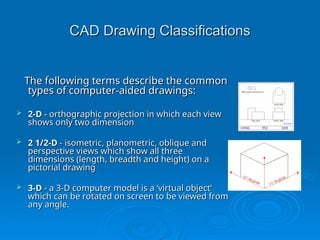
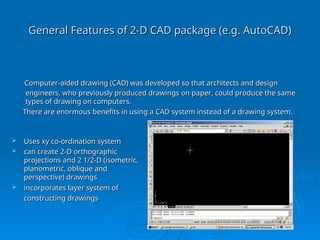
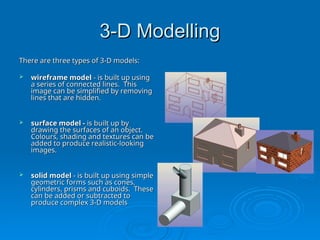
The document discusses computer-aided drawing (CAD), detailing its classifications including 2D, 2.5D, and 3D models, which allow architects and engineers to create designs digitally. It highlights the advantages of CAD over traditional methods, such as speed, flexibility, and space efficiency, emphasizing the role of 3D modeling in design and simulation. Additionally, it covers computer animation and simulation, explaining how advanced graphics enable quick and realistic representations for training, testing, and predicting real-life scenarios.