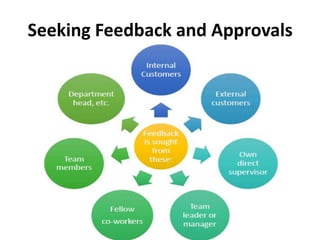
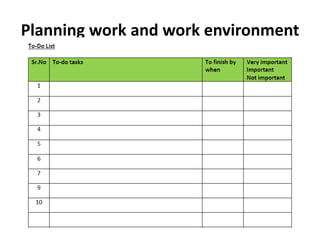
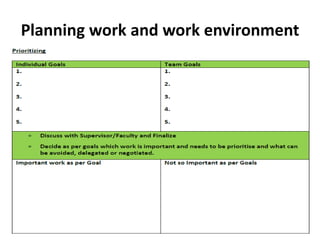
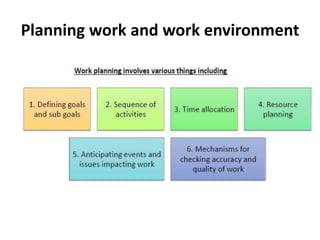
Establishing good working relationships with colleagues has many benefits, including making tasks easier to complete, increasing productivity, and getting ideas and feedback. It is important to understand one's own scope of work and responsibilities clearly to plan work better, build trust, and reduce conflicts. Organizations have policies and procedures to help with regulatory compliance, optimize performance, and reduce errors. Maintaining confidentiality of information is important for legal and business reasons, and organizations have policies for securely storing and disposing of confidential documents and data.