Recommended
PDF
42 regulation of respiration 14th
PPTX
42 regulation of respiration
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
39 pulmonary circulation, pulmonary edema, and pleural fluid 14th
PDF
PDF
43 respiratory insufficiency pathophysiology, diagnbosis, oxygen therapy 14th
PDF
38 pulmonary ventilaiton 14th
PPTX
PDF
45 physiology of deep sea diving and other hyperbaric conditions 14th
PDF
41 transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood and tissue fluids 14th
PDF
PDF
PPTX
40 gas exchange & diffusion
PDF
20 cardiac output, venous return, and their regulation
PDF
17 local and humoral control of tissue blood flow
PDF
15 vascular distensibility and functions of the arterial and venous systems
PPTX
41 transport of o2 and co2 in blood and tissue fluids
PPTX
PDF
23 heart valves and heart sounds; valvular and congenital heart defects
PDF
44 aviation, high altitude, and space physiology 14th
PDF
40 principles of gas exchange; diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide 14th
PDF
14 pressure, flow, and resistance
PDF
21 muscle blood flow & cardiac output during exercise; the coronary circu...
PDF
18 nervous regulation of the circulation and rapid control of arterial pressure
PDF
01 functional organization of the human body
PDF
31 acid base regulation 14th
PPTX
PDF
63 general principles of gastrointestinal function motility, nervous control,...
PDF
64 propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract (from ox1 carbon)
More Related Content
PDF
42 regulation of respiration 14th
PPTX
42 regulation of respiration
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
39 pulmonary circulation, pulmonary edema, and pleural fluid 14th
PDF
PDF
43 respiratory insufficiency pathophysiology, diagnbosis, oxygen therapy 14th
PDF
38 pulmonary ventilaiton 14th
Similar to 43 respiratory insufficiency
PPTX
PDF
45 physiology of deep sea diving and other hyperbaric conditions 14th
PDF
41 transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood and tissue fluids 14th
PDF
PDF
PPTX
40 gas exchange & diffusion
PDF
20 cardiac output, venous return, and their regulation
PDF
17 local and humoral control of tissue blood flow
PDF
15 vascular distensibility and functions of the arterial and venous systems
PPTX
41 transport of o2 and co2 in blood and tissue fluids
PPTX
PDF
23 heart valves and heart sounds; valvular and congenital heart defects
PDF
44 aviation, high altitude, and space physiology 14th
PDF
40 principles of gas exchange; diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide 14th
PDF
14 pressure, flow, and resistance
PDF
21 muscle blood flow & cardiac output during exercise; the coronary circu...
PDF
18 nervous regulation of the circulation and rapid control of arterial pressure
PDF
01 functional organization of the human body
PDF
31 acid base regulation 14th
PPTX
More from Osamu Yamaguchi
PDF
63 general principles of gastrointestinal function motility, nervous control,...
PDF
64 propulsion and mixing of food in the alimentary tract (from ox1 carbon)
PDF
61 the autonomic nervous system and the adrenal medulla
PDF
65 secretory functions of the alimentary tract
PDF
62 cerebral blood flow,cerebrospinal fluid,and brain metabolism
PDF
66 digestion and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract
PDF
72 dietary balances; regulation of feeding; obesity and starvation; vitamins ...
PDF
60 states of brain activity sleep,brain waves,epilepsy,psychoses,and dementia
PDF
67 physiology of gastrointestinal disorders
PDF
74 body temperature regulation and fever
PDF
75 introduction to endocrinology
PDF
68 metabolism of carbohydrates and formation of adenosine triphosphate
PDF
PDF
76 pituitary hormones and their control by the hypothalamus
PDF
77 thyroid metabolic hormones
PDF
79 insulin, glucagon, and diabetes mellitus
PDF
78 adrenocortical hormones
PDF
PDF
73 energetics and metabolic rate
PDF
43 respiratory insufficiency 1. 2. 3. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
pH
ガラス電極で測定
CO2
NaHCO3溶液とCO2が平衡になる.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Eq.
pH=6.1+log[HCO3
-/CO2]
O2
polarography
陰性の白金電極に流れる電流が,PO2と比例
する.
血液ガスとpH
4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
長年の喫煙による閉塞性,破壊性変化
1. 慢性感染
ニコチンによる繊毛運動障害.粘液の過剰分泌,肺胞
マクロファージの抑制
2. 慢性的気道閉塞
感染,過剰粘液,気管支上皮の炎症性浮腫
3. 空気とらえ込み現象と肺胞の過伸展
肺胞壁を50-80%破壊.
慢性肺気腫
9. 10. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
1. 細気管支病変
気道抵抗を増大,呼吸仕事量増大
2. 肺胞壁の喪失
拡散面積減少
3. 不均一な閉塞性病変の分布
換気血流比の不均等分布
→生理的シャント,生理的死腔
4. 肺胞壁の喪失
肺毛細血管の喪失→肺高血圧→右心不全
肺気腫の生理学的側面
11. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
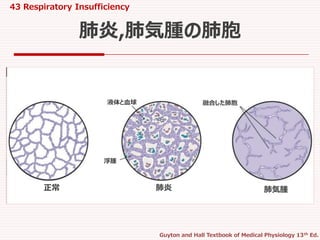
肺炎球菌を起炎菌とする細菌性肺炎が多い
肺胞に液体と血球が漏れ出る.
肺葉全体,あるいは全肺に拡大
肺は”硬化像 consolidation”を呈する
肺胞が,液体と細胞成分で満たされた状態を指す.
肺炎
12. 13. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
肺炎による酸素化能の悪化
肺動脈血
酸素飽和度60%
右肺静脈
酸素飽和度
97%
左肺静脈
酸素飽和度
60%
肺炎
大動脈:
血液1/2=97%
1/2=60%
平均酸素飽和度
=78%
14. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
無気肺と酸素化能
肺動脈血
酸素飽和度60%
右肺静脈
酸素飽和度
97%
無気肺
左肺静脈
酸素飽和度
60%
流量 正常の
1/5
大動脈:
血液5/6=97%
1/6=60%
平均酸素飽和度
=91%
15. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
3-5%の人が一生の経過中に経験
空中の外部物質に対する難治性気道過敏症
患者の70%は,30歳以下
花粉やスモッグ(老人)に対するアレルギー
IgE抗体が関与
花粉が肥満細胞と反応して以下の物質を遊離して局所の
浮腫と細気管支の攣縮を引き起こす.
ヒスタミン,
slow-reacting substances of anaphylaxis
(leukotriene)
Eosinophilic chemotactic factor
Bradykinin
経年変化として,胸郭のビア樽化 barrel chest
喘息
16. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
マクロファージによる感染組織への侵入
繊維組織による病巣の遮断walling-off
未治療だと3%の患者でwalling-off起こら
ず,大きな膿瘍腔を形成
最終的には
1. 呼吸仕事量増大
2. 拡散障害
3. 換気血流比の不均等分布
結核
17. 18. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
1. 外因性の原因による肺の酸素化障害
a. 大気中の酸素不足
b. 低換気(神経筋疾患)
2. 肺疾患
a. 抵抗増大,コンプライアンス低下などによる低換気
b. 肺胞換気血流比異常
c. 拡散障害
低酸素血症
19. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
3. 静脈-動脈シャント(心内右左シャント)
4. 血液による組織への酸素移送の異常
a. 貧血ないし異常ヘモグロビン
b. 循環血液量不足
c. 局所循環不全(末梢,能,冠循環)
d. 組織浮腫
5. 組織の酸素利用障害
a. 細胞酸化酵素の中毒
b. 毒,ビタミン欠乏などによる酸素利用障害
低酸素血症
20. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
シアン中毒
シアンがcytochrome oxidaseの活性をブ
ロック
組織細胞酸化酵素の欠損
Beriberi病
ビタミンB欠乏による,酸素利用,炭酸ガス形
成が障害される.
組織の酸素利用障害
21. 22. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
大気の低酸素
酸素療法は,非常に有効
低換気による低酸素
酸素療法は,非常に有効だが,高炭酸ガス血症を改
善するものではない.
拡散障害による低酸素
肺胞気酸素分圧を100から600mmHg程度まで
上昇するので有効.
低酸素の原因と酸素療法
23. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
肺水腫と酸素療法
酸素テント療法中の肺胞気酸素分圧
正常肺胞気酸素分圧
肺水腫+酸素療法
肺水腫 酸素療法なし
動脈端 静脈端
肺毛細血管内の血液
毛細血管血
肺胞ないし血中のPO2(mmHg)
24. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
貧血,異常Hb,脱水,シャント
肺胞ですでに正常な酸素が利用可能で,酸素療法の
有効性は乏しい. (ただし溶存酸素をmaxまで増や
すのは,CO中毒などの場合有効.)
組織の酸素利用が障害されている場合.
酸素療法は,無効.
低酸素の原因と酸素療法
25. 43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
皮膚がブルーであることをさす言葉
還元型Hbが過剰になった状態
還元型Hbは暗紫色で,それが皮膚を透過して
見える状態.
還元型Hb>5g/dlで出現
Hb<5gl/dlの貧血患者では出現しない.
多血症患者では,他に異常がなくてもチアノー
ゼを呈することがありうる.
チアノーゼ
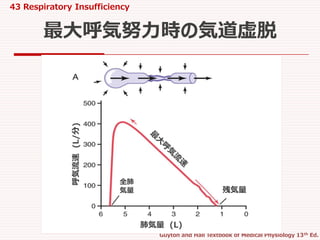
26. 27. Editor's Notes #5 肺は,含気量が多いほど気道が,外側に伸展されて保たれやすい.
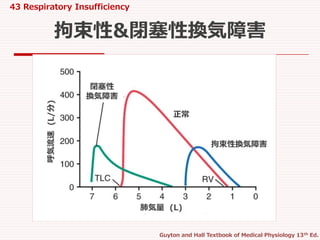
逆に,含気量が少なくなるほど,気道も弛緩して容易に虚脱しやすく最大呼気流速が遅くなる. #6 拘束性換気障害では,TLVもRVも減少していて,最大呼気流速も正常肺のそれに至らない.
繊維化をおこす疾患
肺結核
珪肺
亀背
側弯
線維性胸膜炎
閉塞性換気障害では,TLC,RVともに増加しているが,最大呼気流速は著明に低下している
閉塞性換気障害をおこす疾患
喘息
肺気腫
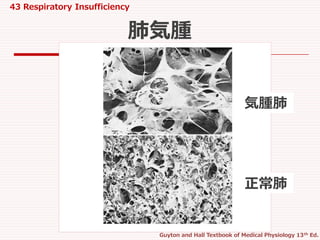
#10 Contrast of the emphysematous lung (top) with the normal lung (bottom),
showing extensive alveolar destruction in emphysema.

![43 Respiratory Insufficiency
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th Ed.
pH
ガラス電極で測定
CO2
NaHCO3溶液とCO2が平衡になる.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Eq.
pH=6.1+log[HCO3
-/CO2]
O2
polarography
陰性の白金電極に流れる電流が,PO2と比例
する.
血液ガスとpH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/43respiratoryinsufficiency-180903044942/85/43-respiratory-insufficiency-3-320.jpg)