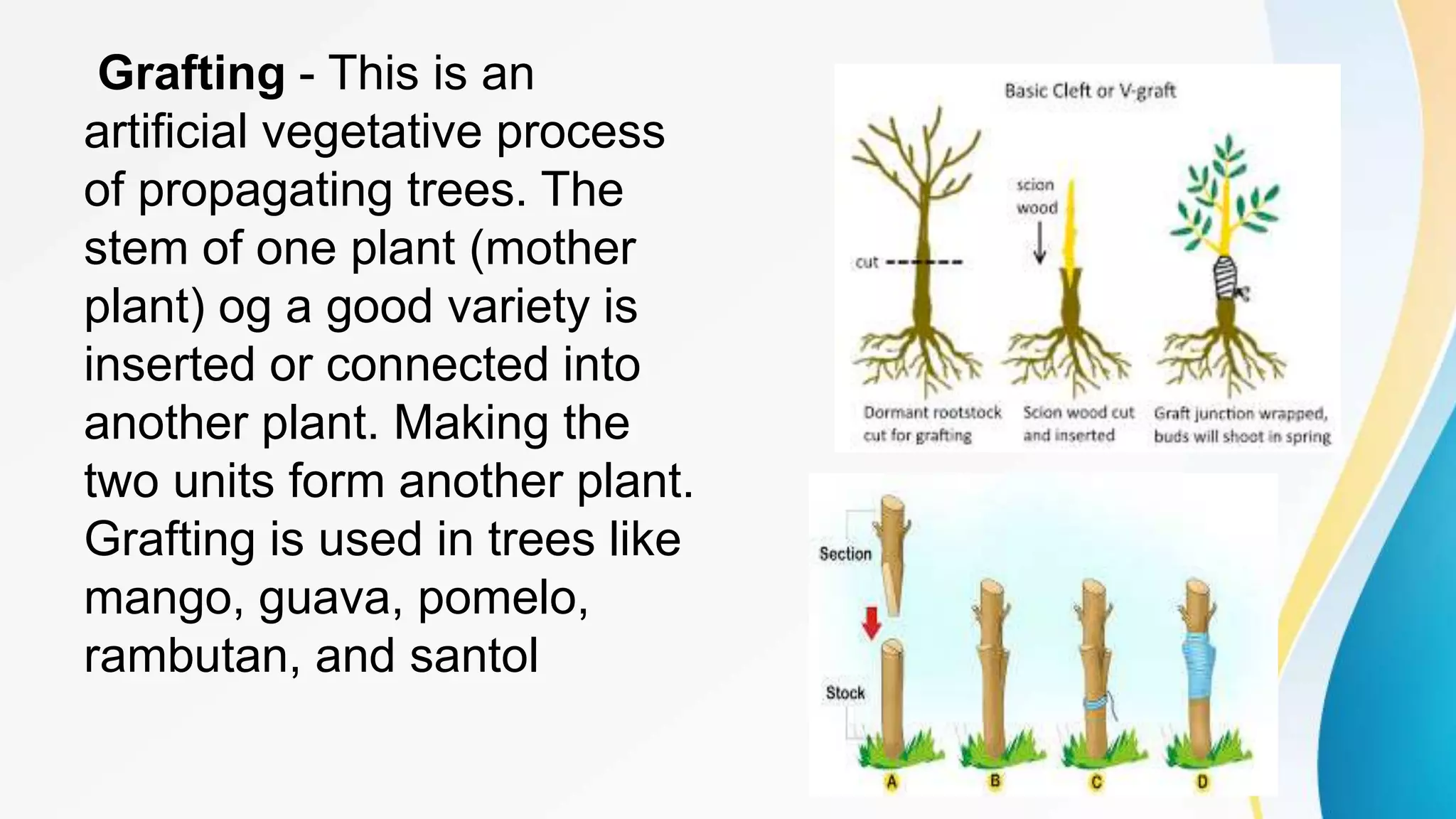
This document discusses various methods of planting and propagating trees. It describes two main methods of planting - direct seeding, where seeds are planted directly in the soil, and indirect seeding, where seedlings are transferred to their permanent location. For propagation, it outlines sexual propagation using seeds and asexual propagation techniques like cutting, grafting, layering, marcotting, and propagation through runners, suckers, bulbs, rhizomes, tubers and more. It provides details on taking care of seedlings and sources for obtaining fruit-bearing trees.