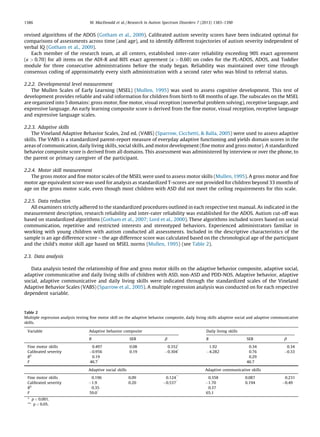
This study examined the relationship between motor skills and adaptive behavior skills in young children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The researchers conducted a multiple regression analysis of 233 children aged 14-49 months with ASD, pervasive developmental disorder-not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS), or developmental delays. The analysis found that fine motor skills significantly predicted adaptive behavior skills in all domains, while gross motor skills predicted daily living skills. Children with weaker motor skills displayed greater deficits in adaptive behaviors. The study concludes that fine and gross motor skills are significantly related to adaptive behavior skills in early childhood ASD.