Embed presentation
Download to read offline





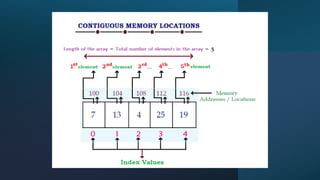







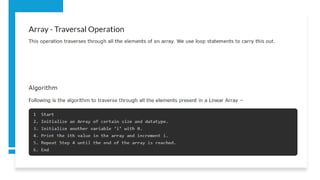
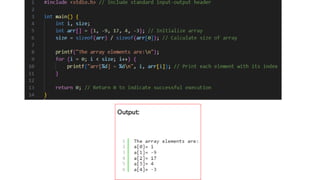

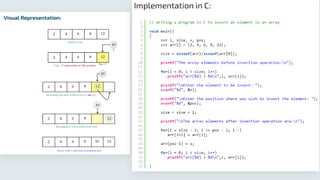







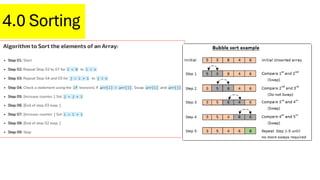






An array is a data structure characterized by fixed size, homogeneous elements, and contiguous memory allocation, allowing efficient indexing and random access. Elements are accessed via an index, typically starting at 0, supporting operations like insertion, deletion, searching, sorting, and updating. While arrays offer advantages such as efficient access, they also have some disadvantages related to their fixed size and limitations in dynamic resizing.






























