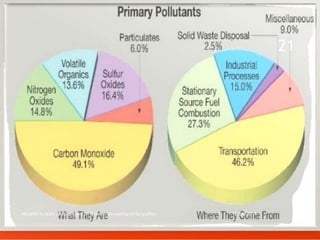
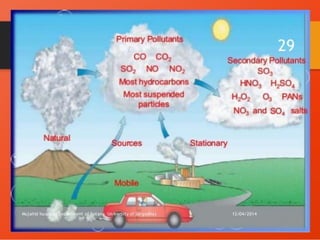
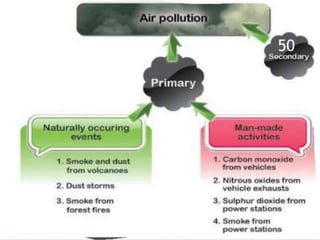
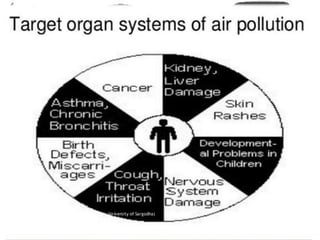
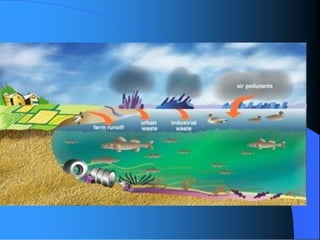
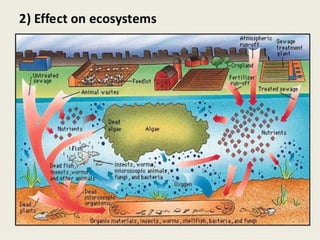
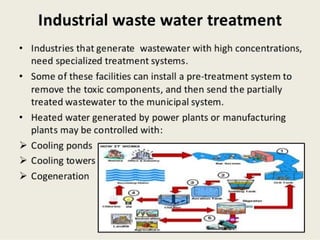
The document discusses various types of environmental pollution including air, water, soil, noise, and nuclear hazards, alongside their effects on health and the environment. It emphasizes the importance of individual roles and community involvement in pollution prevention through proper management practices and education. Control measures for each pollution type are outlined, aiming for sustainable solutions to mitigate harmful environmental impacts.