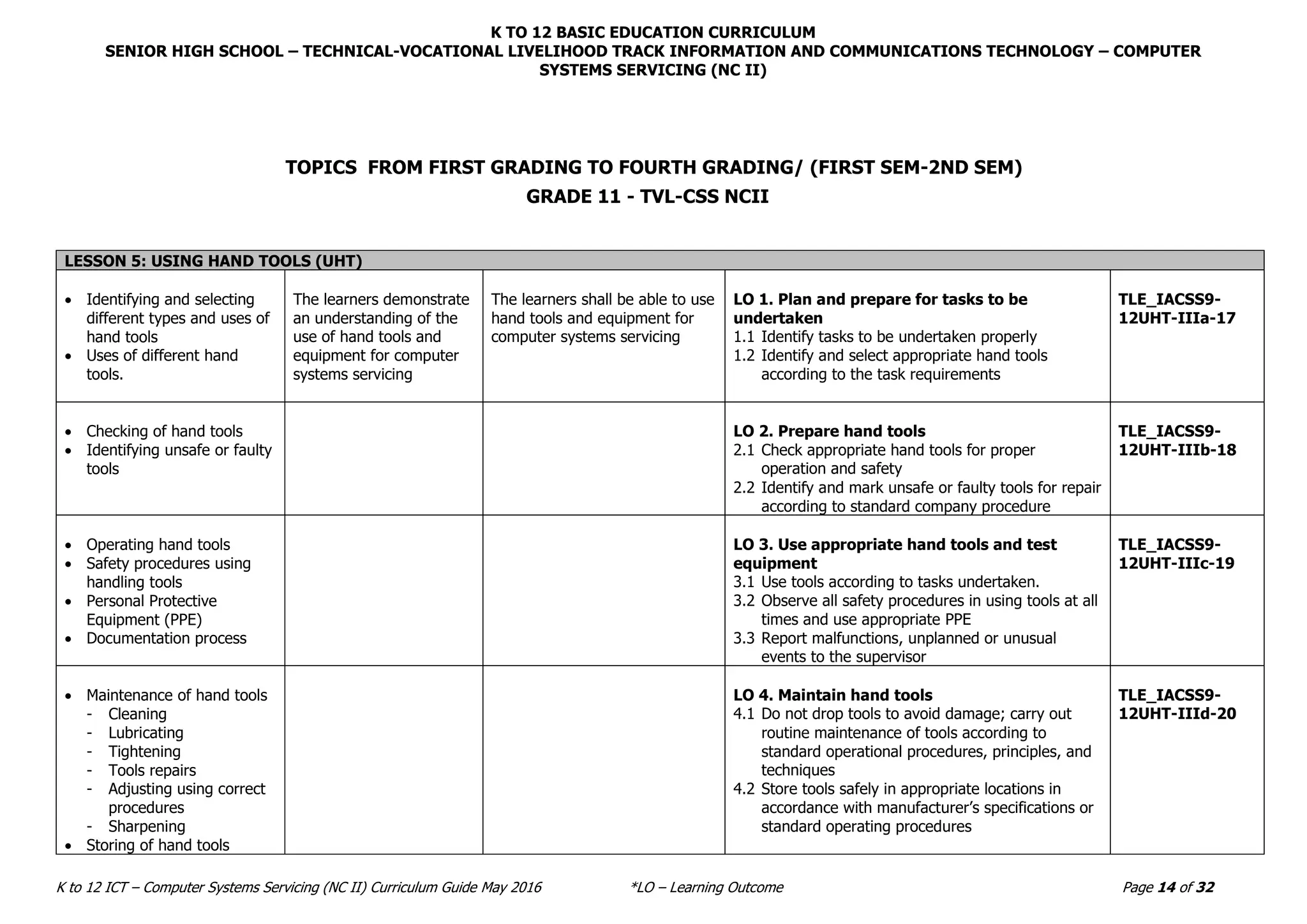
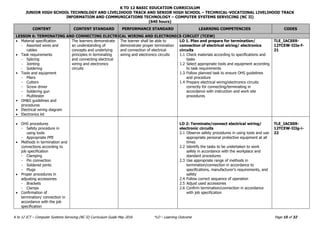
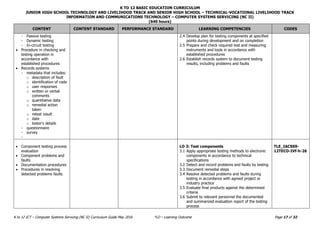
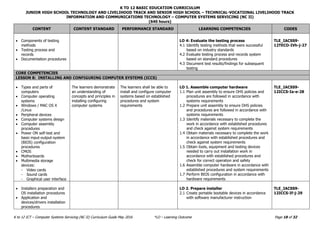
The document outlines the K to 12 curriculum guide for the ICT - Computer Systems Servicing (NC II) track, detailing various lessons focused on using hand tools, terminating electrical wiring, testing electronic components, and installing computer systems. It emphasizes learning outcomes that include safety procedures, proper tool usage, testing methods, and documentation processes. The curriculum aims to equip learners with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively work in computer systems servicing and related fields.