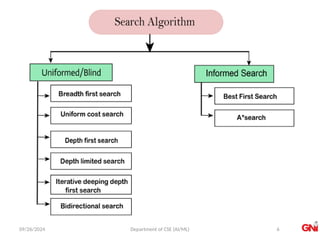
The document provides an overview of an introductory course on Artificial Intelligence, covering fundamental concepts such as intelligent agents and various search algorithms, including breadth-first and depth-first search. It outlines properties of search algorithms such as completeness, optimality, time, and space complexity, and differentiates between uninformed and informed search strategies. Additionally, it discusses applications of both breadth-first and depth-first search algorithms in graph traversal and problem-solving contexts.







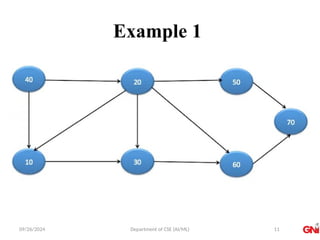
![09/26/2024 Department of CSE (AI/ML)
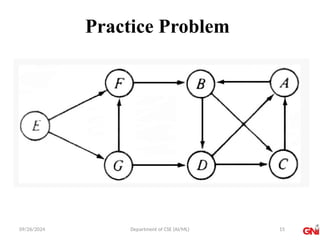
Algorithm
• Step 1: SET STATUS = 1 (ready state) for each node in G
• Step 2: Enqueue the starting node A and set its STATUS =
2 (waiting state)
• Step 3: Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until QUEUE is empty
• Step 4: Dequeue a node N. Process it and set its STATUS
= 3 (processed state).
• Step 5: Enqueue all the neighbours of N that are in the
ready state (whose STATUS = 1) and set
their STATUS = 2
(waiting state)
[END OF LOOP]
• Step 6: EXIT
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22pcoam11session4bfsdfs-240926095952-e8f433df/85/22PCOAM11-Unit-1-Session-4-BFS-DFS-Alg-10-320.jpg)


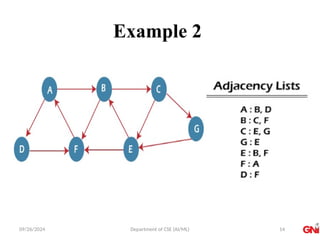


![09/26/2024 Department of CSE (AI/ML)
Algorithm
• Step 1: SET STATUS = 1 (ready state) for each node in G
• Step 2: Push the starting node A on the stack and set its STATUS =
2 (waiting state)
• Step 3: Repeat Steps 4 and 5 until STACK is empty
• Step 4: Pop the top node N. Process it and set its STATUS = 3
(processed state)
• Step 5: Push on the stack all the neighbors of N that are in the ready
state (whose STATUS = 1) and set their STATUS = 2 (waiting state)
• [END OF LOOP]
• Step 6: EXIT
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22pcoam11session4bfsdfs-240926095952-e8f433df/85/22PCOAM11-Unit-1-Session-4-BFS-DFS-Alg-19-320.jpg)