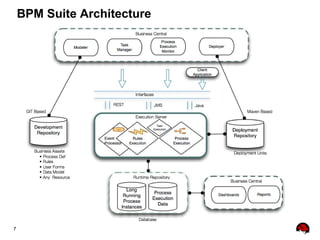
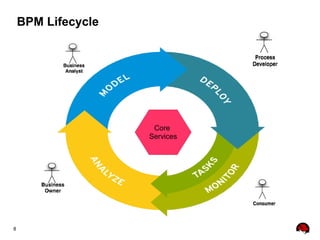
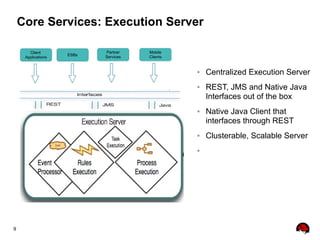
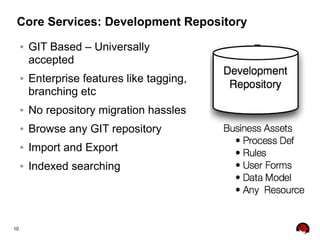
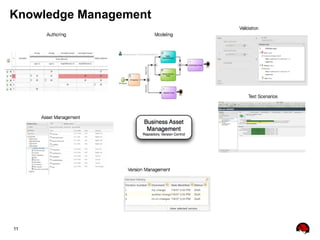
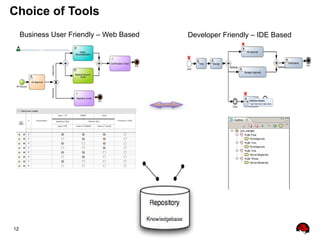
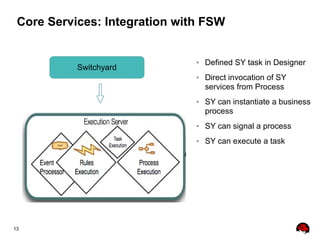
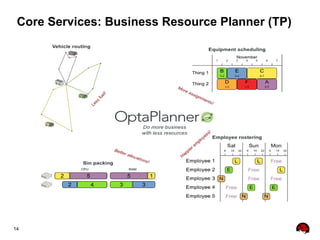
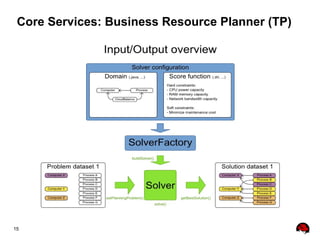
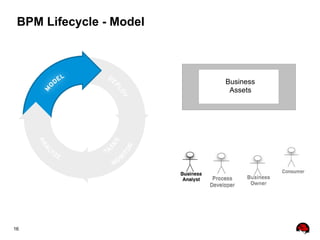
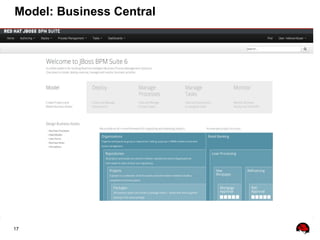
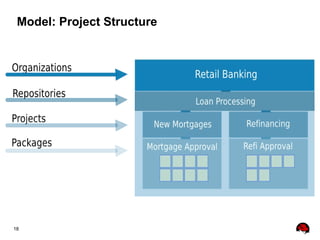
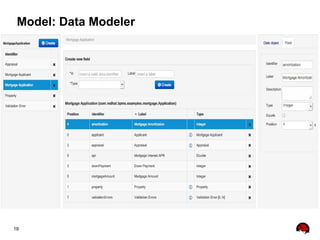
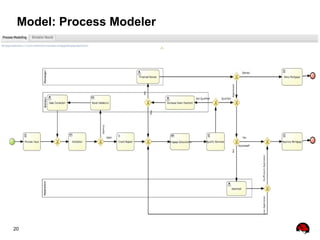
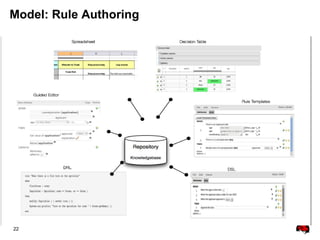
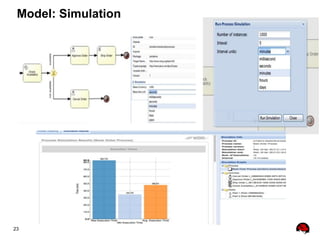
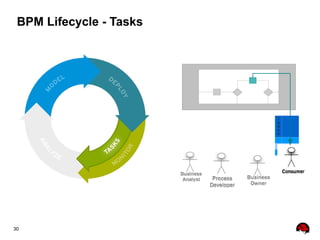
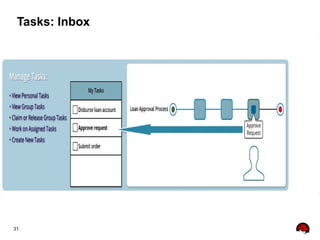
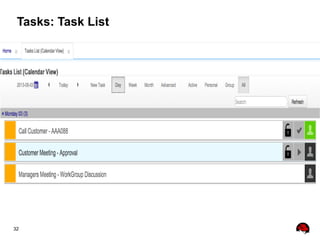
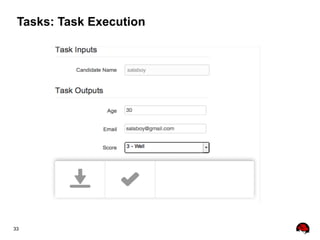
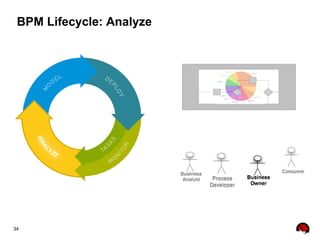
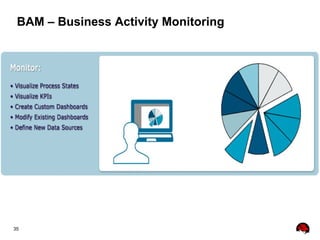
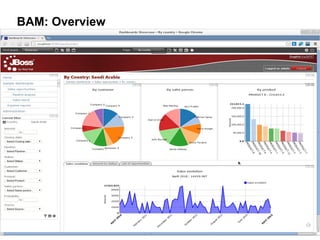
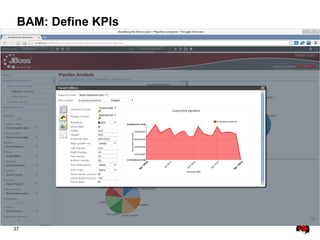
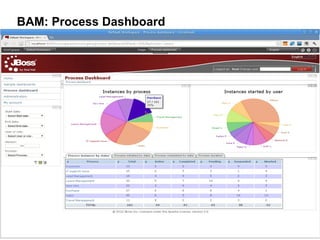
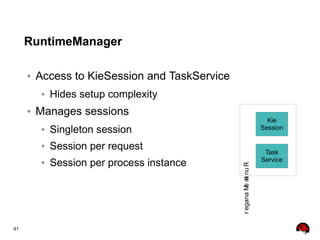
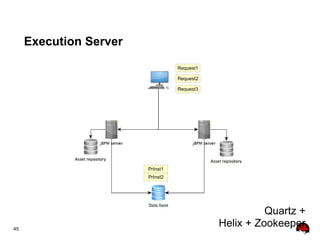
This document provides an overview of the JBoss BPM Suite 6.0 for automating workflows using open source business process management. It describes the core components and features of BPMS 6, including the execution server, development repository, knowledge management, integration with Fuse Service Works, and the business resource planner. The document also outlines the BPM lifecycle involving modeling, deploying, monitoring, and analyzing processes and tasks. It provides examples of using the runtime manager, REST API, and remote client to execute processes and tasks on the clustered execution server.











![47
REST API
http://server.address:port/{application-id}/rest/
runtime
{id: [a-zA-Z0-9-]+} // deploymentId
process
{id: [a-zA-Z0-9-]+}
start * start process [POST]
instance
{id: d} * process instance details [GET]
signal * signal event [POST]
abort * abort process instance [POST]
signal
{id: [a-zA-Z0-9-]+} * signal event [POST]
workitem
{id: d}
complete * complete work item [POST]
abort * abort work item [POST]
execute * execute the given command [POST]
task
{id: d+} * task details [GET]
activate * activate task
claim * claim task [POST]
// etc..
execute * execute the given command [POST]
query * task query](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-03-12automateworkflowswebinar-140323171051-phpapp02/85/Automate-workflows-with-leading-open-source-BPM-47-320.jpg)




