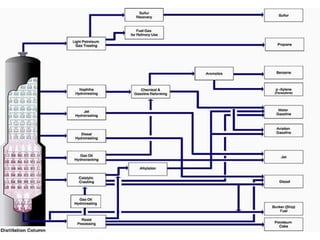
Petroleum refineries process crude oil through separation and conversion steps to produce useful petroleum products. Crude oil is distilled and separated into fractions like gasoline, diesel, and residual fuel oil. Pakistan has several large petroleum refineries that process over 100,000 barrels of crude oil per day into fuels, lubricants, and feedstocks for the chemical industry. Refineries operate complex systems to continuously process crude oil into products through distillation, cracking, reforming, and other processes.



![Refineries in Pakistan
1. Pak-Arab Refinery Ltd. (MCR), 100,000 bbl/d (16,000 m3/d)
2. National Refinery Ltd. (NRL), 64,000 bbl/d (10,200 m3/d)
3. Attock Refinery Ltd. (ARL), 46,000 bbl/d (7,300 m3/d)
4. Byco Petroleum Pakistan Limited (Byco), 150,000 bbl/d
(24,000 m3/d)
5. Pakistan Refinery Ltd. (PRL), 50,000 bbl/d (7,900 m3/d)
6. Enar Petroleum Refining Facility (Enar), 3,000 bbl/d
(480 m3/d)
7. Indus Oil Refinery Ltd, 100,000 bbl/d (16,000 m3/d) (not yet
operational)
8. Grace Refinery Limited (GRL) (120,000 bbl/d)(Under
Construction)
9. Al Motahedon Petroleum Refineries (50,000 bbl/d)(Under
Construction)[19]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240311114146-61ba629d/85/1-Introduction-to-petroleum-refinery-1-class-pptx-4-320.jpg)

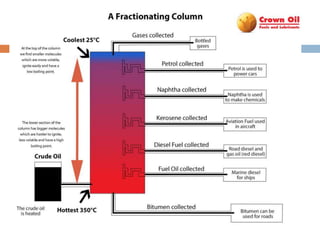
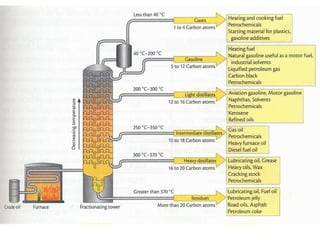
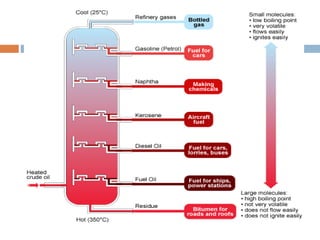
![Major Products
Petroleum products are usually grouped into three categories: light distillates (LPG,
gasoline, naphtha), middle distillates (kerosene, jet fuel, diesel), heavy distillates
and residuum (heavy fuel oil, lubricating oils, wax, asphalt). This classification is
based on the way crude oil is distilled and separated into fractions
(called distillates and residuum) as in the above drawing.[2]
Liquified petroleum gas (LPG)
Gasoline (also known as petrol)
Naphtha
Kerosene and related jet aircraft fuels
Diesel fuel
Fuel oils
Lubricating oils
Paraffin wax
Asphalt and tar
Petroleum coke
Further products (see also below) include
Sulfur
Olefines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240311114146-61ba629d/85/1-Introduction-to-petroleum-refinery-1-class-pptx-9-320.jpg)