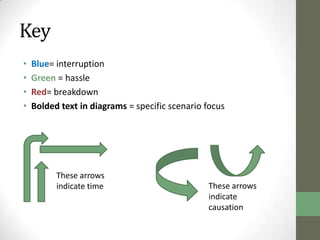
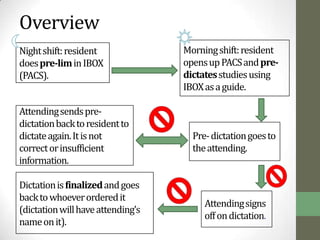
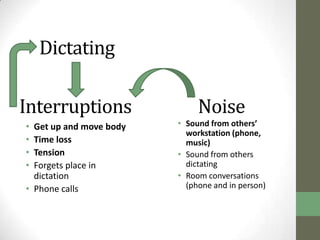
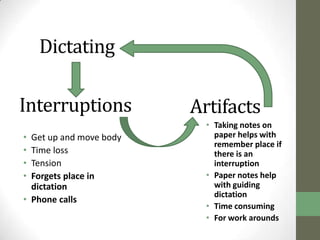
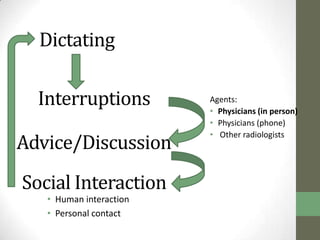
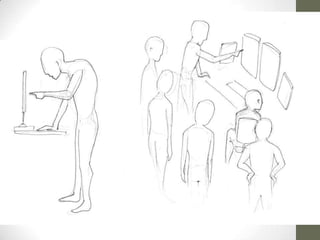
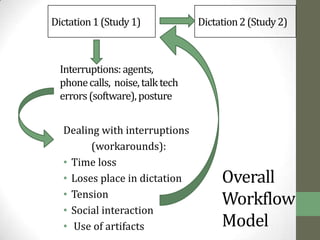
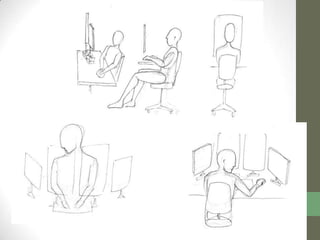
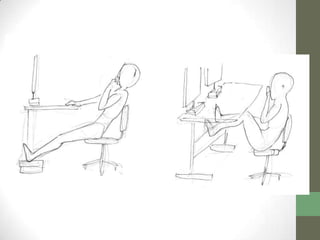
The document summarizes scenarios related to interruptions and hassles experienced by radiologists during dictation. It describes scenarios where a radiologist has trouble contacting an attending physician to sign off on a critical case, experiences technical errors with dictation software, and is interrupted by noise from a nearby station. It also outlines scenarios where radiologists take paper notes to stay on track during interruptions or discuss cases with physicians. The document analyzes radiologists' workflow and proposes design ideas like adjustable workstations, partitions, and integrating dictation devices and mice to reduce posture changes during reading and dictation.
![Scenarios [Dictation]
Cogs 160 Final Presentation
Jenny Chang, Jingwei Li, Samantha Tse
June 2, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/160scenariosdictation-120423232431-phpapp02/75/160-scenarios-dictation-1-2048.jpg)