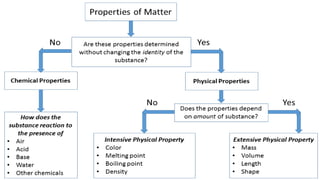
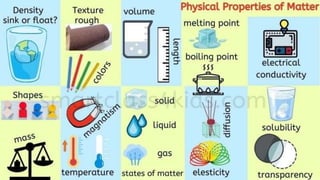
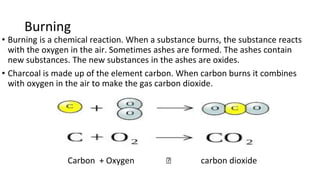
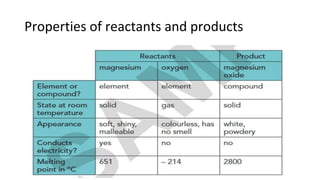
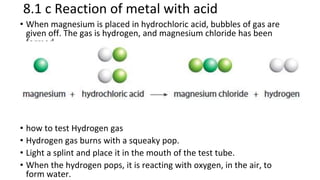
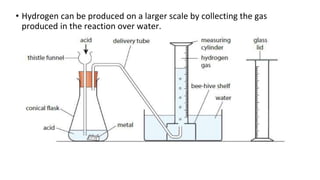
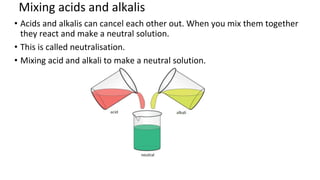
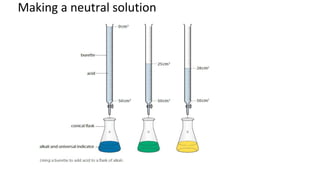
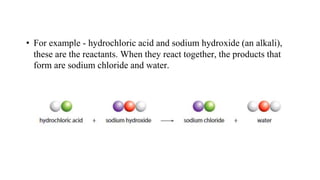
The document discusses various chemical reactions, including the formation of new substances from reactants such as metals reacting with oxygen, water, or acids. It highlights the concept of neutralization, the importance of acids and alkalis, and examples of reactions observable in everyday life. Additionally, it covers how to detect chemical reactions and their effects, including gas evolution and color changes.