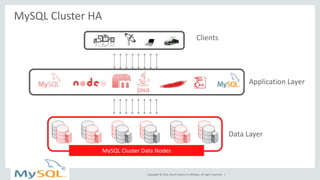
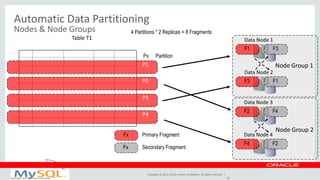
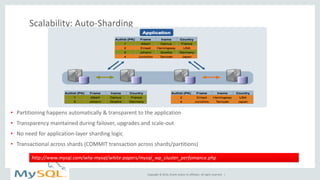
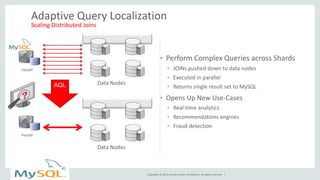
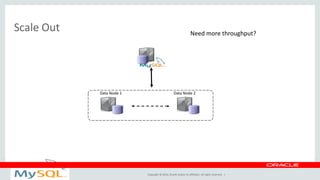
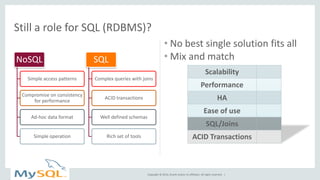
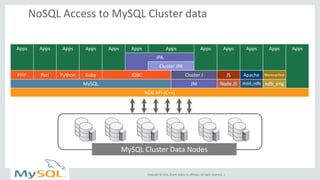
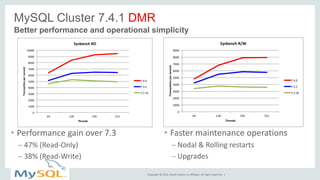
This document provides an overview and summary of MySQL Cluster. It discusses how MySQL Cluster provides high availability, scalability and performance through features like auto-sharding, multi-master replication, ACID compliance, and built-in high availability. It also provides examples showing how MySQL Cluster can scale to handle over 1 billion updates per minute and discusses how operations like restarts have been improved in MySQL Cluster 7.4.1.