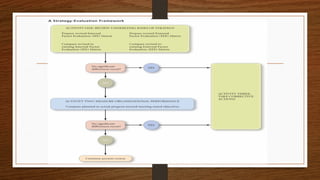
The document outlines the importance and challenges of strategic monitoring, evaluation, and control in organizations. It emphasizes Richard Rumelt's four criteria for evaluating strategies: consistency, consonance, feasibility, and advantage, and discusses the need for contingency planning due to dynamic internal and external environments. The evaluation process becomes increasingly complex due to environmental unpredictability and rapid changes in business dynamics.