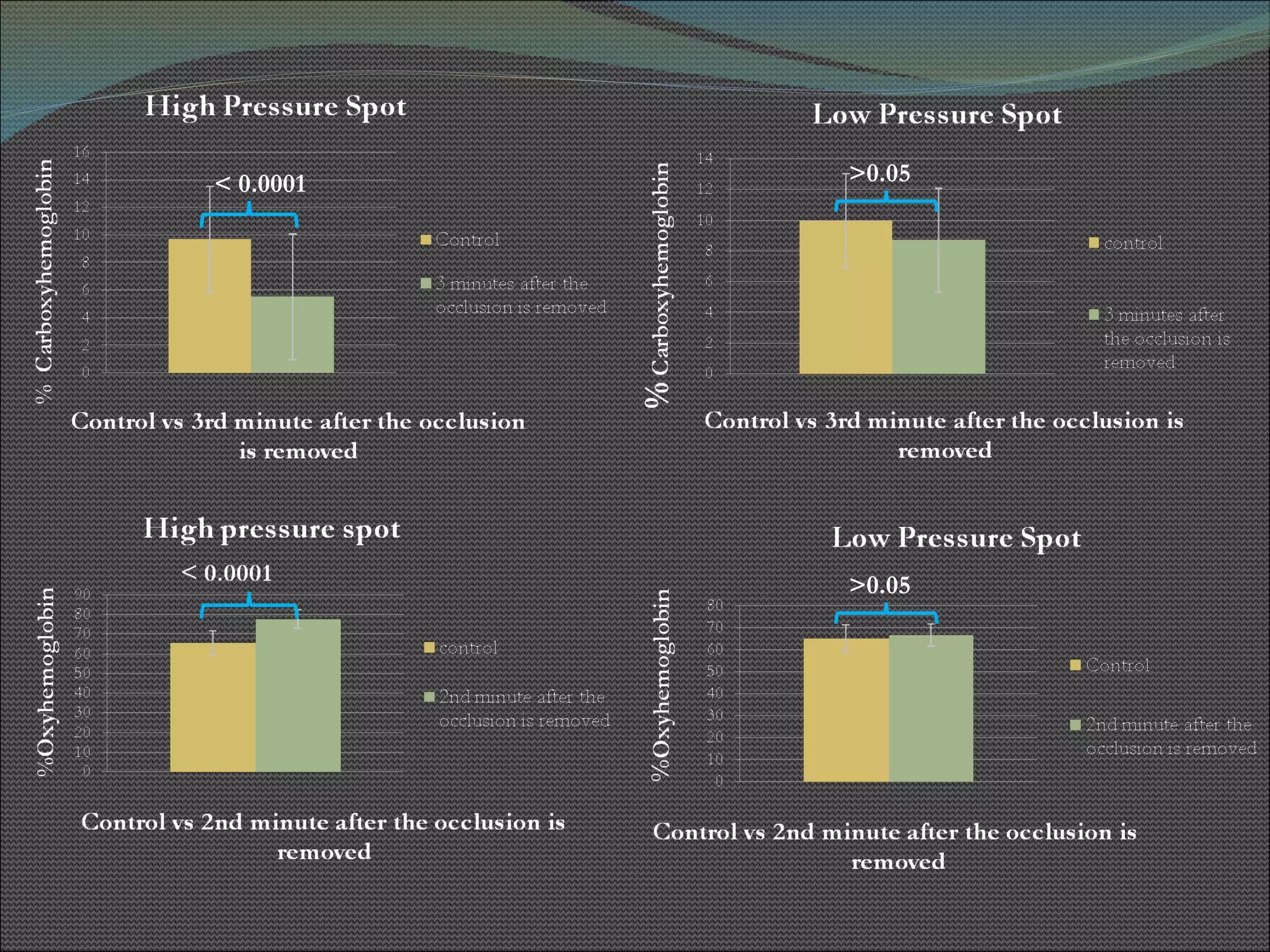
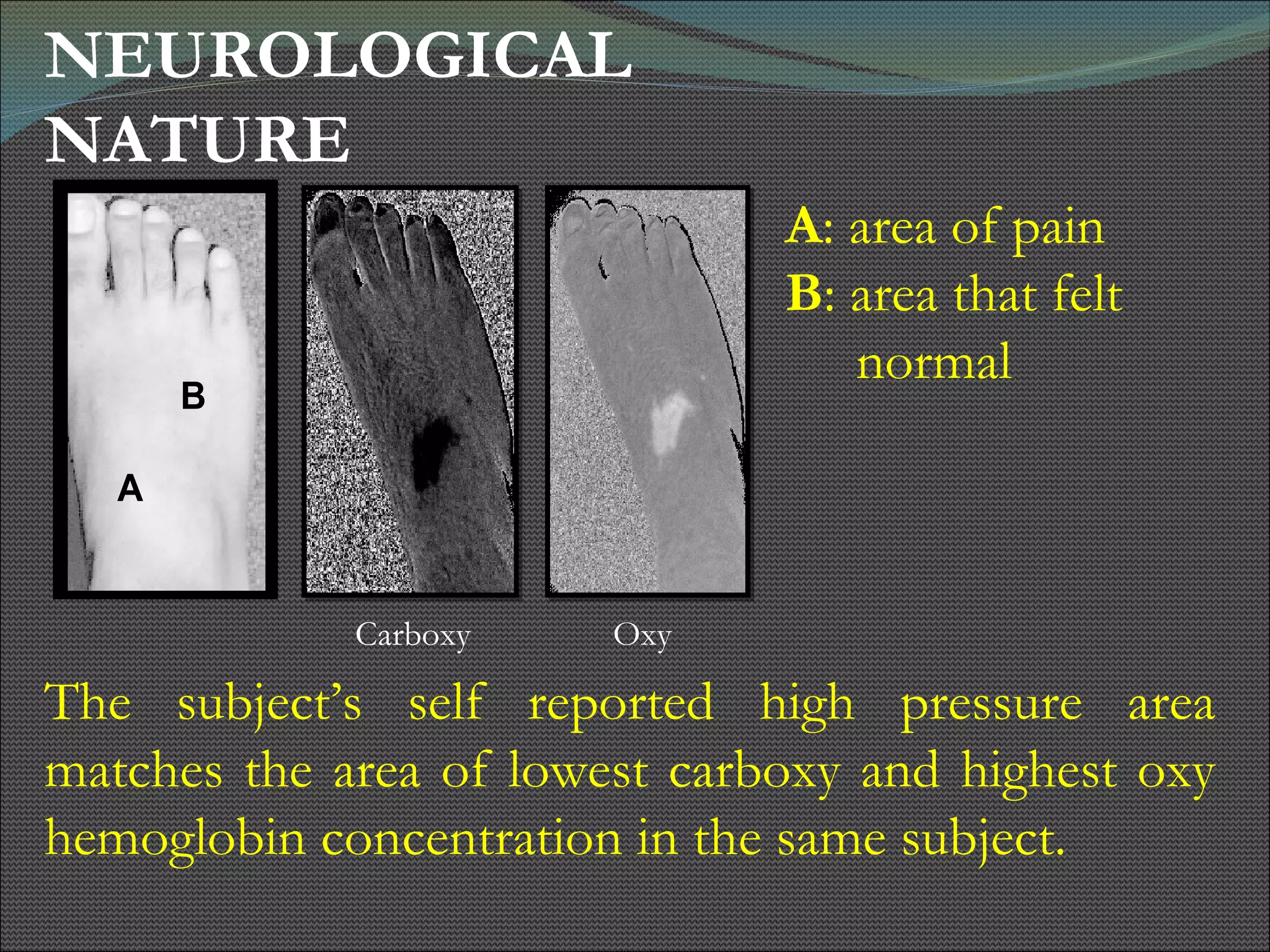
The document presents research using hyperspectral imaging to visualize biochemical changes in tissue during ischemia and reactive hyperemia. A non-invasive imaging system was developed to measure oxyhemoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin levels with spatial resolution. The study aimed to identify areas of high pressure on the feet by comparing biochemical levels during ischemia and reperfusion in those areas to self-reported pain levels. Results showed oxyhemoglobin increased and carboxyhemoglobin decreased significantly in high pressure areas during reperfusion, supporting the use of this technique to identify areas at risk for foot ulcers in diabetic patients.