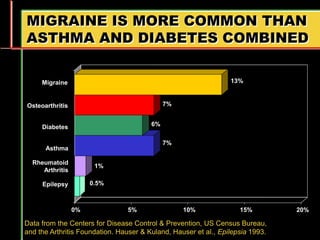
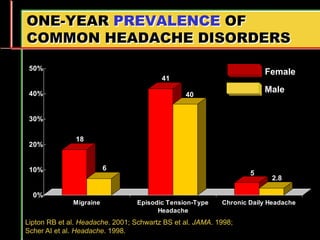
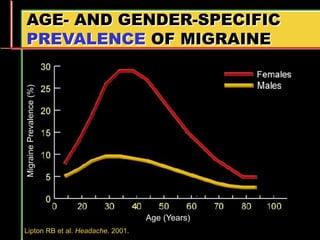
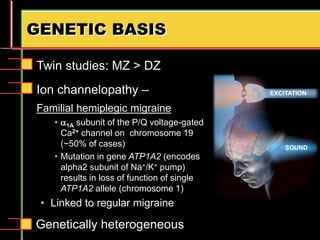
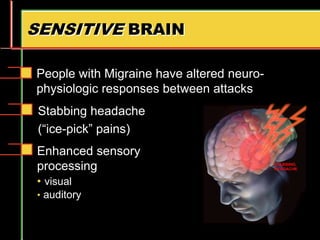
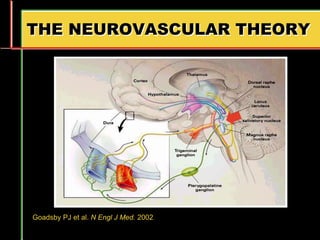
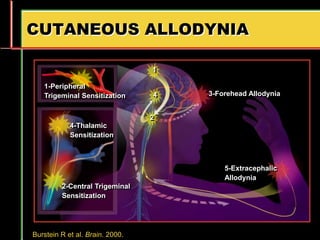
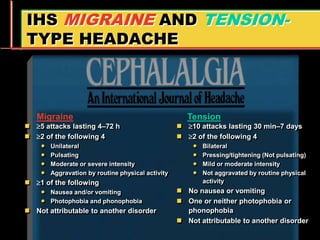
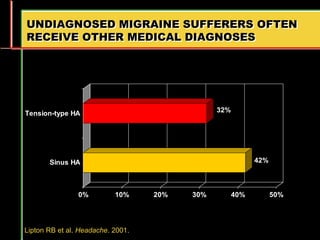
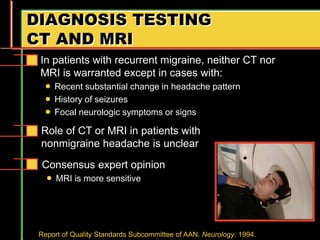
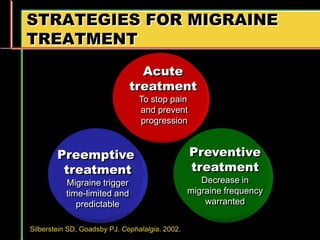
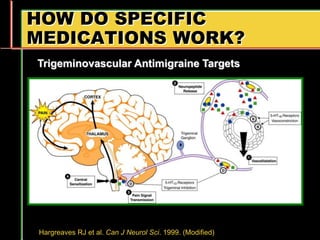
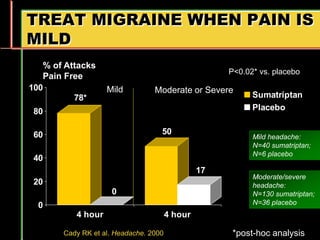
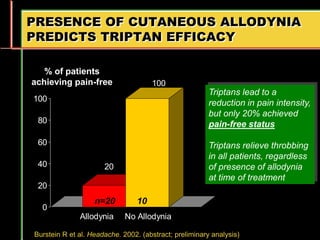
Migraine is a common neurological disorder that affects over 36 million people in the United States. It is more prevalent in females and peaks between the ages of 25-55. Migraine has significant individual and societal burden. It is characterized by recurrent episodes of moderate to severe headache with associated symptoms like nausea, sensitivity to light and sound. The pathophysiology involves changes in the brain and involves neurovascular mechanisms. Treatment involves acute treatments to stop individual attacks as well as preventive treatments to reduce attack frequency. Lifestyle modifications and avoidance of triggers can also help control migraine.