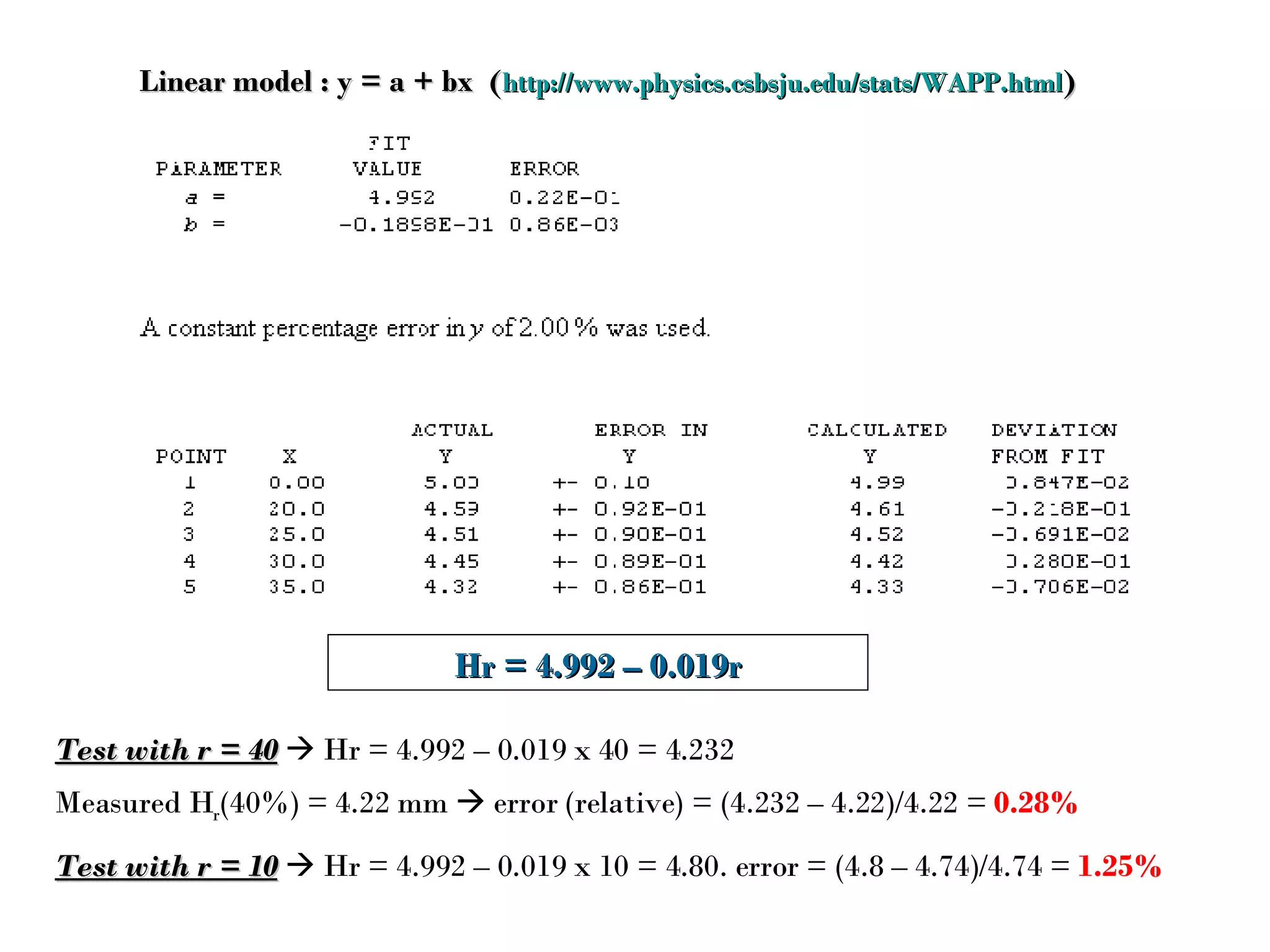
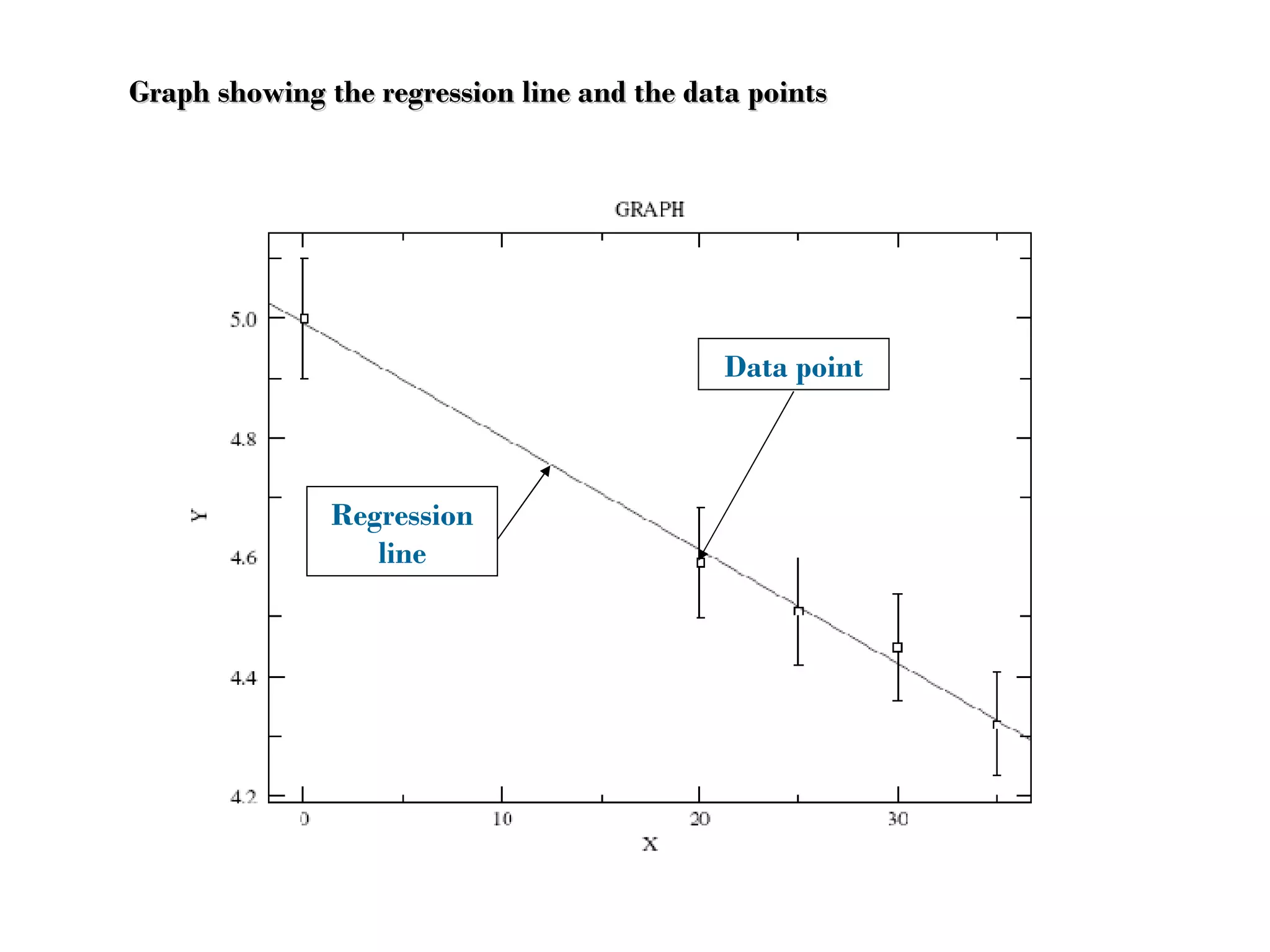
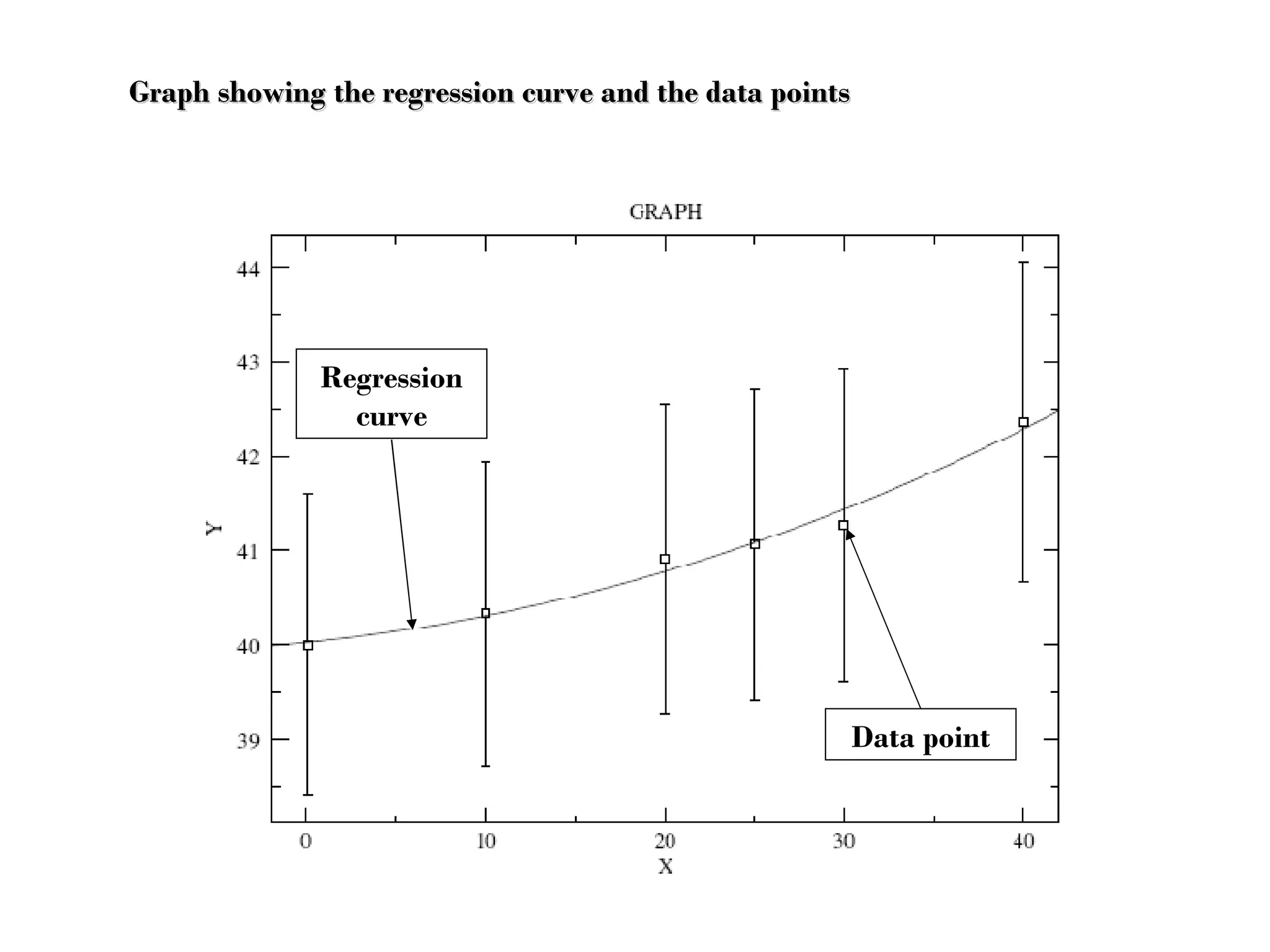
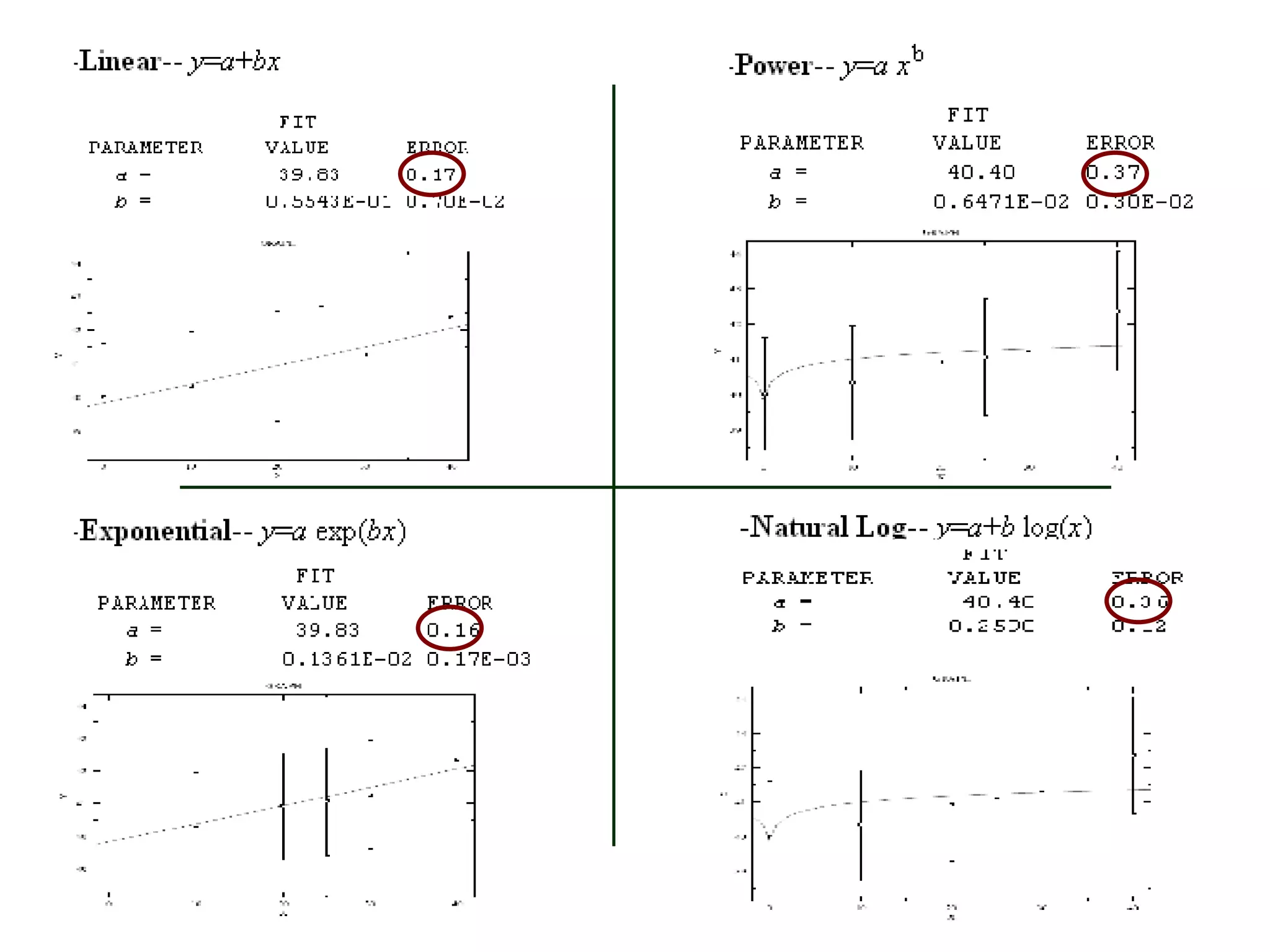
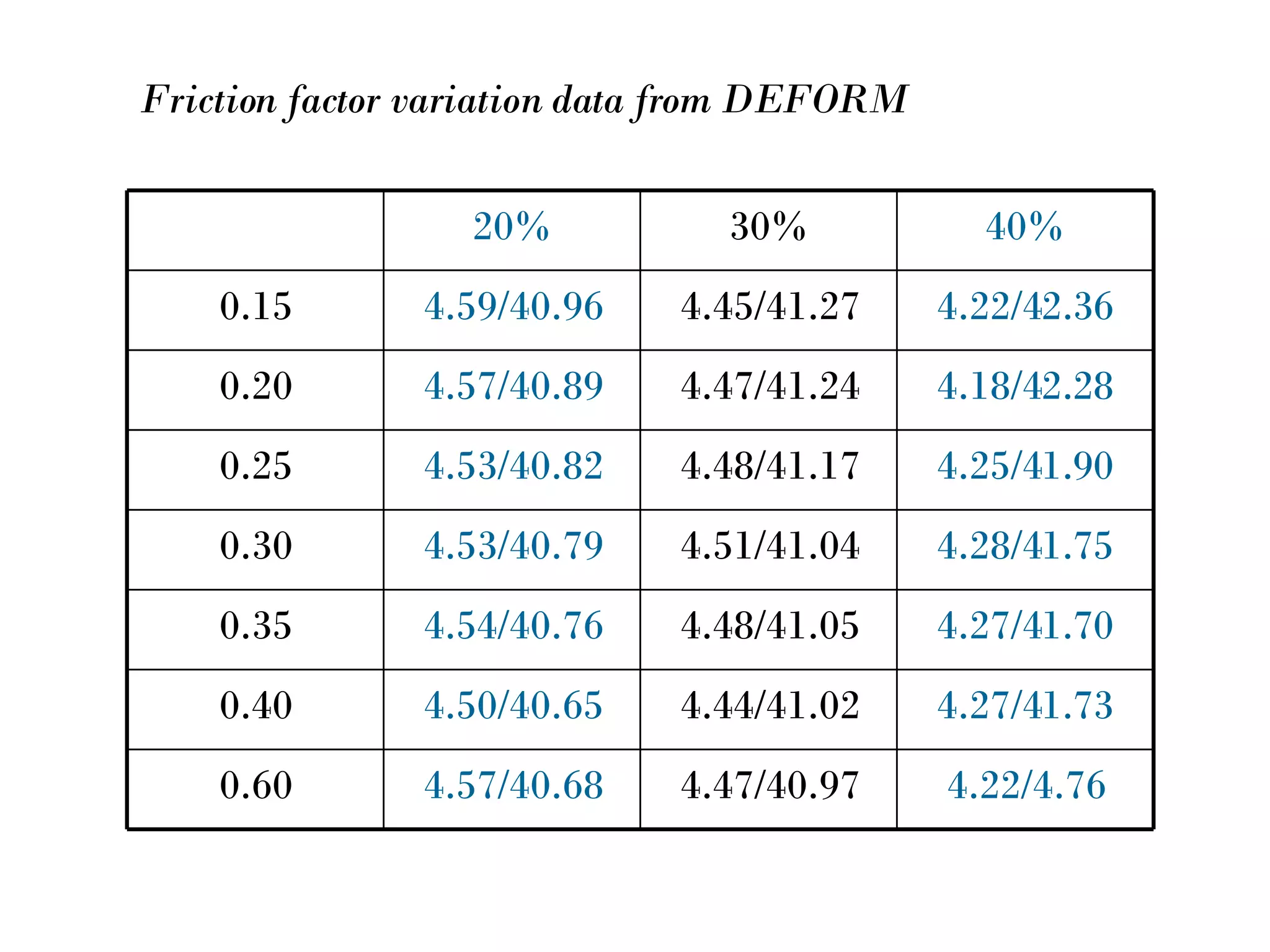
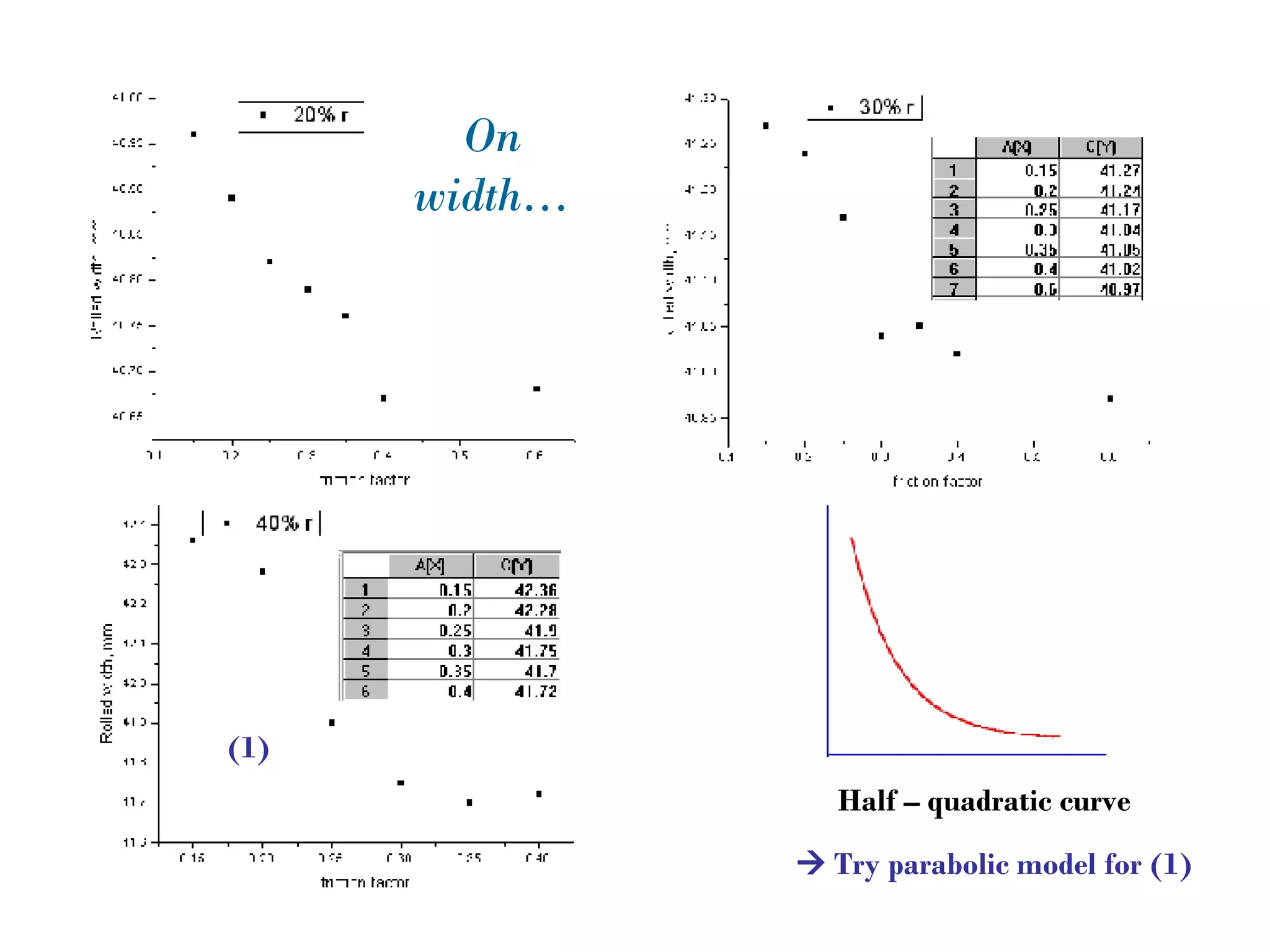
The document discusses using mathematical functions to model relationships between input and output variables in a rolling simulation. A linear model was found to accurately predict central height from thickness reduction with less than 1% error. A quadratic model also accurately predicted spread from thickness reduction with less than 1% error. Friction was found to not significantly affect central height, and a quadratic model described the relationship between spread and friction with under 1% error. Further modeling of additional variables is suggested.