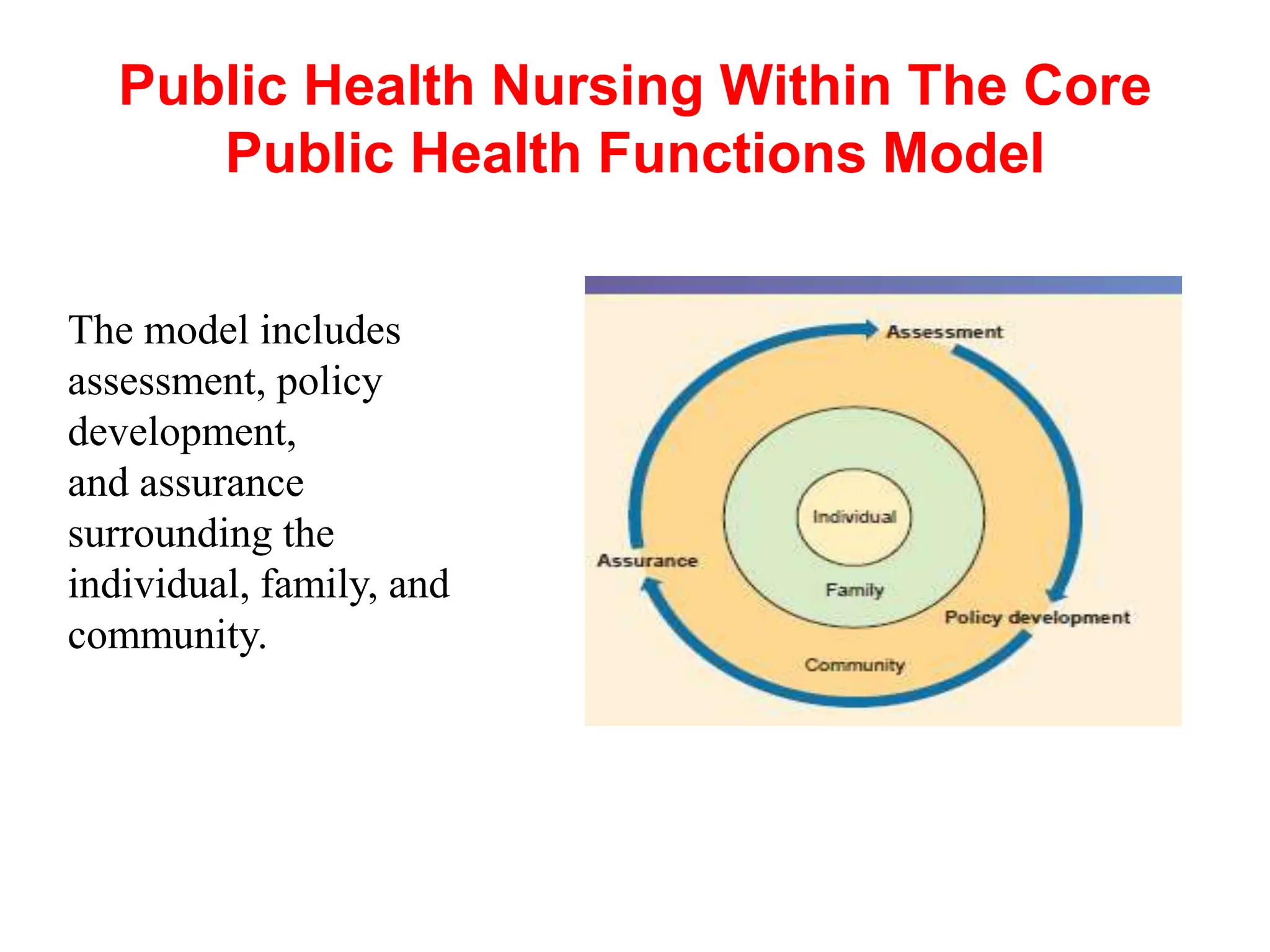
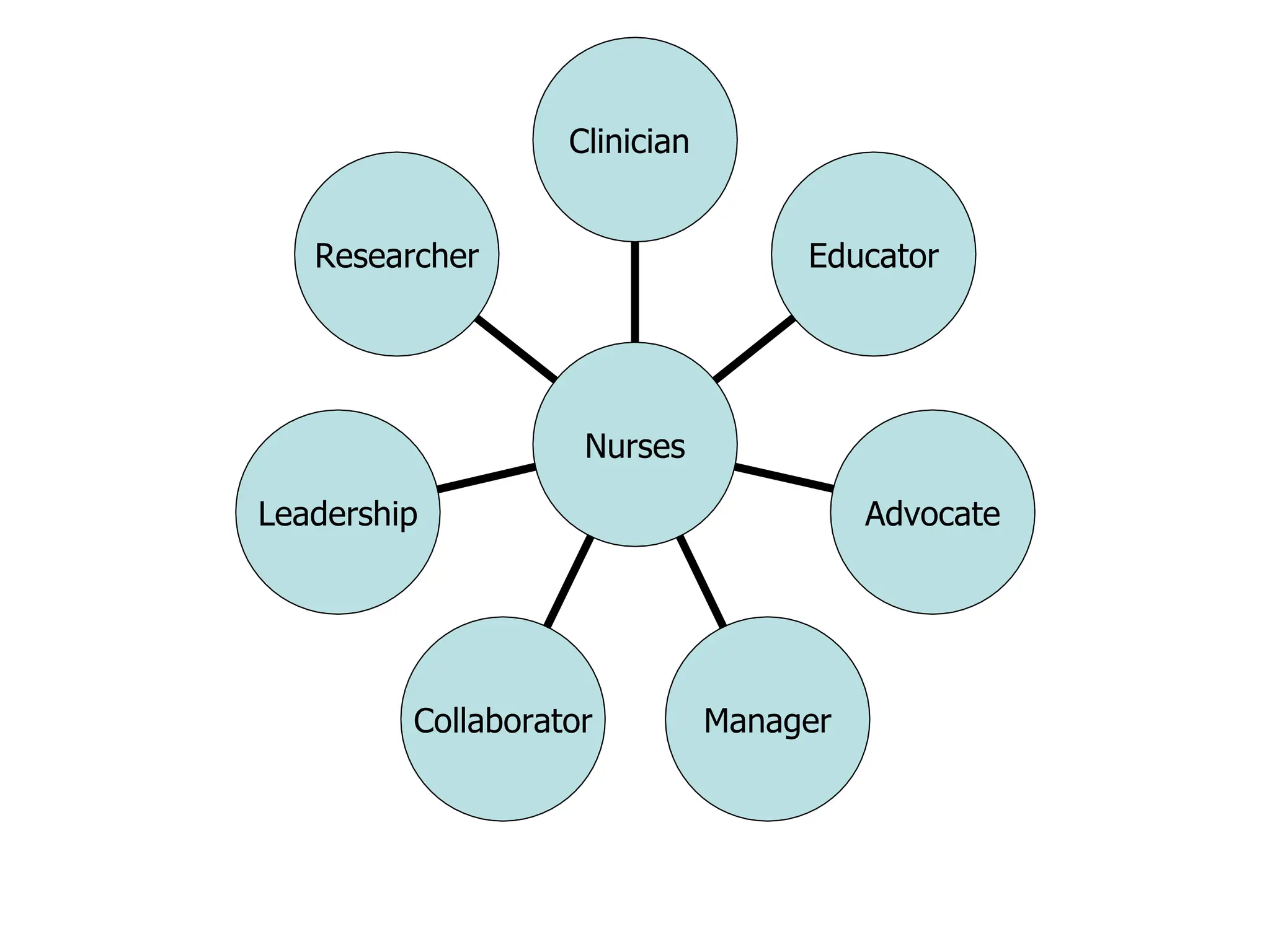
The document outlines the core public health functions and various roles of community health nursing, emphasizing the importance of assessment, policy development, and assurance for improving community health. It details seven key roles of community health nurses: clinician, educator, advocate, manager, researcher, collaborator, and leader, each contributing uniquely to health promotion and patient care. Additionally, it highlights settings where community health nursing occurs, such as homes, schools, and community health centers.