This document provides instructions for solving various problems related to seismic wave travel times and distances. It describes how to use seismic wave travel curves to determine:
1) The travel time of P and S waves given an epicenter distance.
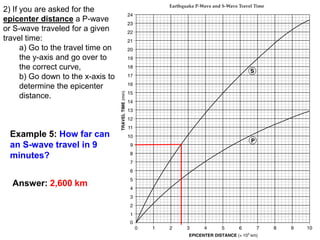
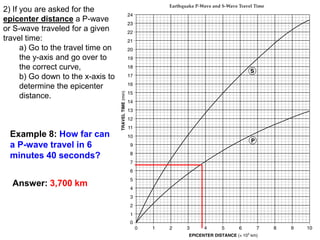
2) The epicenter distance given a travel time.
3) The arrival time at a station given origin time, distance and wave type.
4) The origin time given arrival time, distance and wave type.
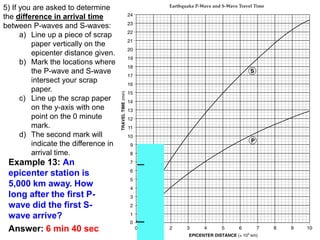
5) The difference in arrival times between P and S waves at a given distance.
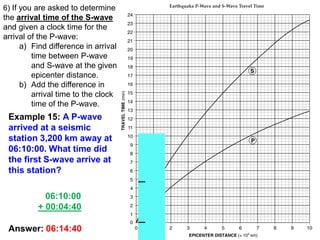
6) The arrival time of the S wave given the P wave arrival time and distance.
7) The arrival time of the P wave given