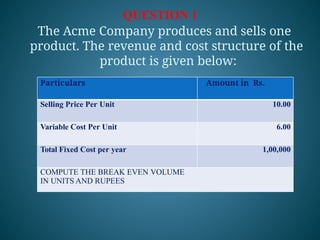
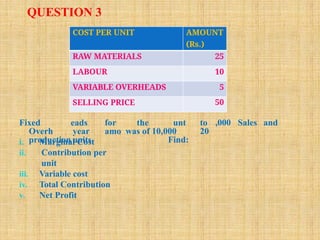
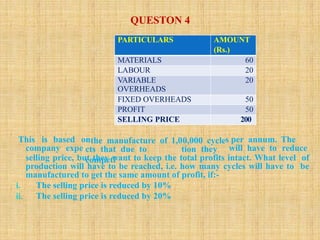
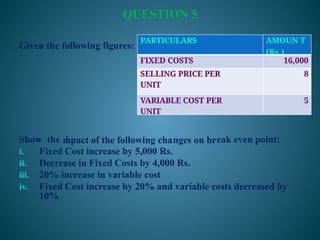
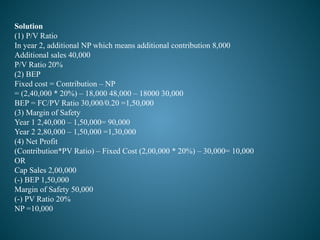
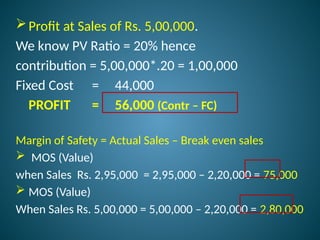
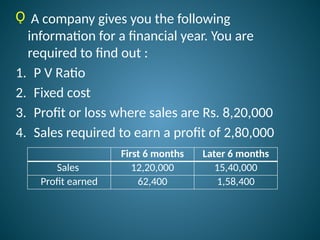
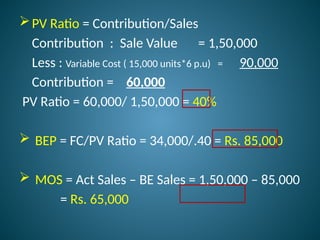
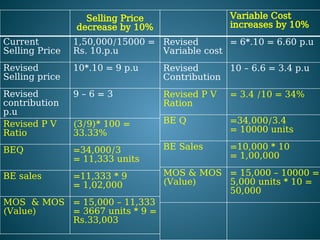
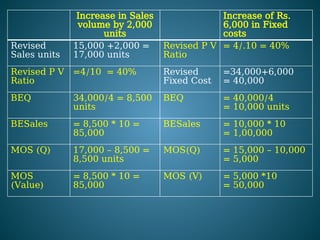
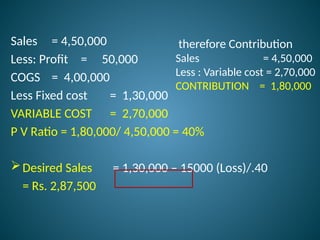
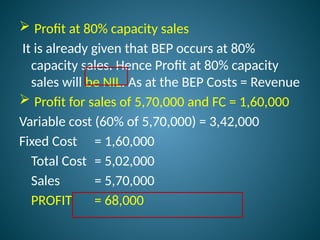
The document outlines marginal costing concepts and formulas, detailing calculations related to sales, variable costs, contributions, and profits. It provides examples of calculating break-even points, profit volume ratios, and required sales to achieve specific profit targets. Additionally, it discusses the impact of changes in costs and sales on profitability and presents exercises for practical application.