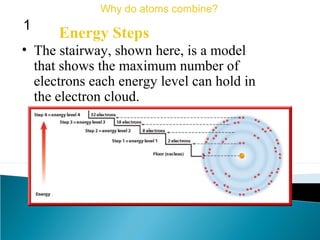
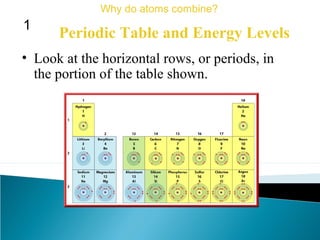
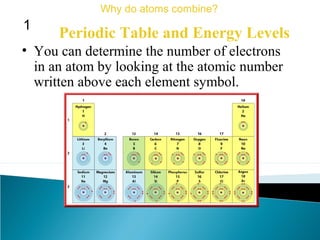
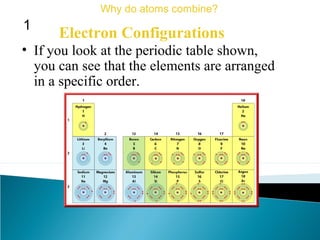
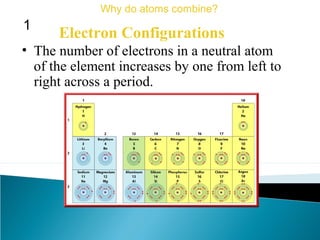
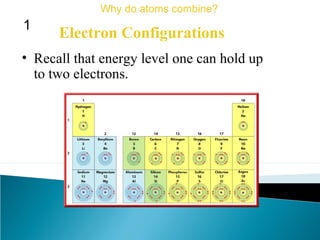
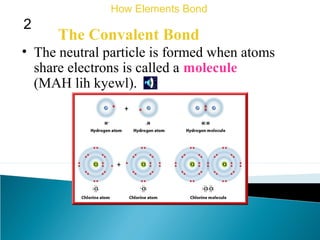
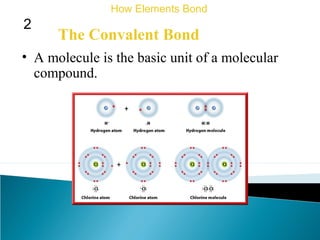
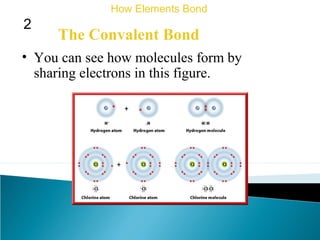
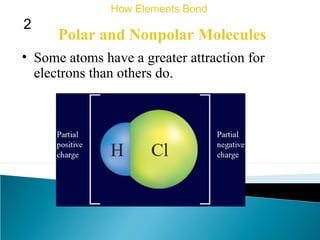
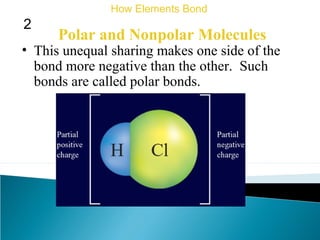
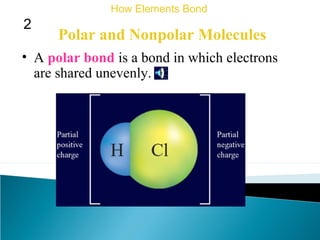
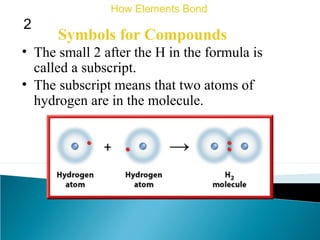
This document discusses atomic structure and how atoms bond. It begins by explaining that atoms are made up of protons and neutrons in the nucleus, and electrons in electron clouds surrounding the nucleus. Atoms bond by losing, gaining, sharing, or pooling electrons to achieve stable electron configurations like noble gases. For example, sodium loses an electron to become positively charged and chlorine gains an electron to become negatively charged, allowing them to bond ionically as sodium chloride. Magnesium can lose both of its outer electrons to form bonds.