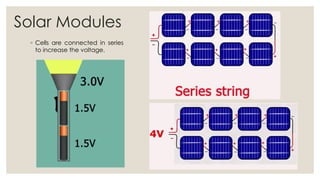
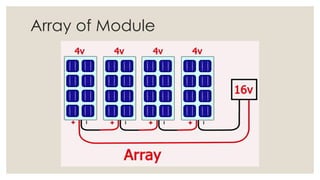
This document discusses solar energy and photovoltaic systems. It begins by presenting the objectives of describing different types of solar power, explaining the source of solar energy as the sun, estimating available solar power, and describing the design and components of solar collectors and photovoltaic systems. It then explains that photovoltaic devices convert sunlight directly into electrical energy using solar cells typically made of silicon. The components of solar panels and how they work to convert sunlight to electricity is also described. Formulas for calculating solar panel conversion efficiency and sizing photovoltaic systems are provided.