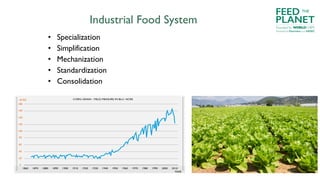
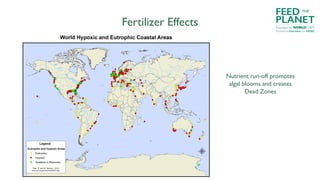
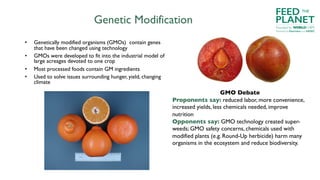
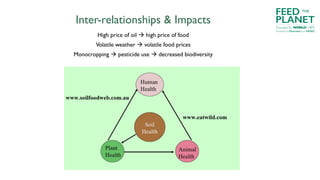
The document discusses the risks and benefits of industrial versus ecological agriculture, emphasizing the importance of biodiversity and local food systems in light of environmental and health impacts. It highlights the dangers of monocultures, pesticide reliance, and genetic modifications while promoting organic agriculture as a sustainable alternative. The text encourages culinary professionals to advocate for and implement sustainable practices, supporting local producers and educating consumers about food choices.