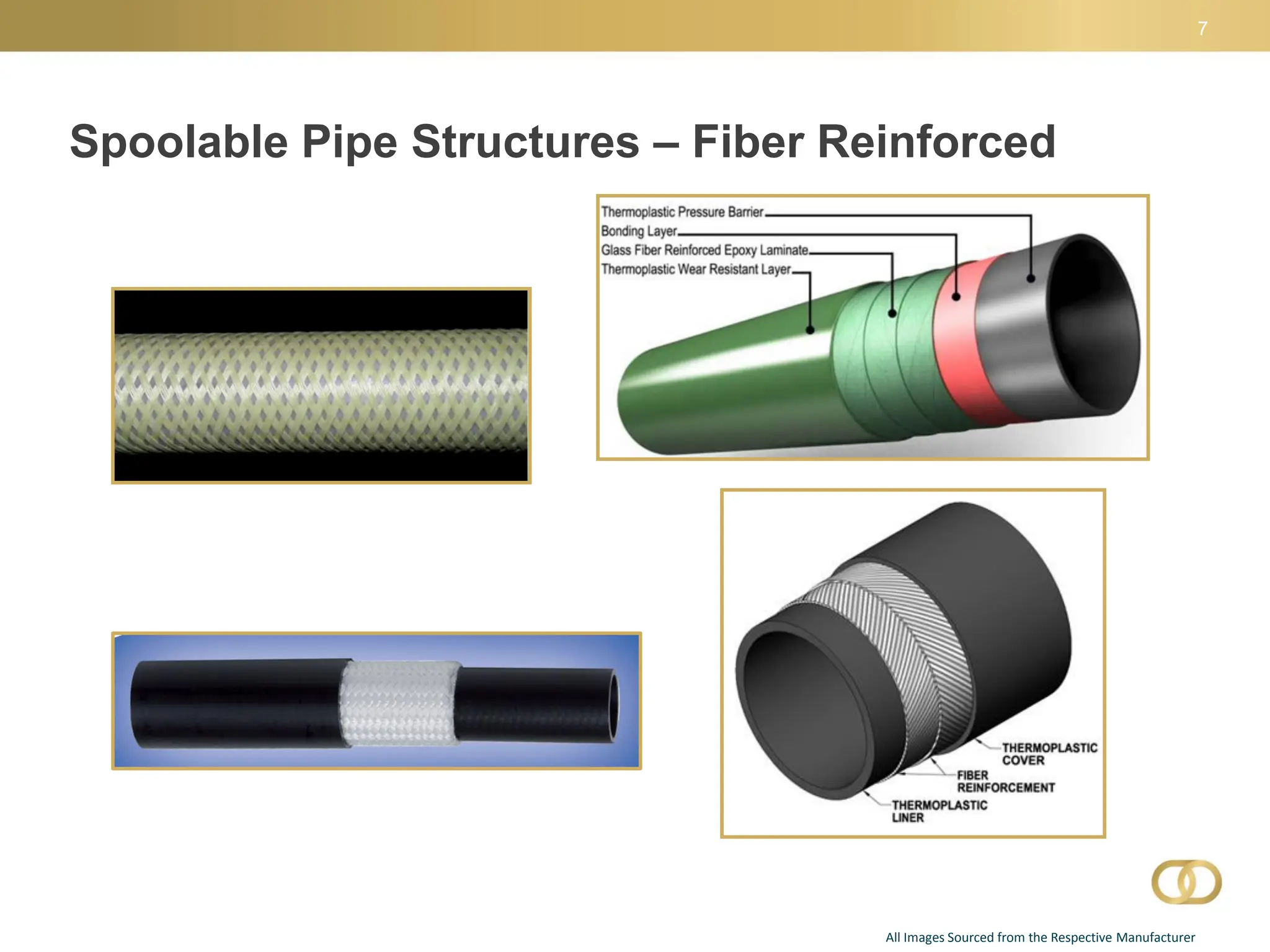
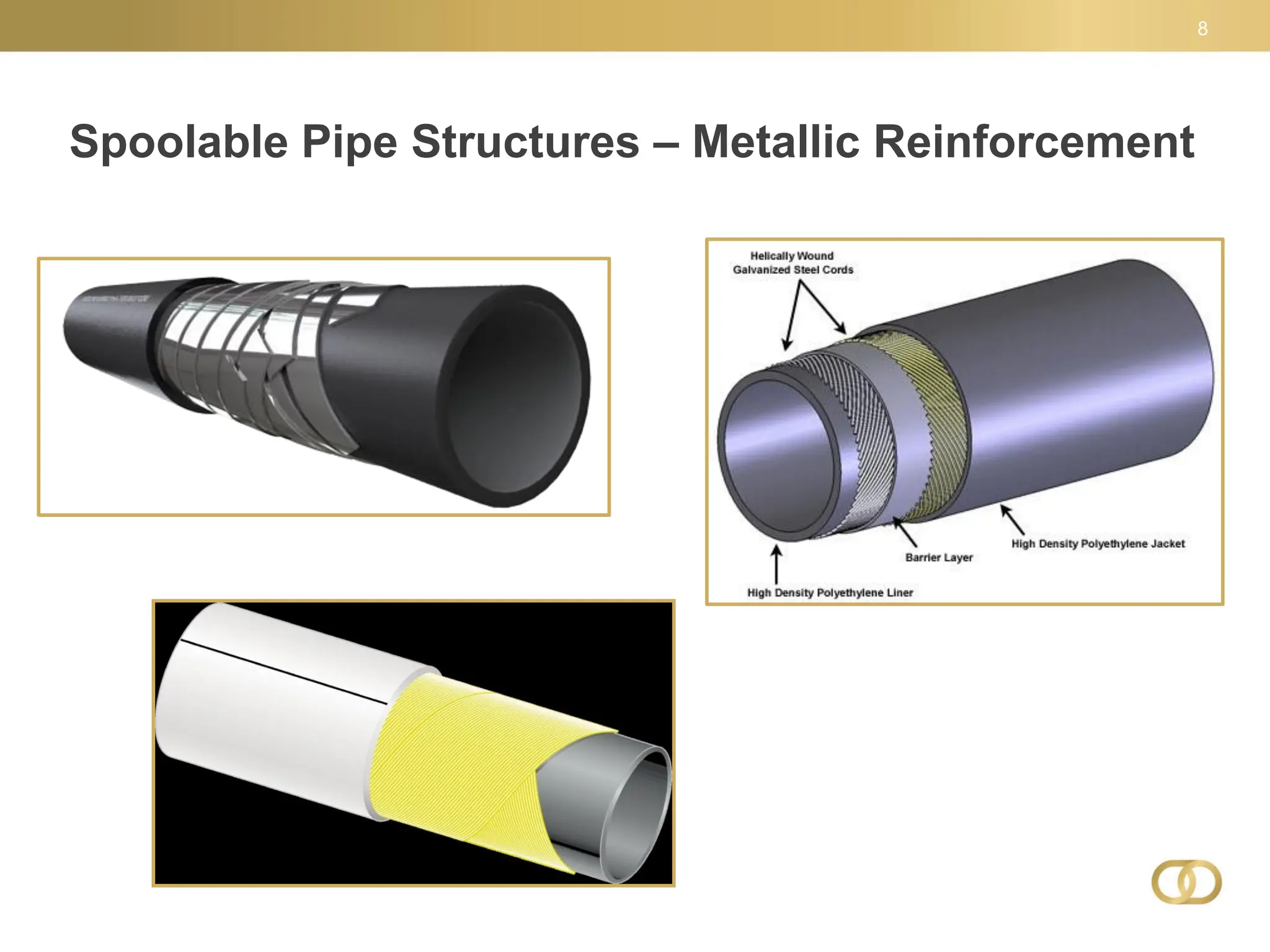
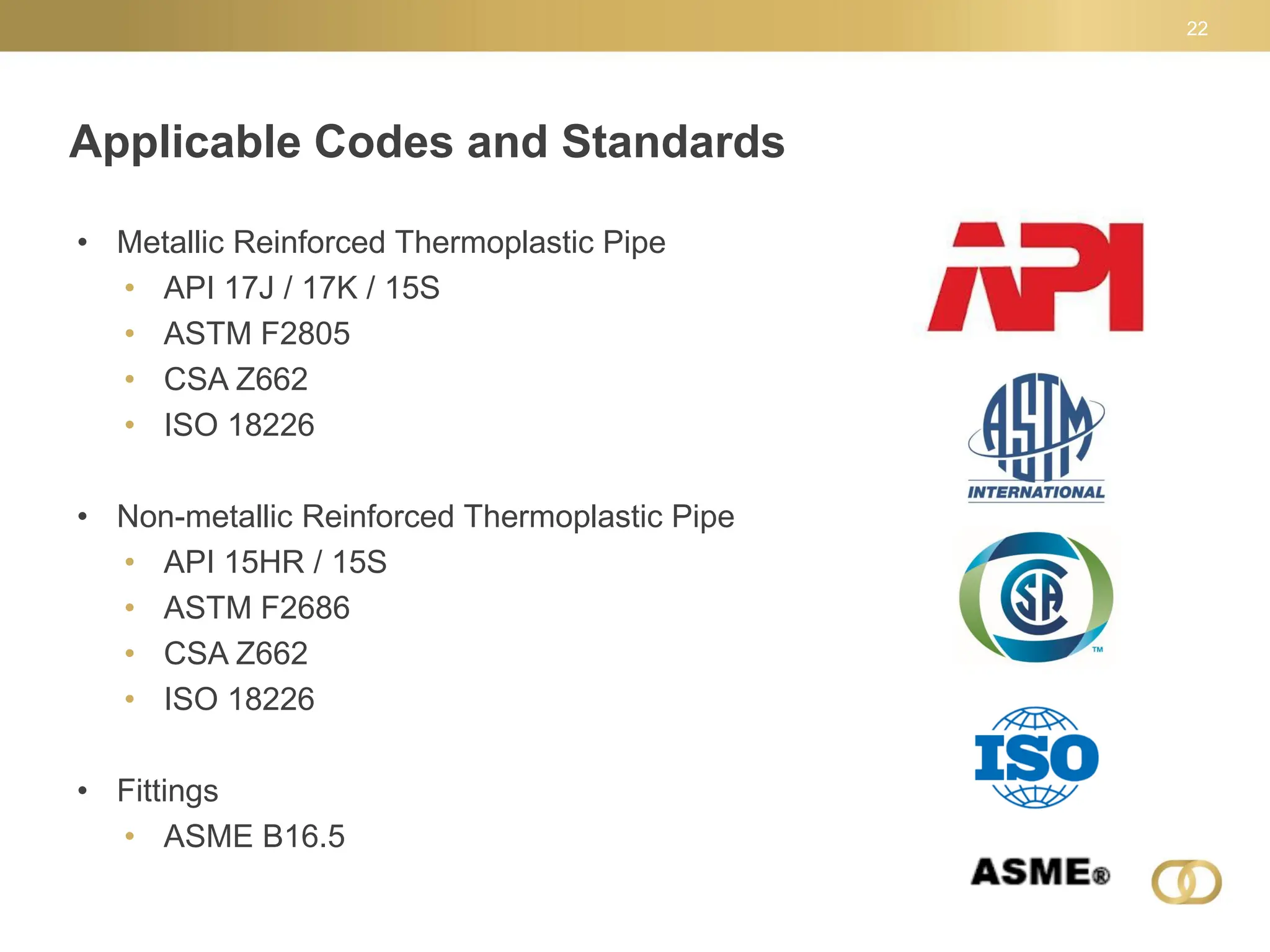
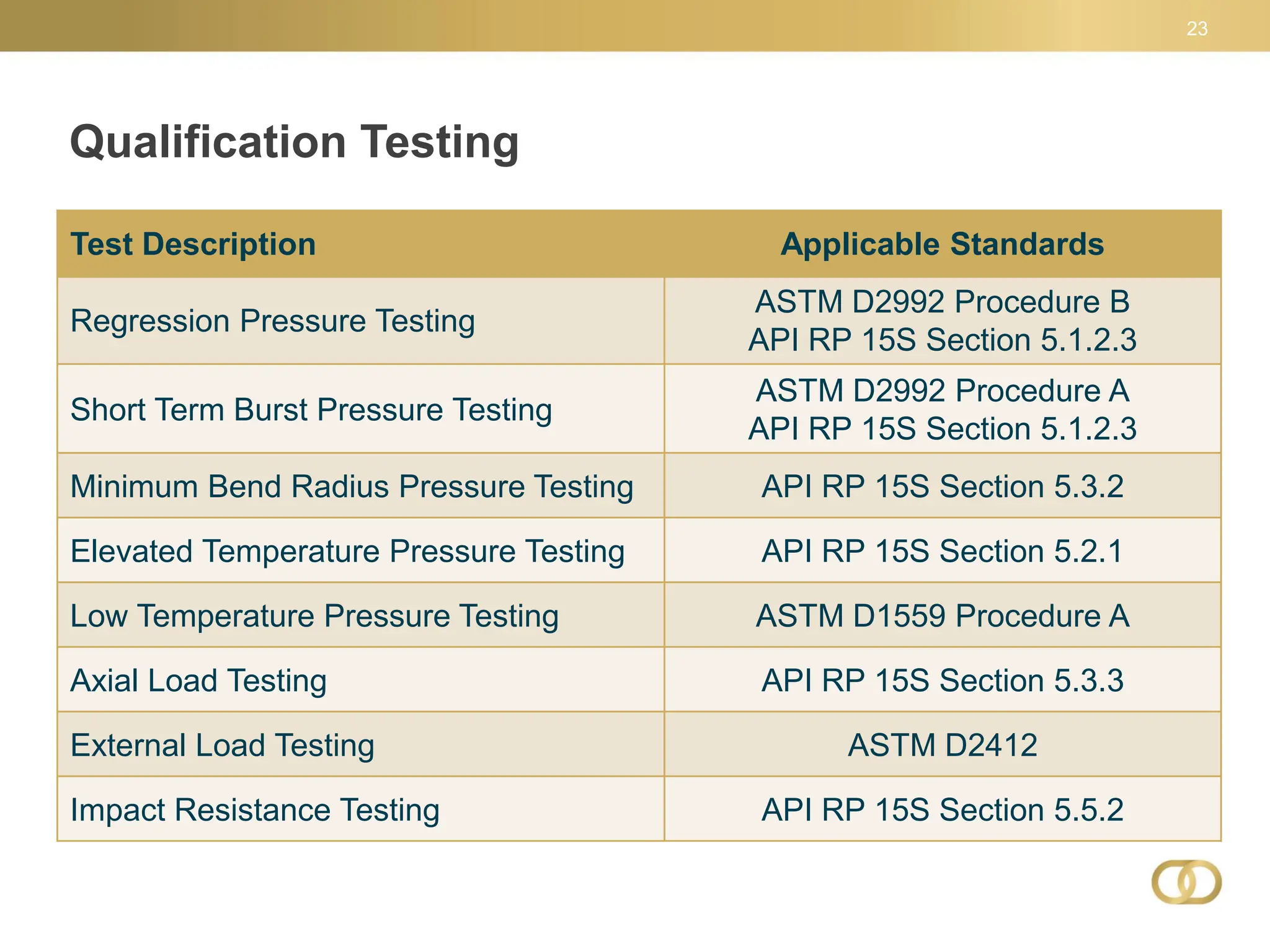
The document outlines key aspects of composite linepipe technology presented at a conference, discussing various types of pipeline materials, their advantages and disadvantages, as well as installation methods and applicable codes and standards. It emphasizes the benefits of spoolable composite reinforced thermoplastic piping, including cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and higher pressure capacities, while also addressing some limitations such as lack of regulatory history. The document also highlights the need for special permits for regulated composite pipelines and presents a snapshot of the evolving regulatory environment surrounding these technologies.


![Crude Oil and Gas Pipeline Materials
3
• Steel Pipe
• Coated Steel Pipe (Fusion Bonded Epoxy [FBE])
• Uncoated Steel Pipe (Bare Pipe)
• Cathodically Protected Steel Pipe
• Unprotected Steel Pipe (Not Cathodically Protected)
• Cast Iron Pipe
• Fiberglass Pipe
• Polyethylene Pipe
• Composite Pipe
• Nylon Pipe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-compositelinepipetechnology-240927155940-76f024b3/75/1111-Composite-Line-pipe-Technology-pdf-3-2048.jpg)