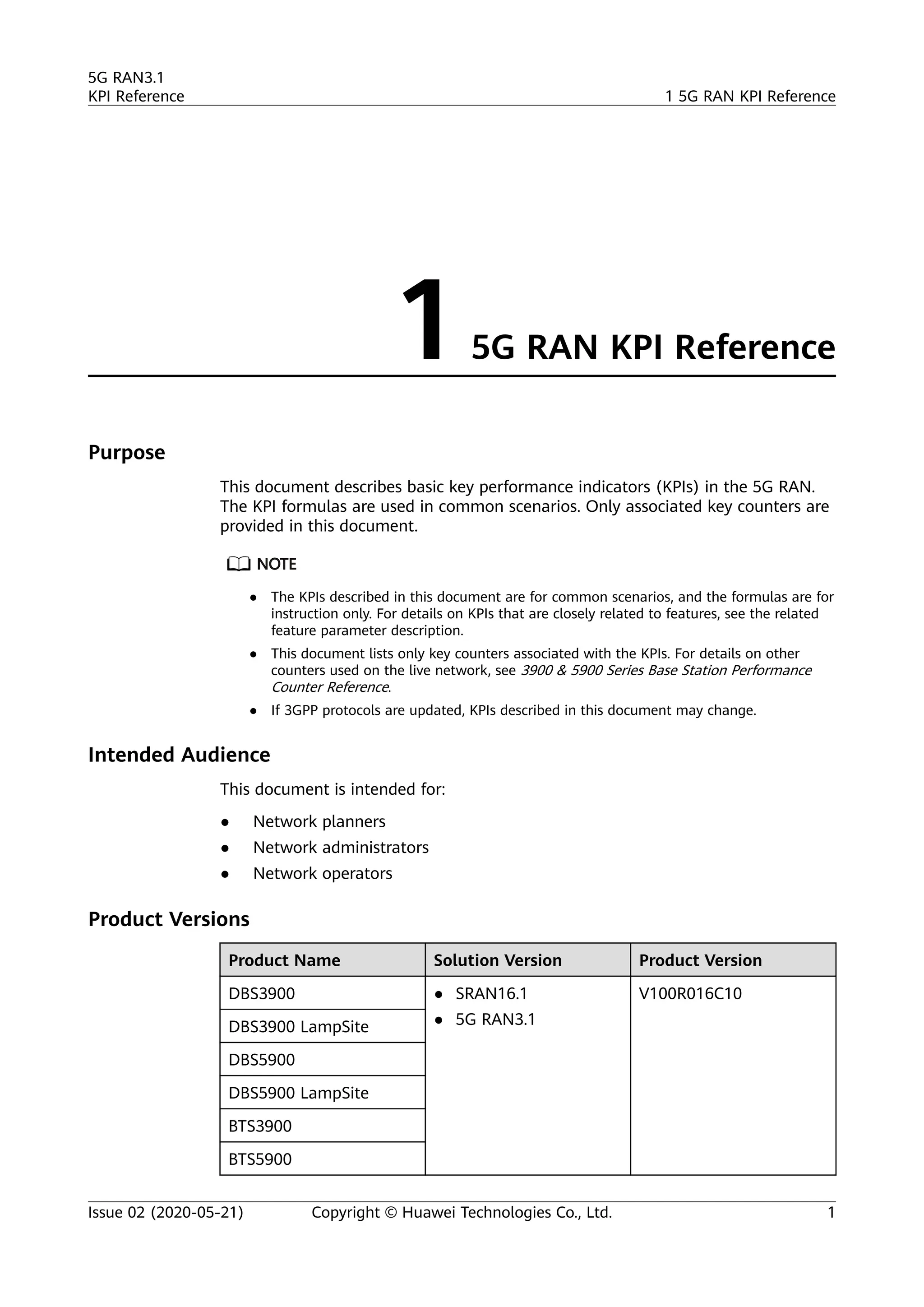
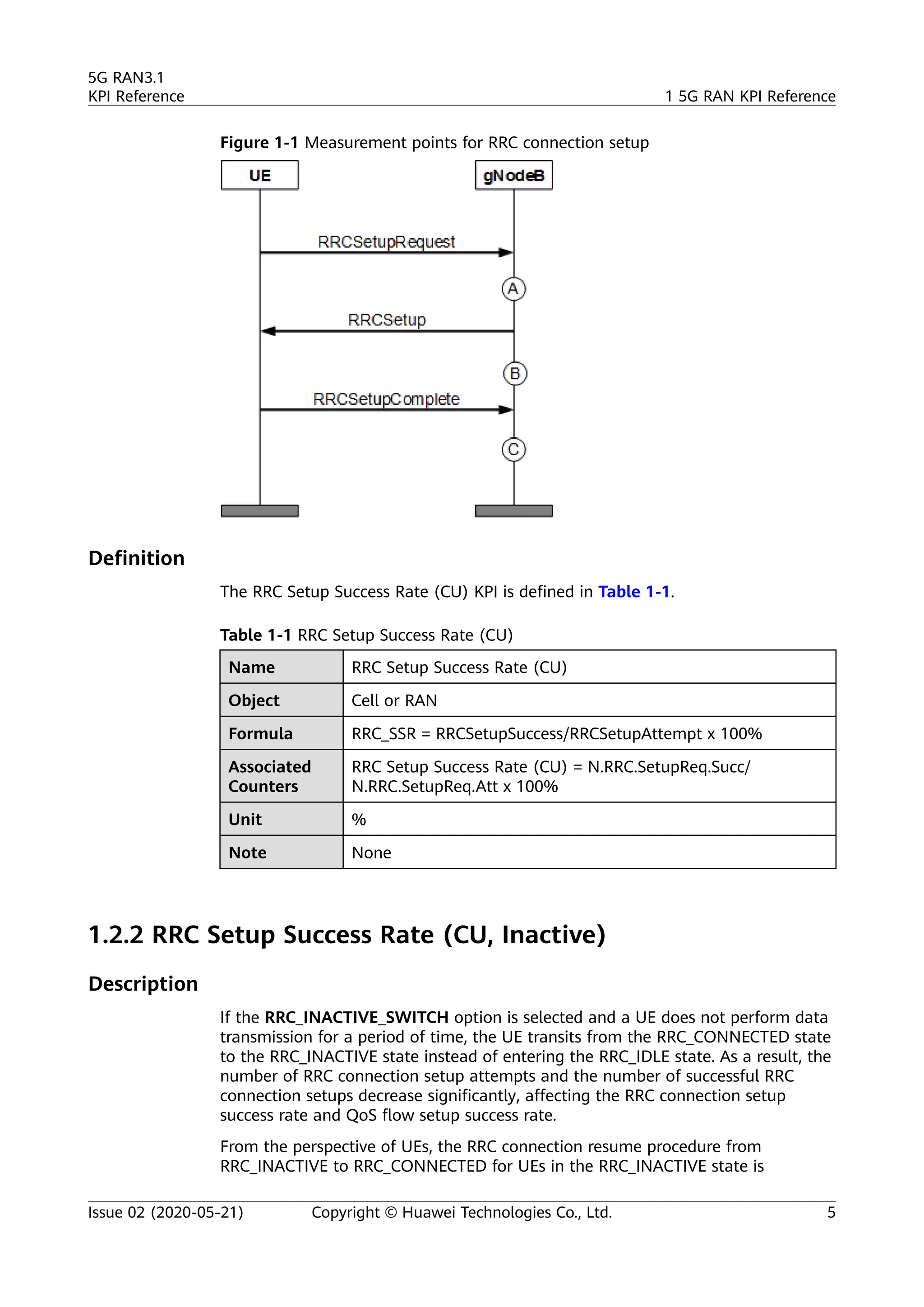
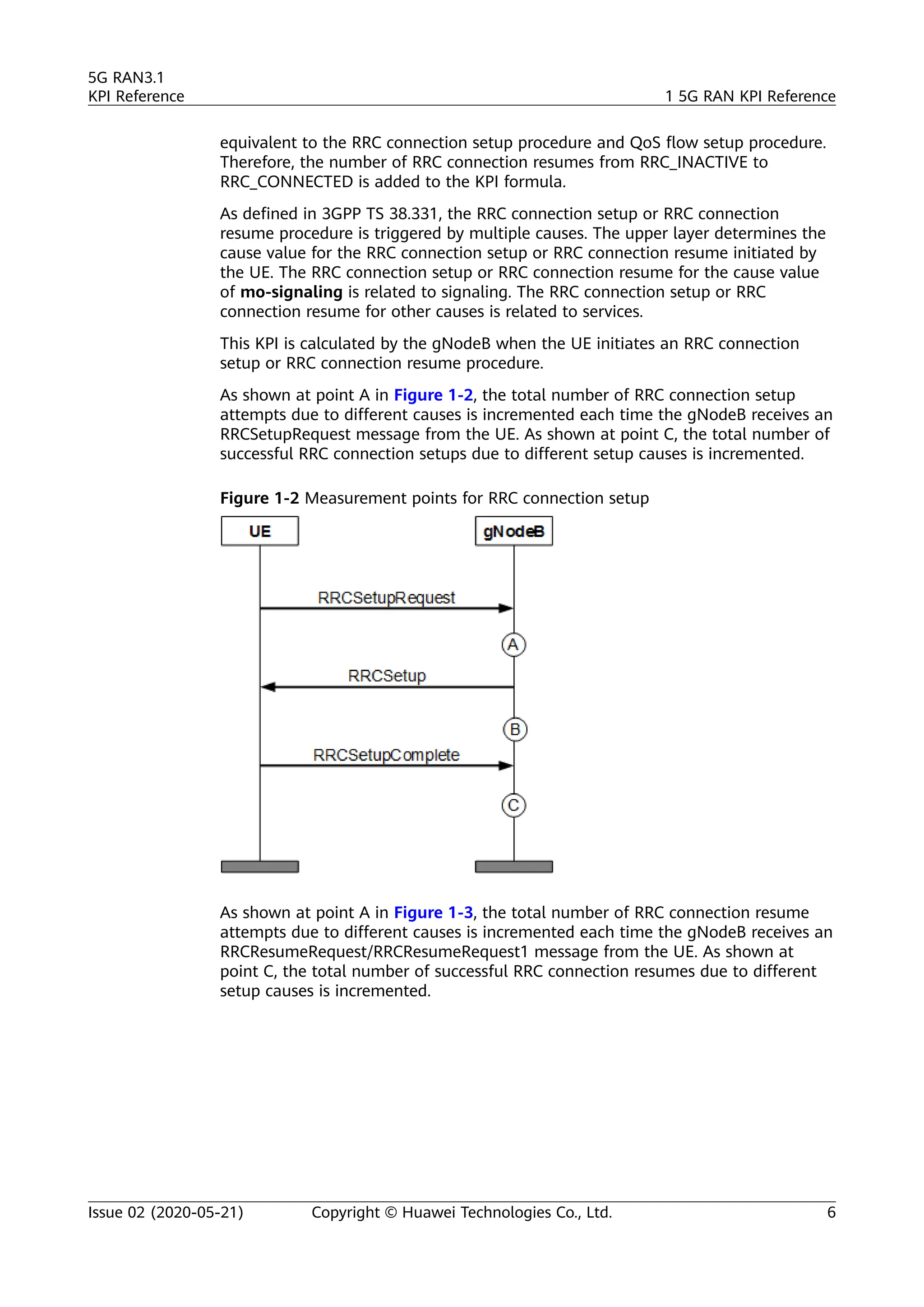
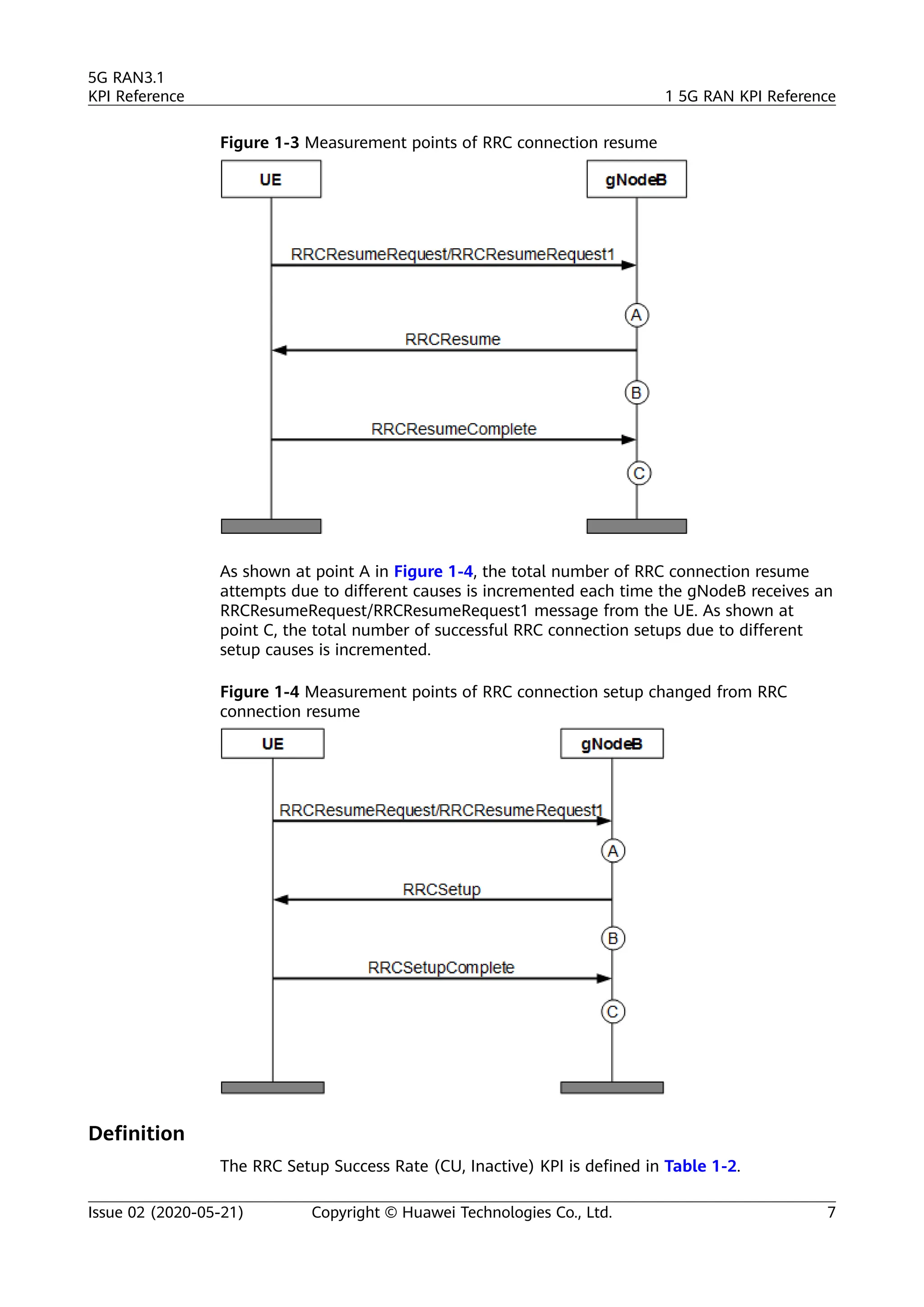
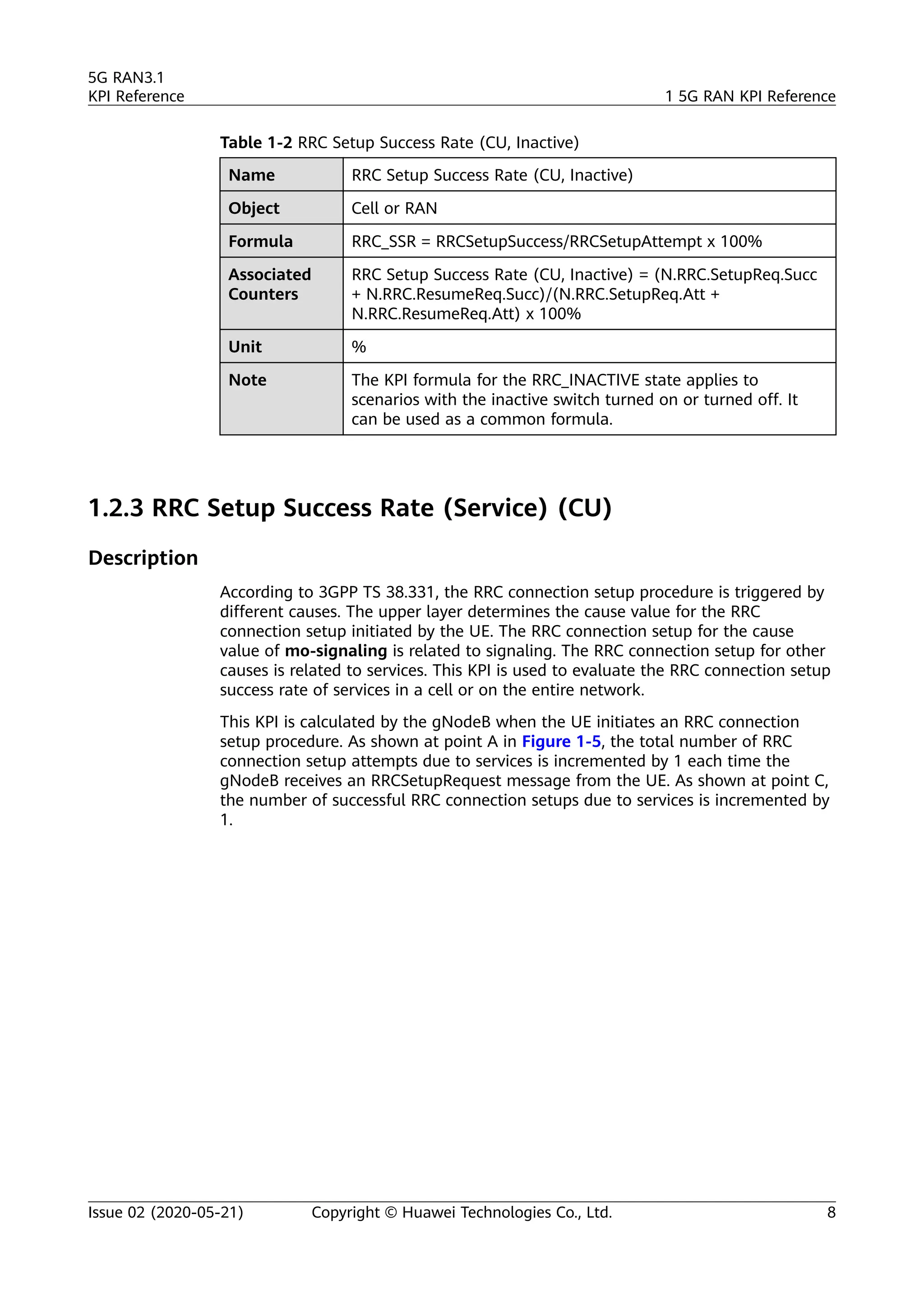
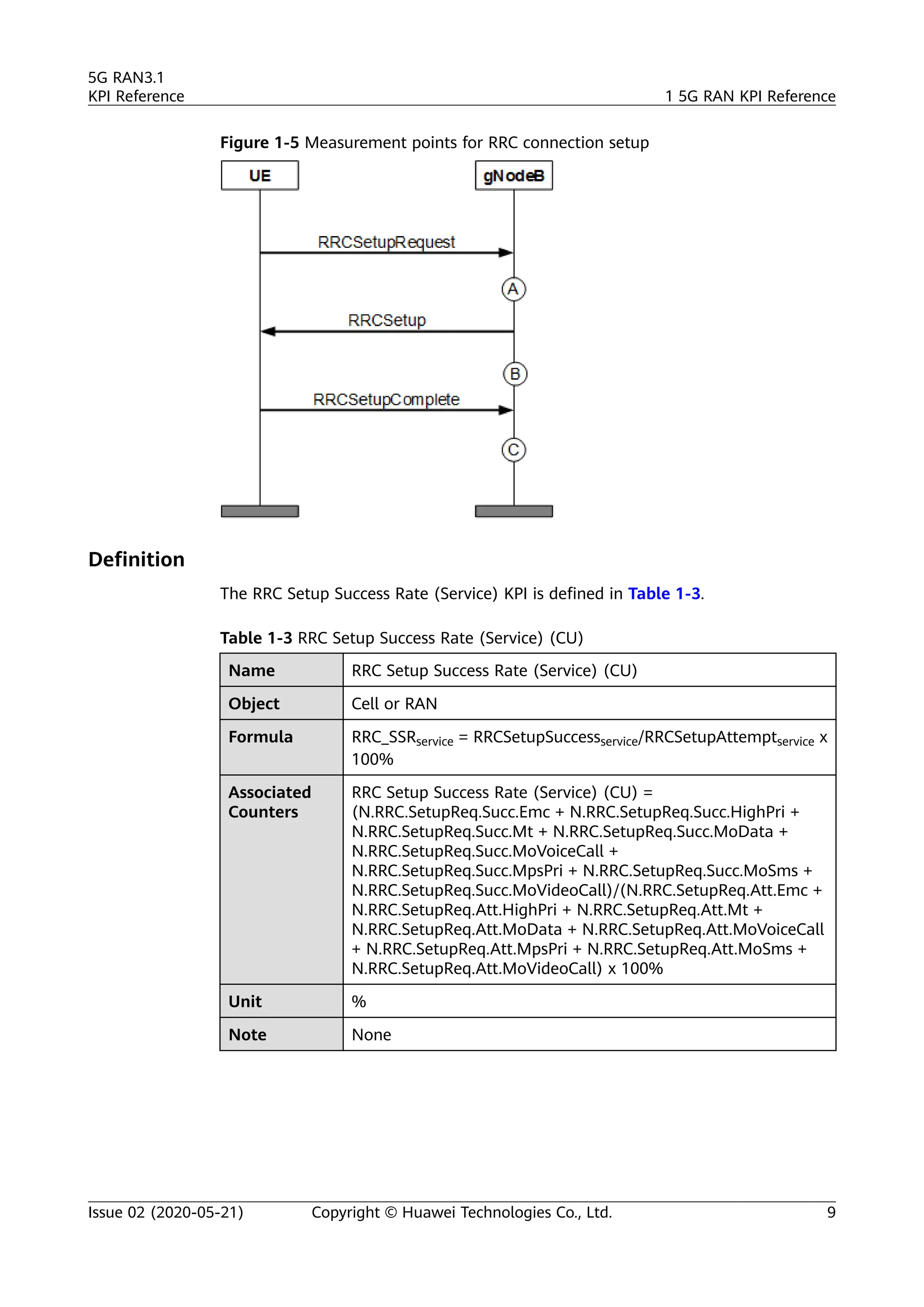
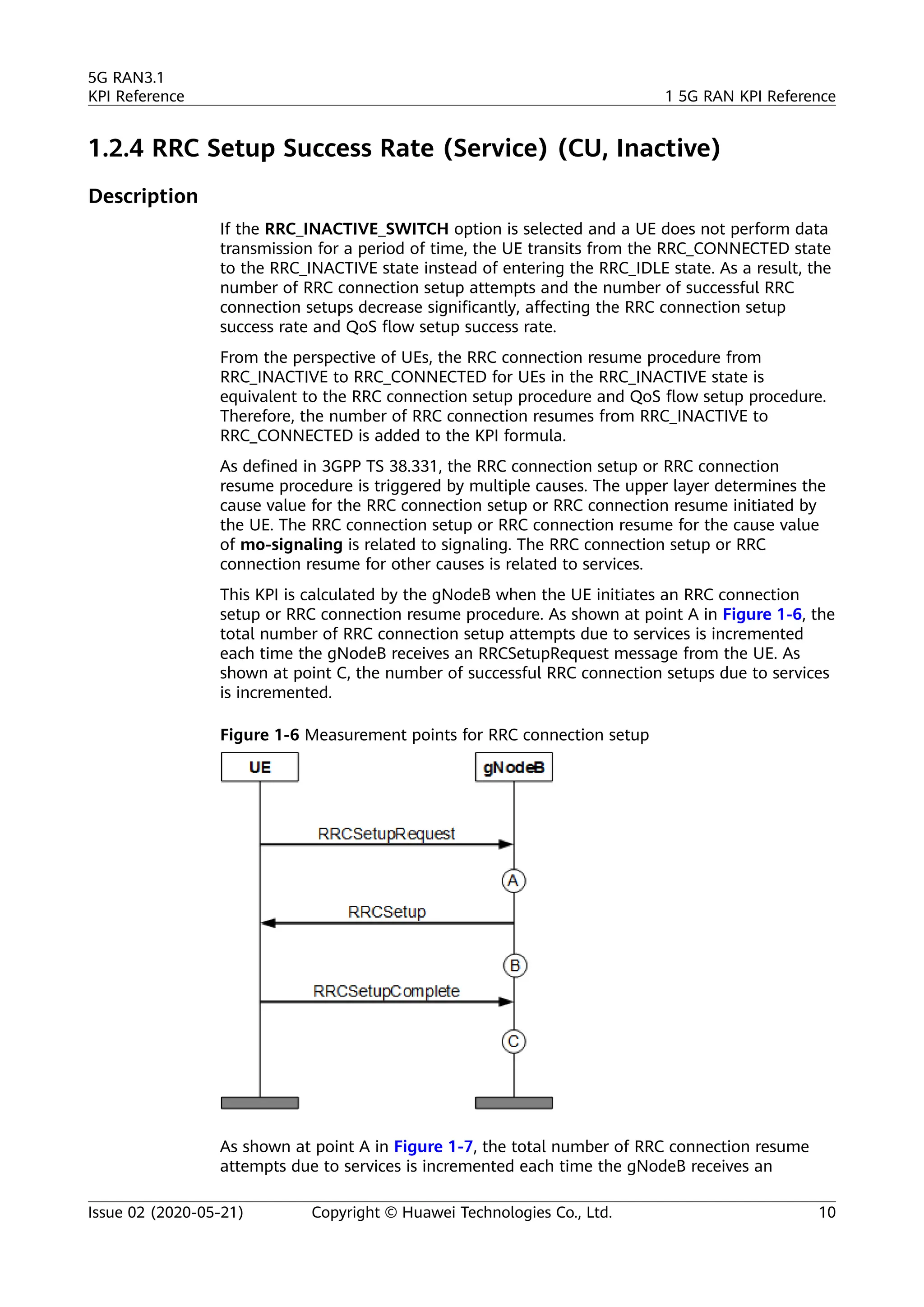
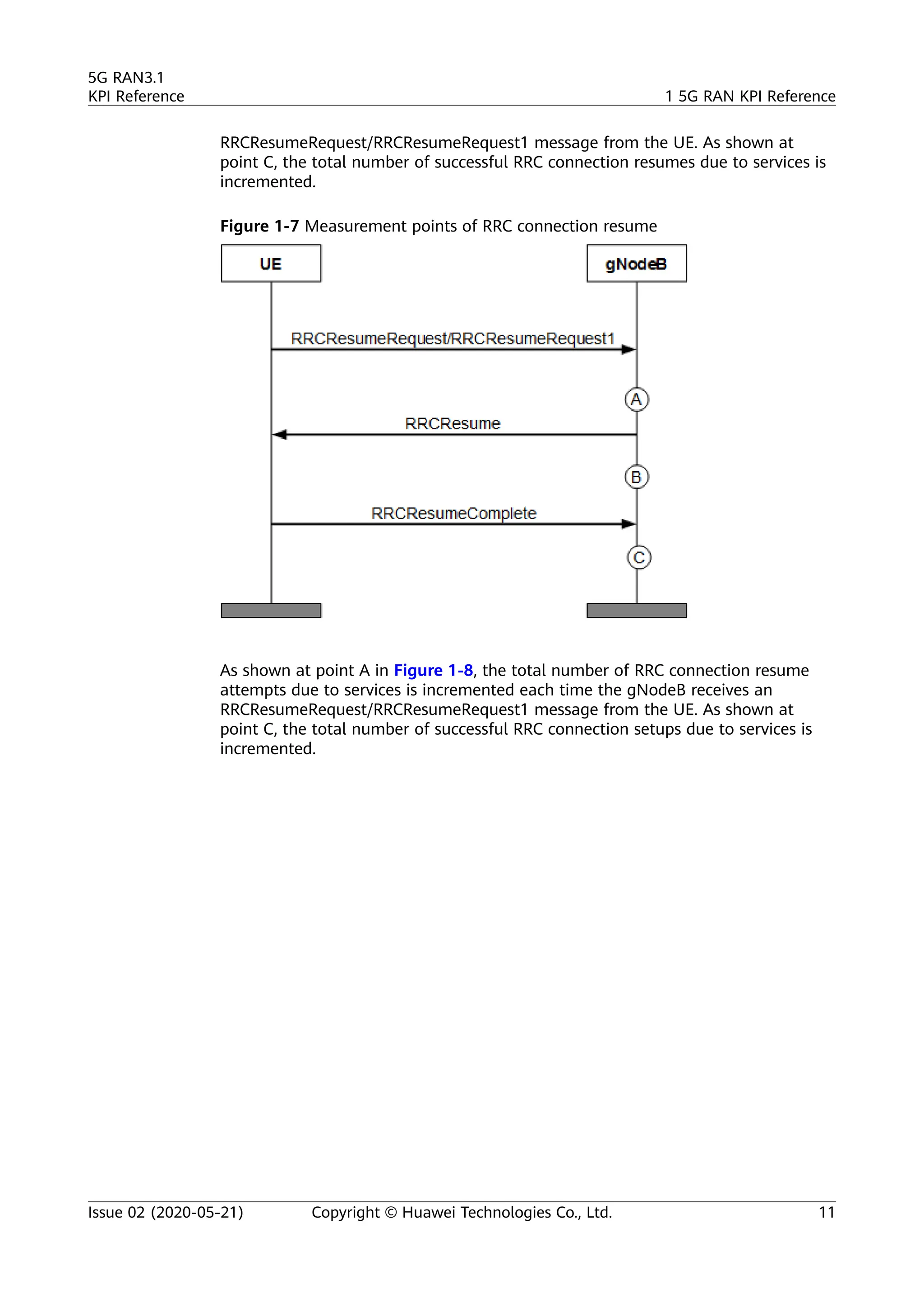
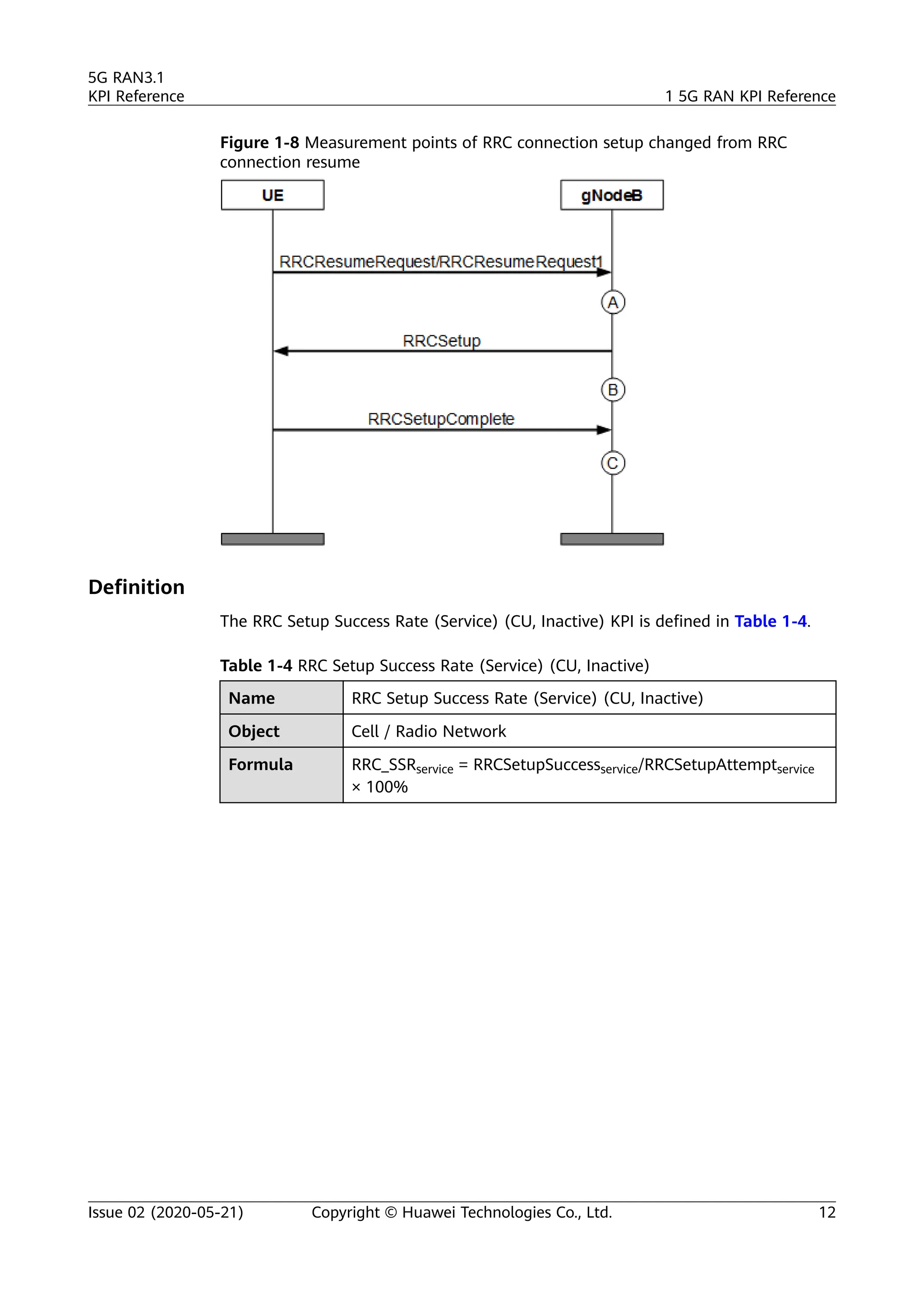
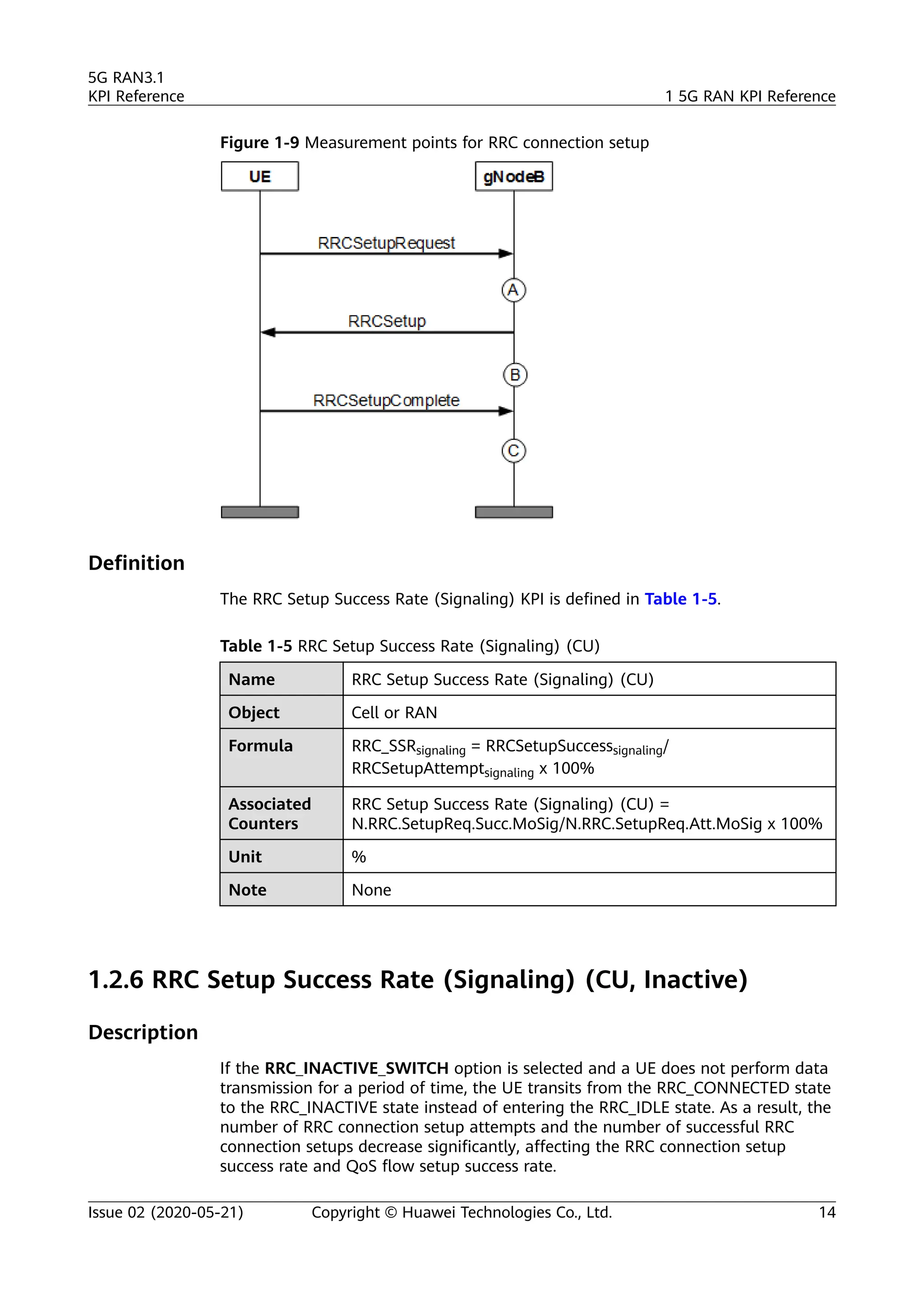
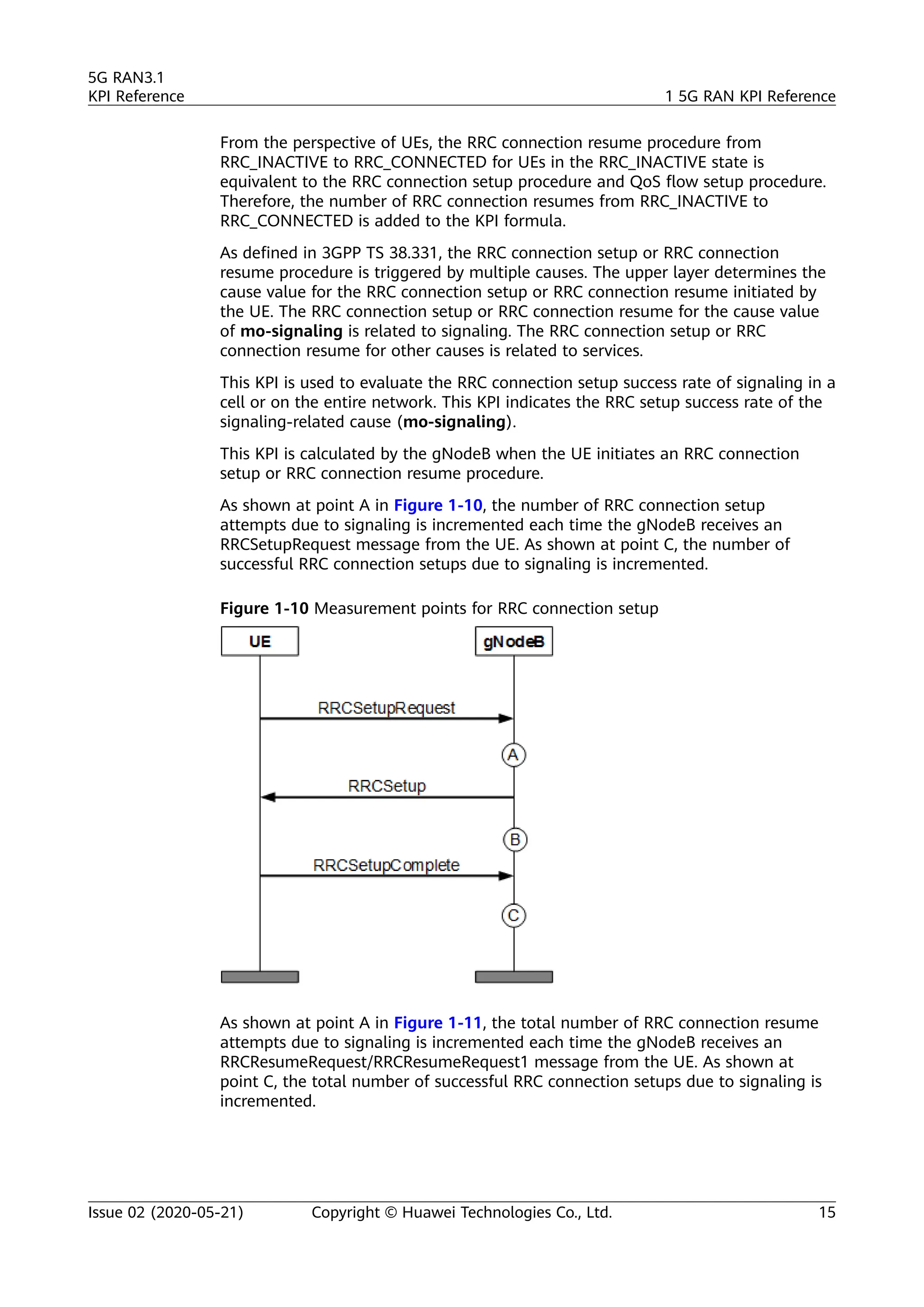
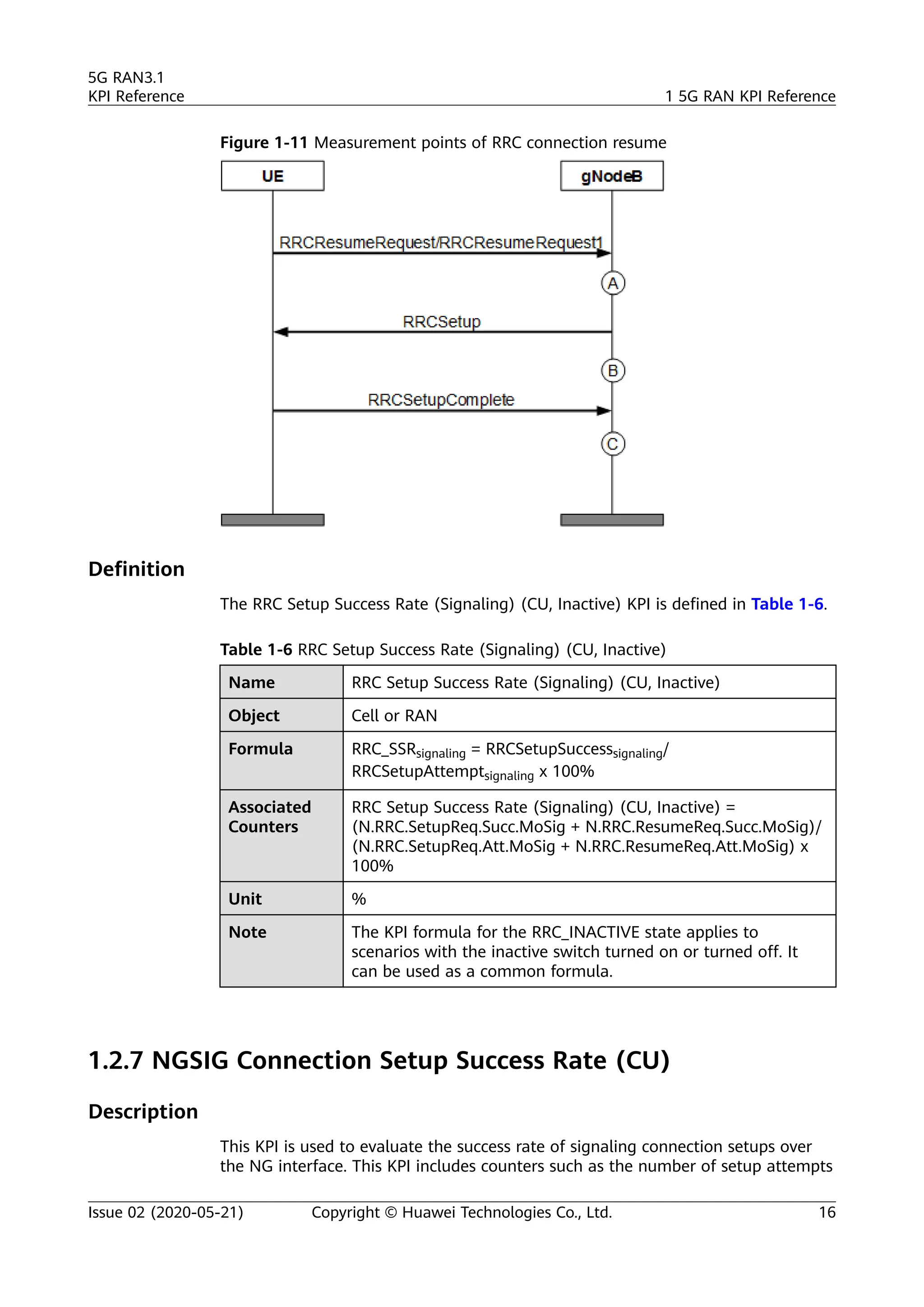
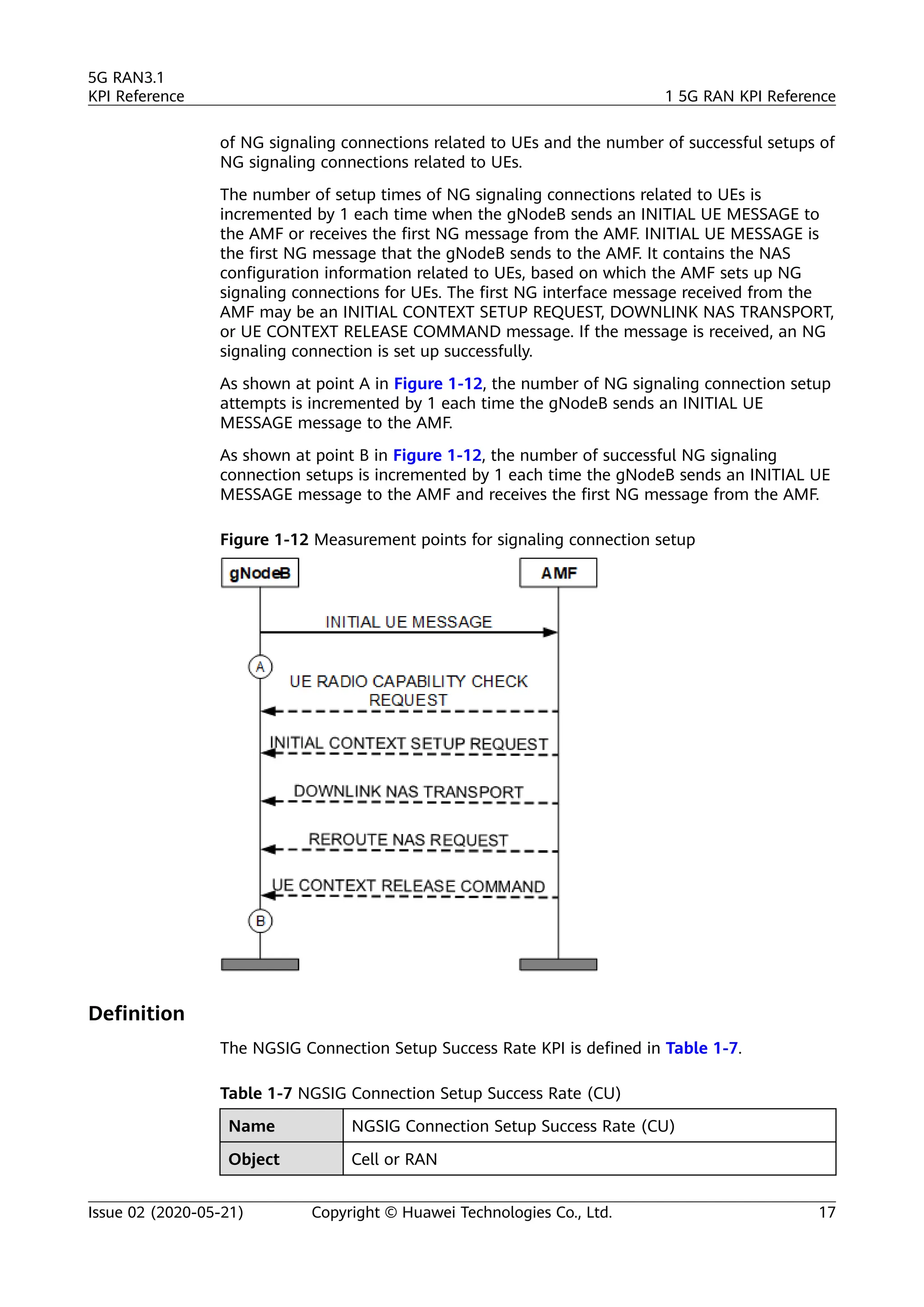
The document outlines key performance indicators (KPIs) for the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) and details changes made in the second commercial release. It includes various KPIs related to accessibility, retainability, mobility, service integrity, utilization, availability, and traffic, providing formulas and definitions for each. The intended audience consists of network planners, administrators, and operators, with a focus on ensuring practical implementation in live network scenarios.