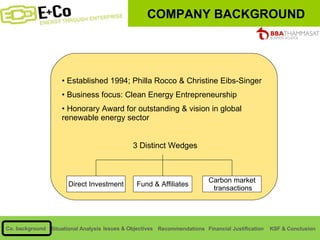
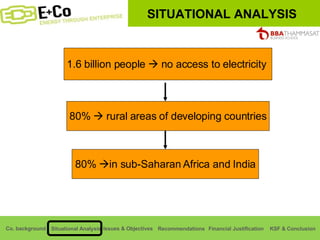
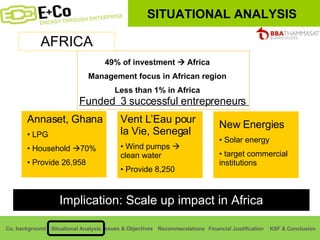
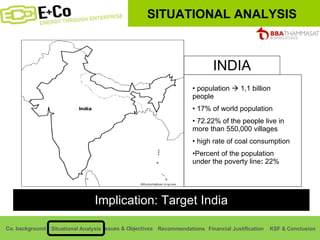
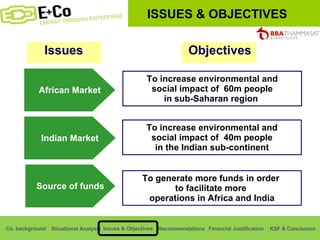
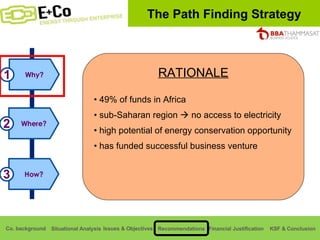
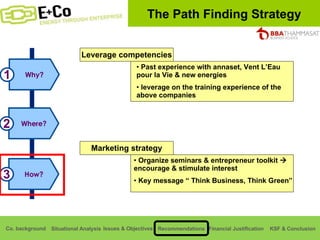
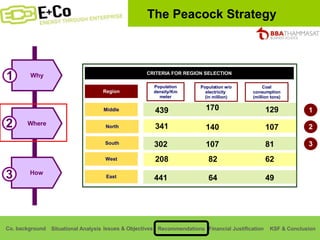
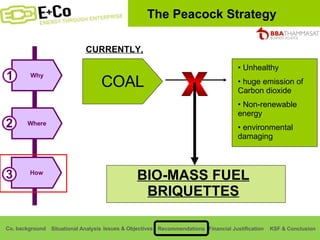
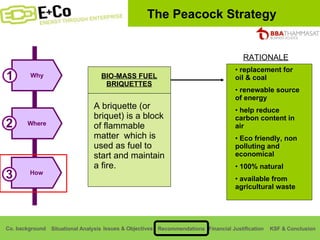
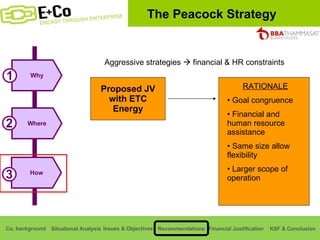
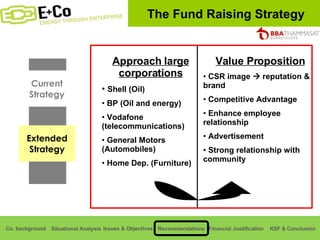
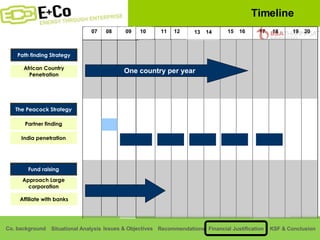
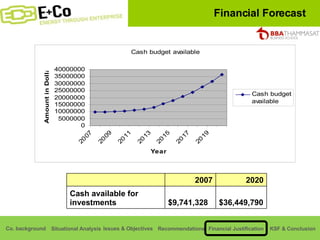
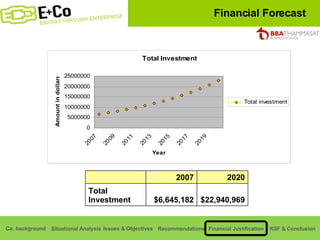
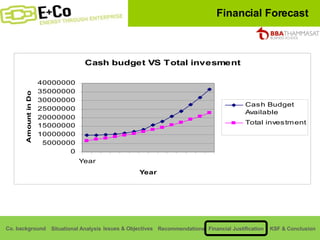
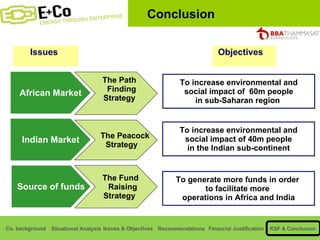
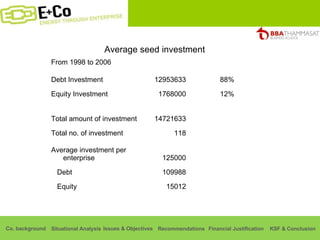
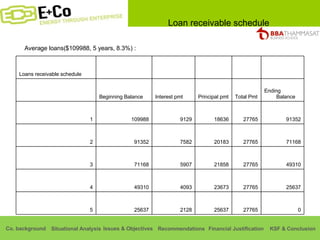
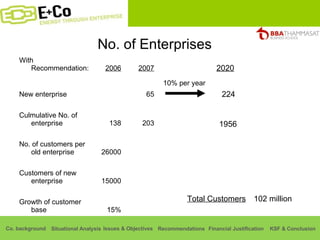
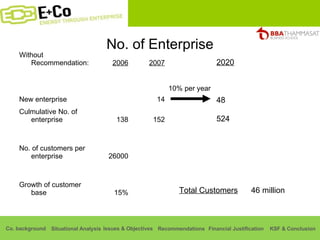
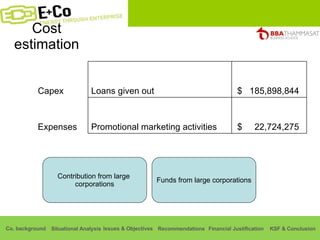
Thammasat Consulting Group provides a summary of their business background and situational analyses of energy access in Africa and India. They identify issues in these markets and objectives to increase environmental/social impact. Strategies proposed include the Path Finding Strategy to invest in sub-Saharan Africa, the Peacock Strategy targeting reduced coal use in India, and the Fund Raising Strategy to generate more funds. Financial projections estimate $36 million cash available for investments by 2020.