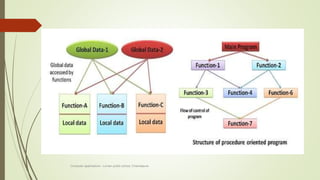
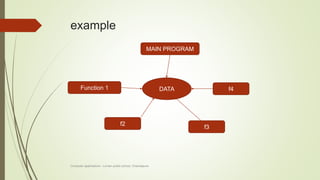
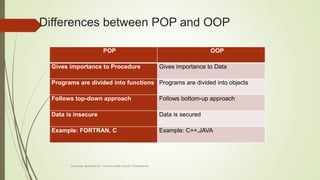
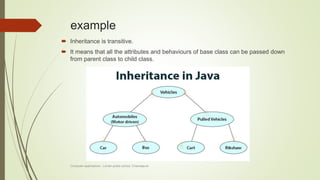
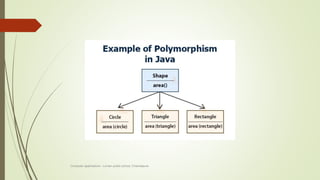
The document introduces object-oriented programming concepts. It explains that OOP is based on objects and classes, with classes acting as blueprints for objects. Some key principles of OOP discussed include abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Procedural programming is also introduced, and its differences from OOP are outlined. Examples are provided to help illustrate various concepts like classes, objects, abstraction, and encapsulation.