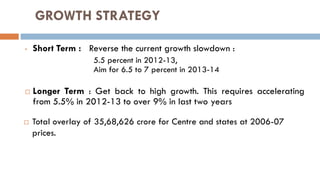
The 12th Five Year Plan aims to promote faster, more inclusive and sustainable growth in India after high growth but increasing inequities in the 11th Plan. It sets a core target of 8.2% economic growth along with manufacturing growth of 10% and poverty reduction. Key priorities include improving access to education, health and infrastructure while ensuring balanced regional development and closing gender and social gaps. The plan proposes three scenarios for growth and inclusiveness depending on the level of implementation but is limited in metrics to properly measure inclusive growth.