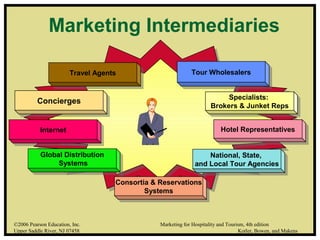
This document discusses distribution channels and how they are used to move products and services to consumers. It defines distribution channels as independent organizations involved in making products available, and notes their role in guiding customers toward products. The document also discusses how digitalization and connectivity are impacting distribution, comparing direct channels like company websites versus indirect channels like intermediaries. Finally, it outlines different domains of e-commerce like business-to-consumer and business-to-business and how they relate to distribution online.