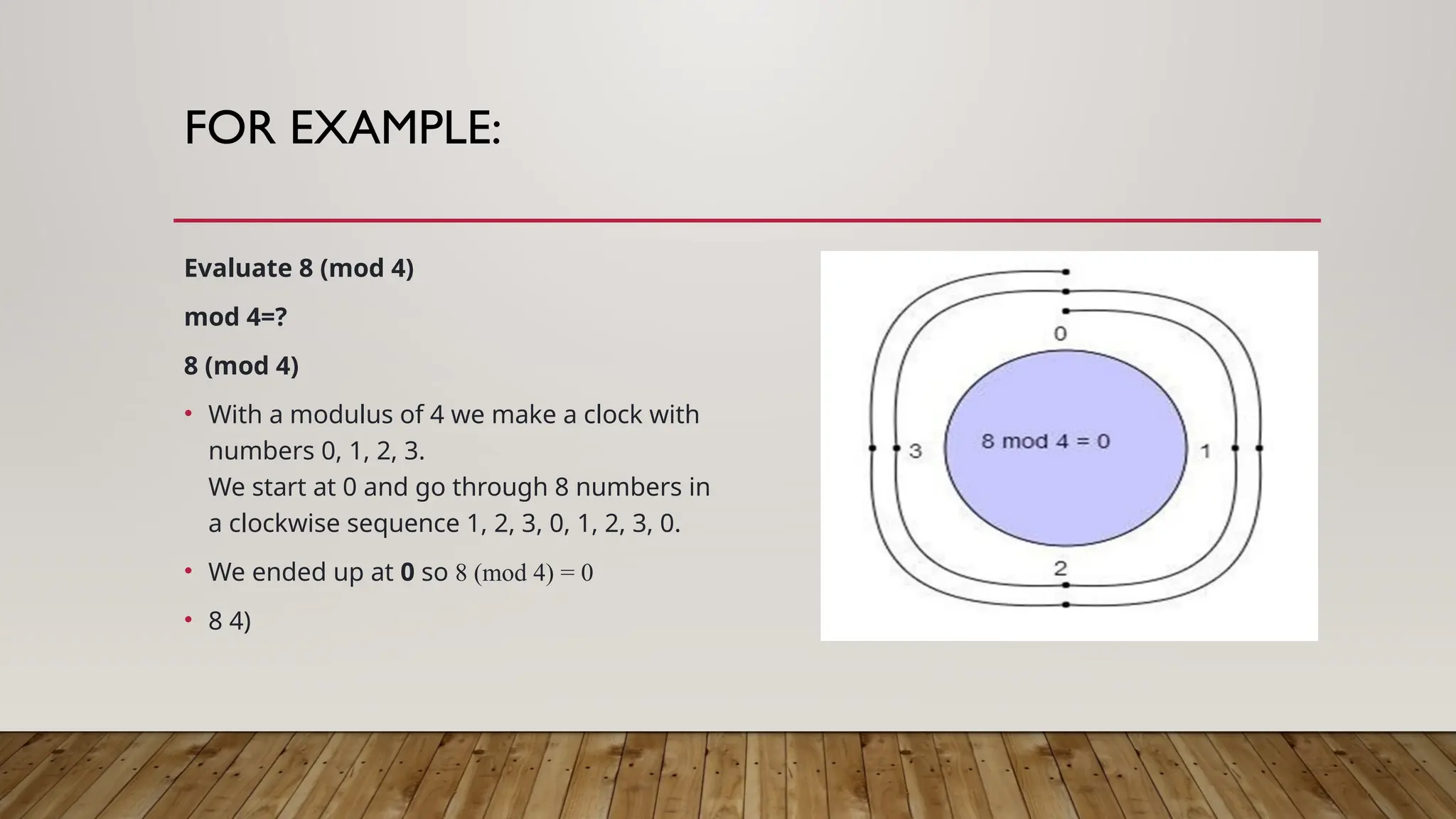
The document discusses modular arithmetic, developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss, focusing on its definition, applications in pure mathematics and practical uses such as checksums. It explains the concept of 'clock arithmetic' and provides examples of evaluating numbers using modulus. Additionally, it introduces group theory, detailing its branches like linear algebraic groups and Lie groups.