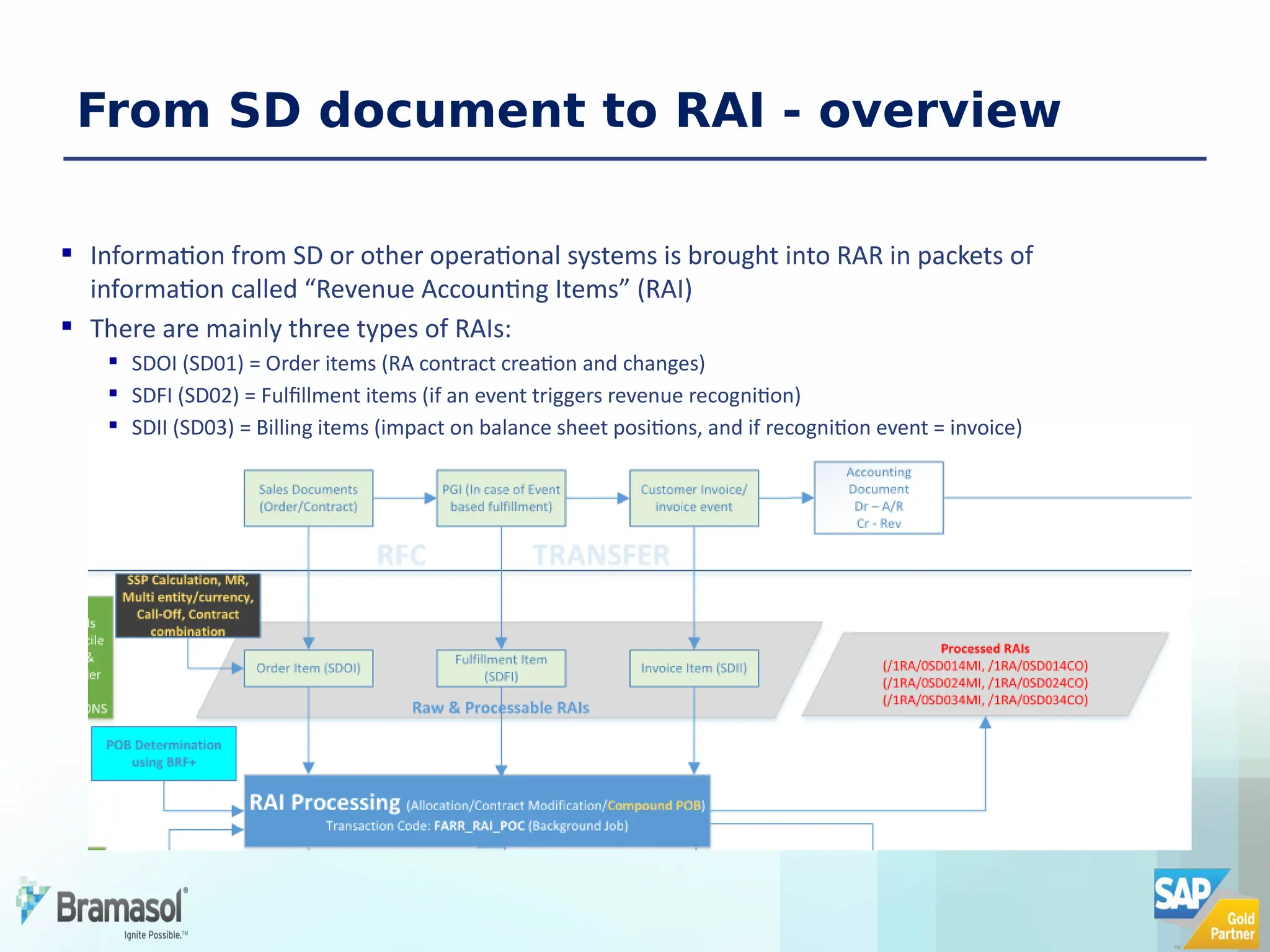
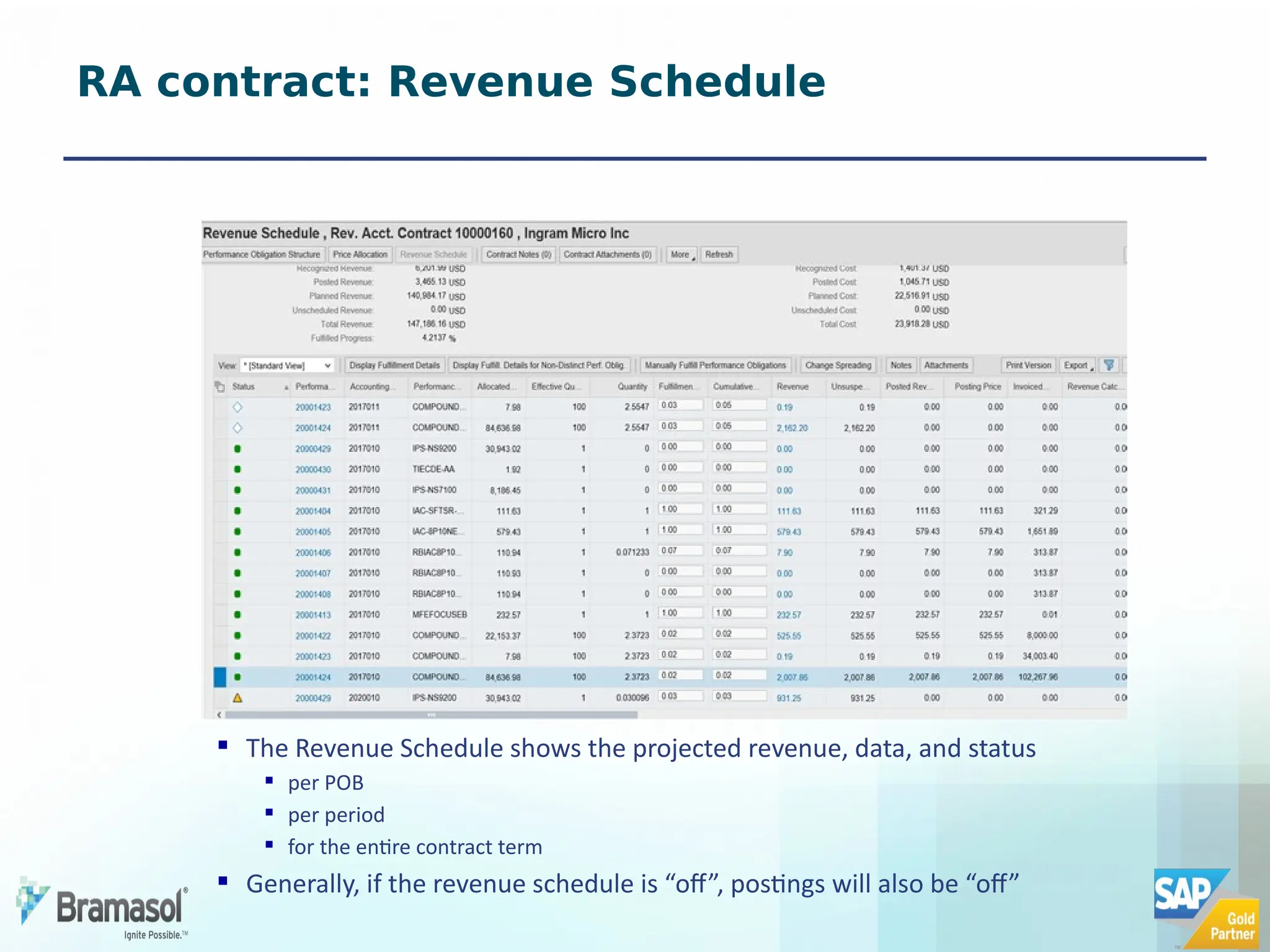
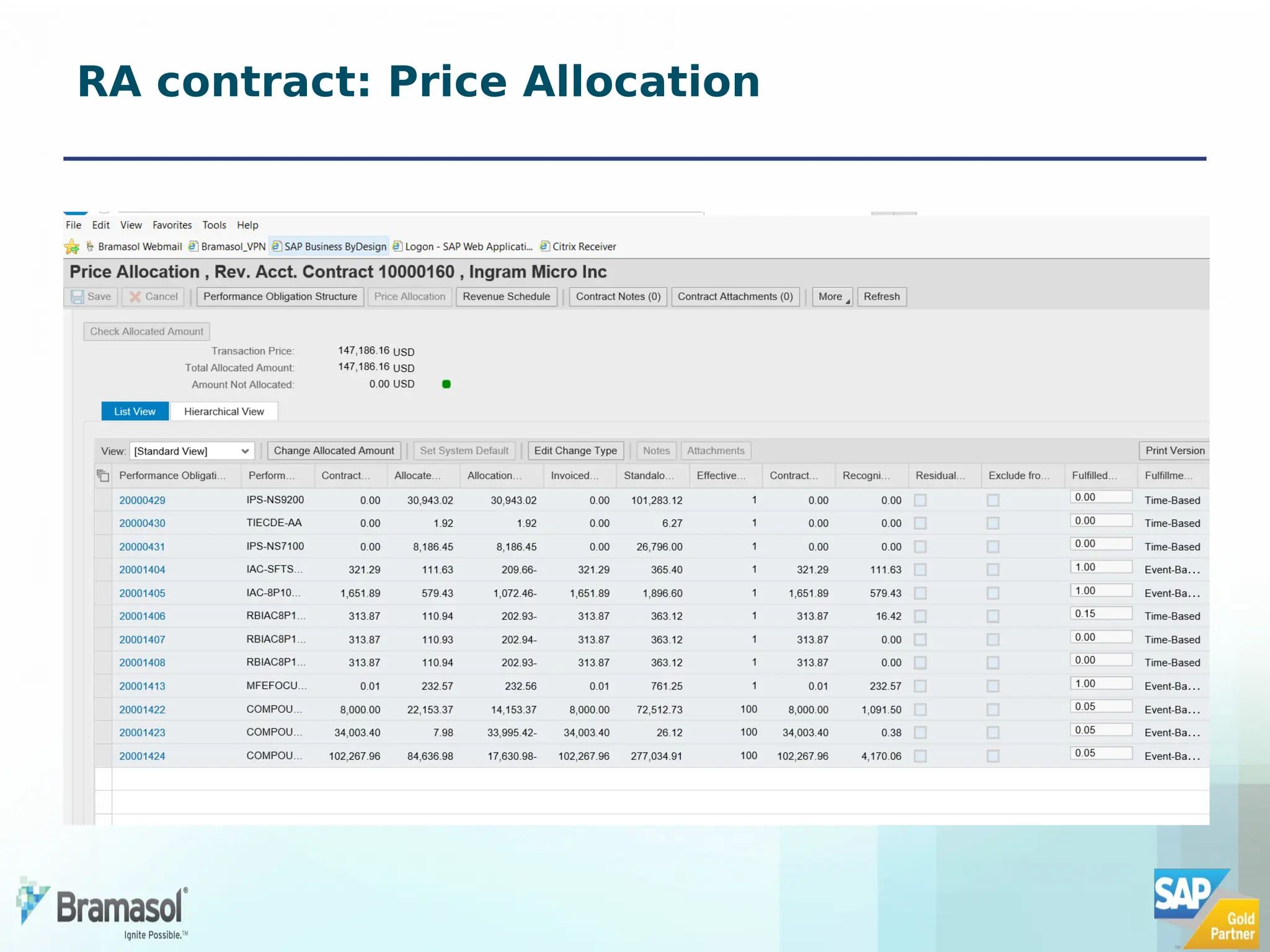
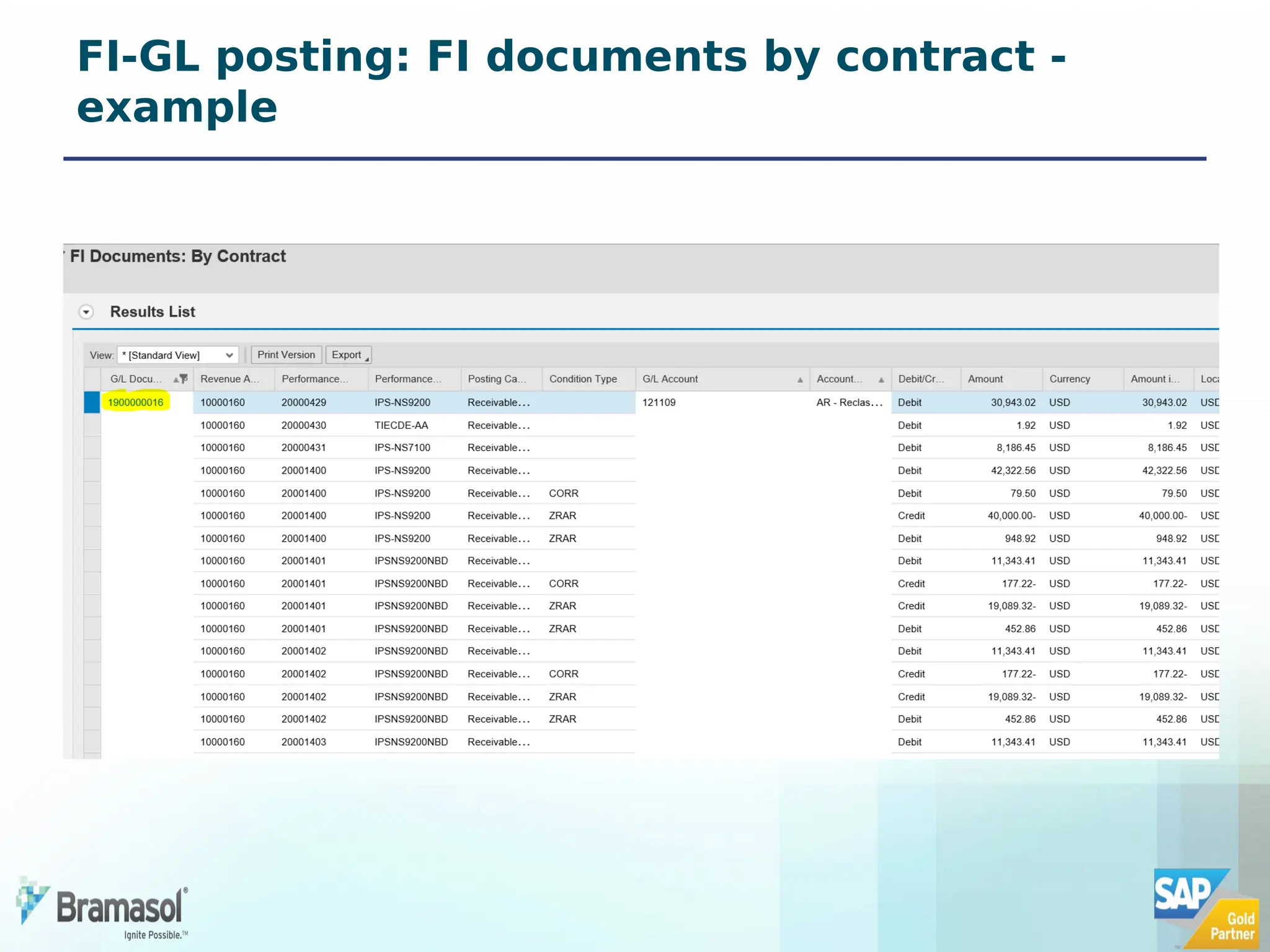
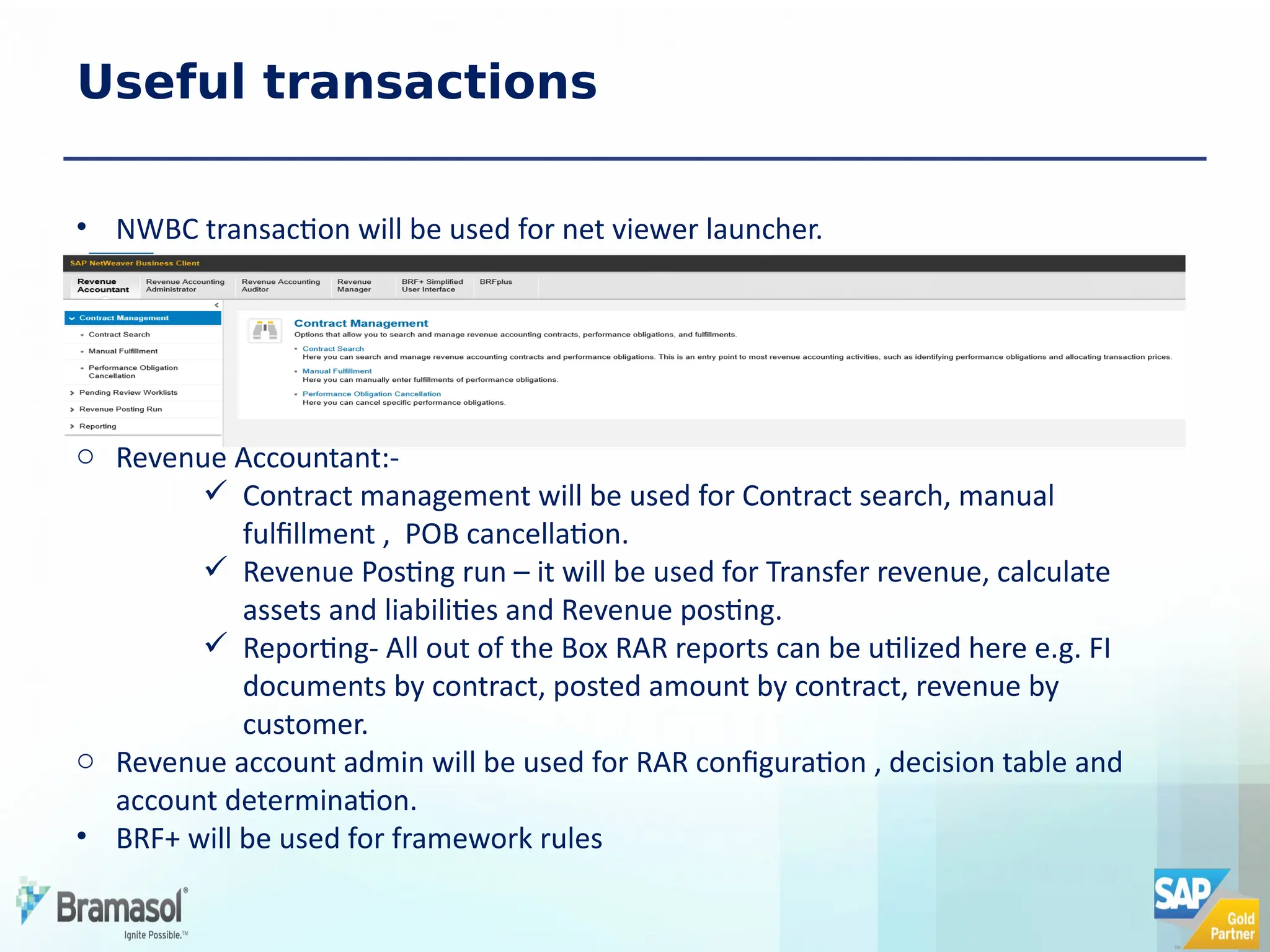
The document outlines the features and functionalities of a new revenue accounting module (RAR) by SAP, designed to comply with the IFRS 15 five-step model for revenue recognition. It highlights the complexities in revenue recognition, providing a structured approach for handling contracts, performance obligations, transaction pricing, and fulfillment management. The module aims to streamline revenue accounting processes and improve compliance for both B2B and B2C sales arrangements, addressing gaps in previous SAP offerings.