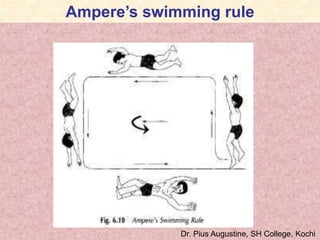
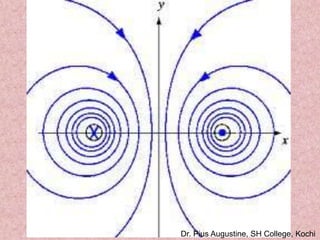
This document provides information about electromagnetism and magnetic fields produced by electric currents. It discusses Hans Christian Oersted's experiment in 1820 that discovered a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field. It then describes the magnetic fields produced by straight and circular current-carrying conductors. Additional topics covered include the right-hand rule, electromagnets, solenoids, and applications such as the electric bell. Diagrams illustrate many of the concepts and experimental setups.