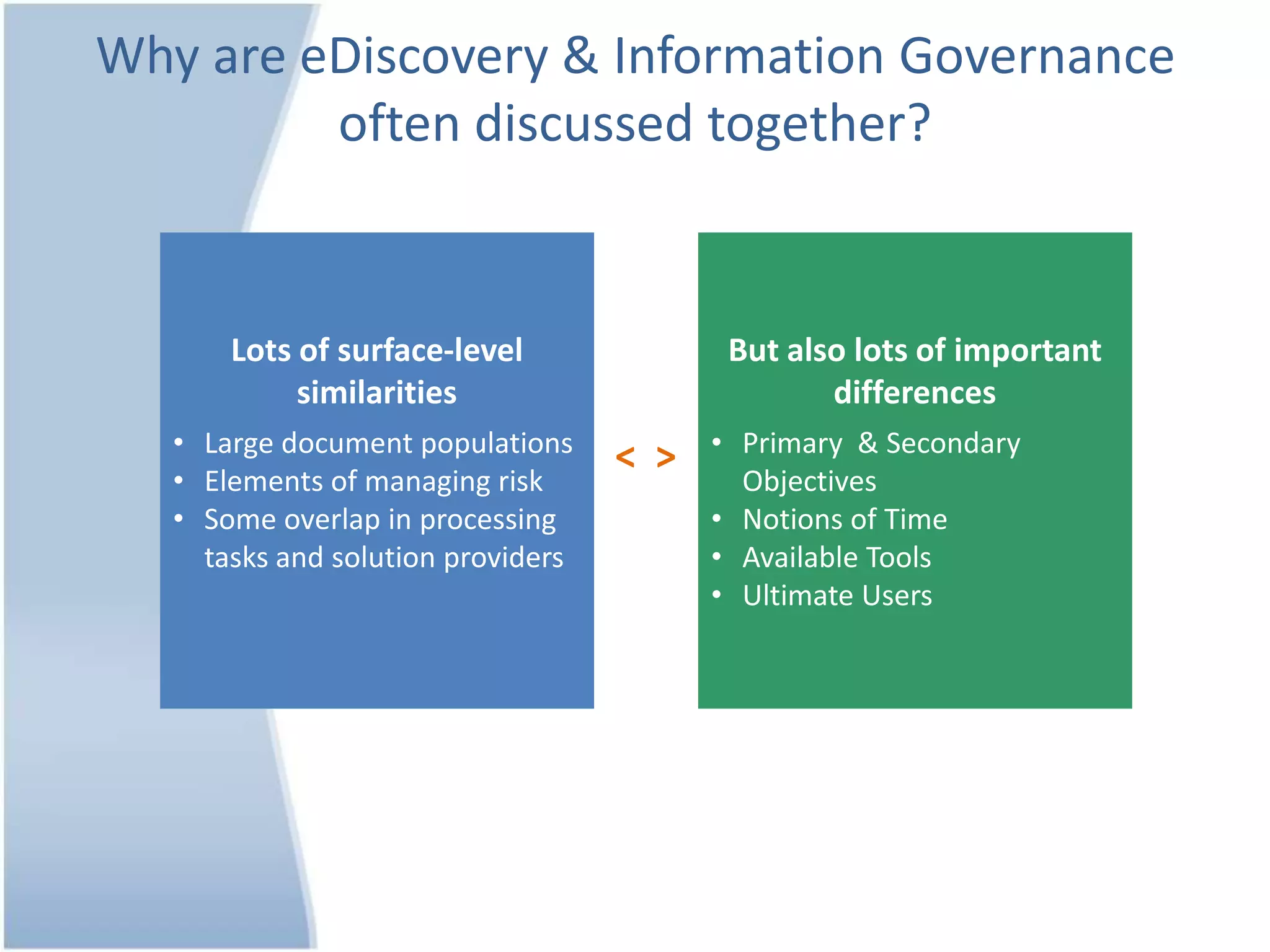
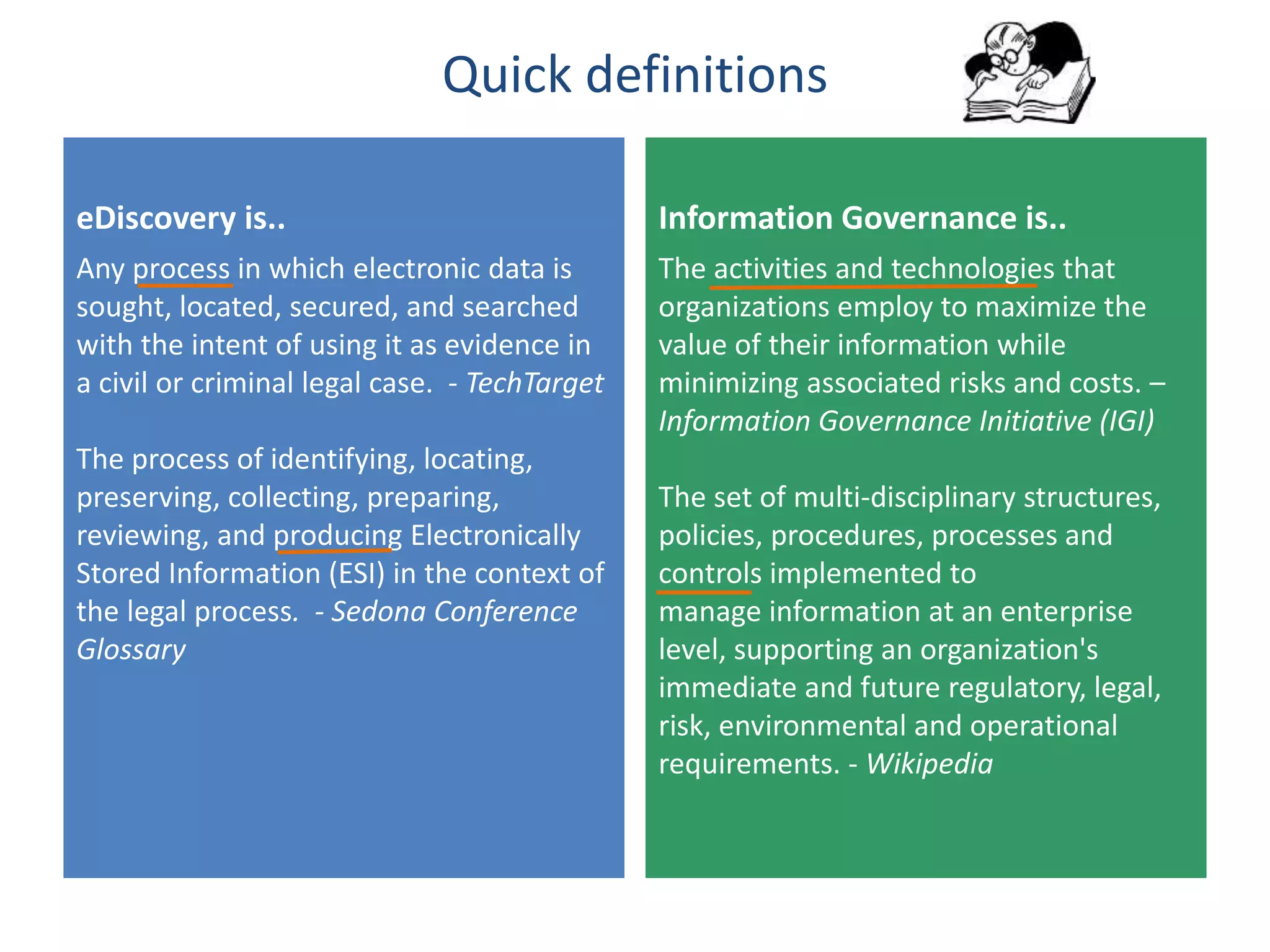
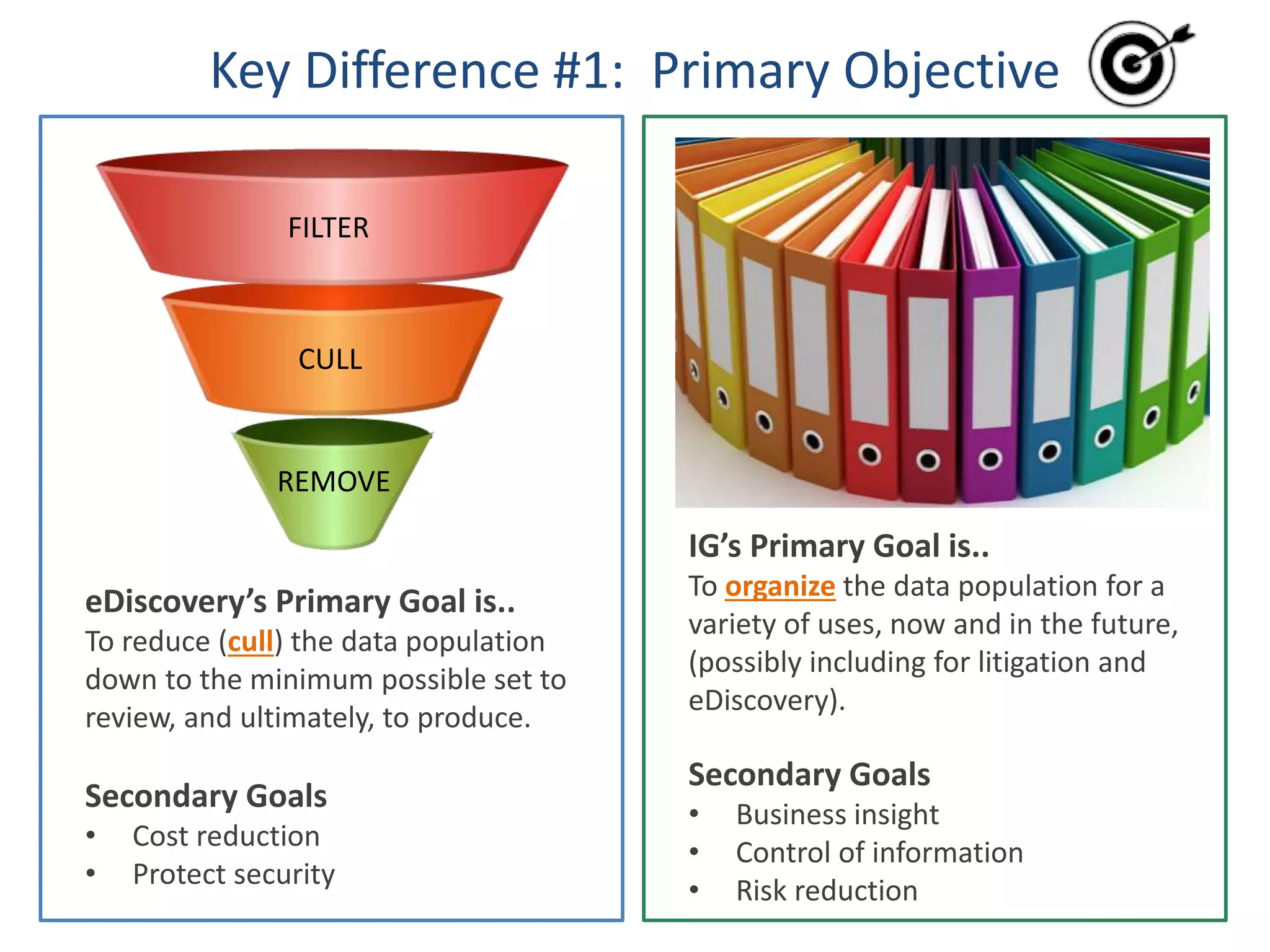
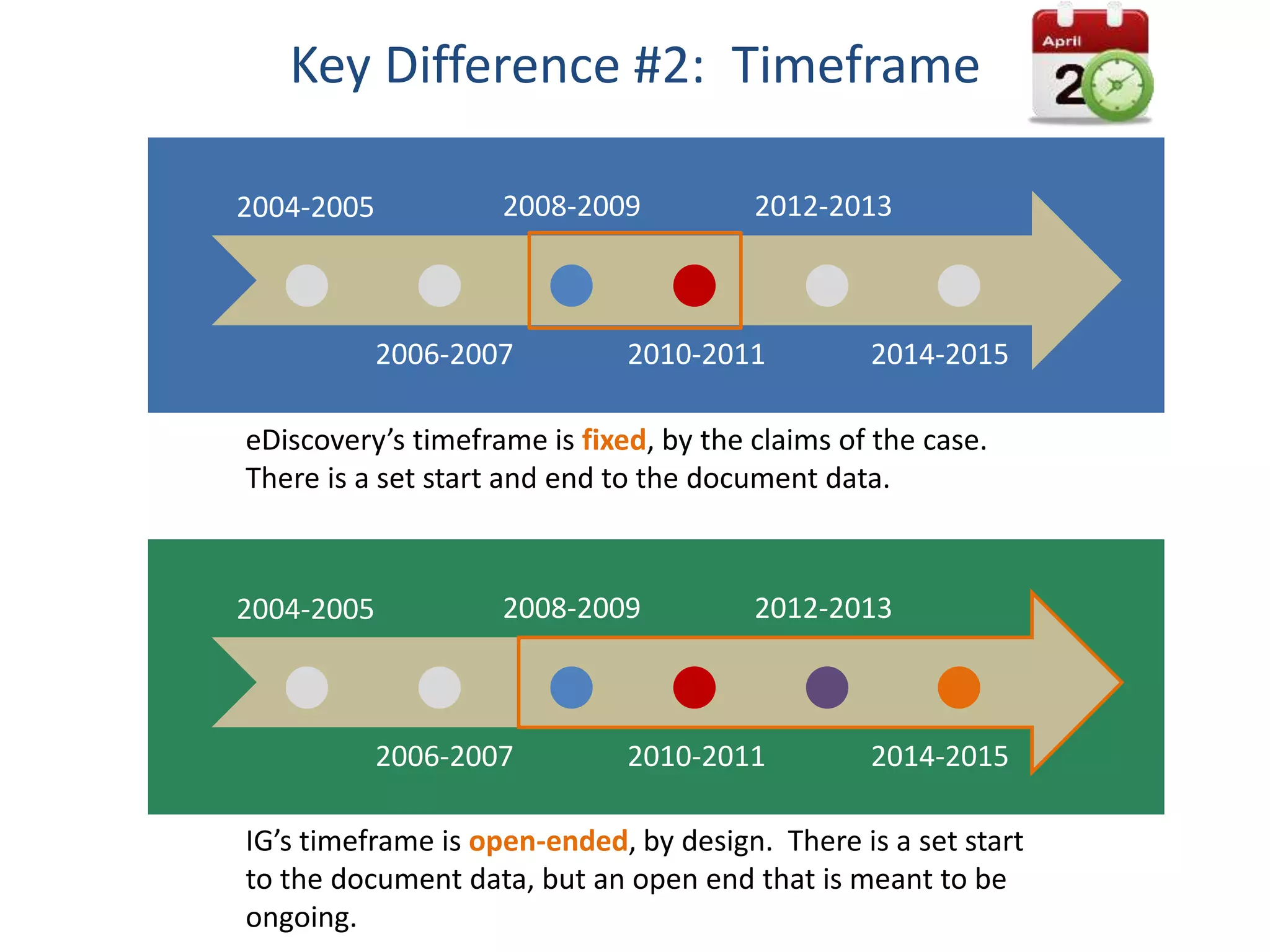
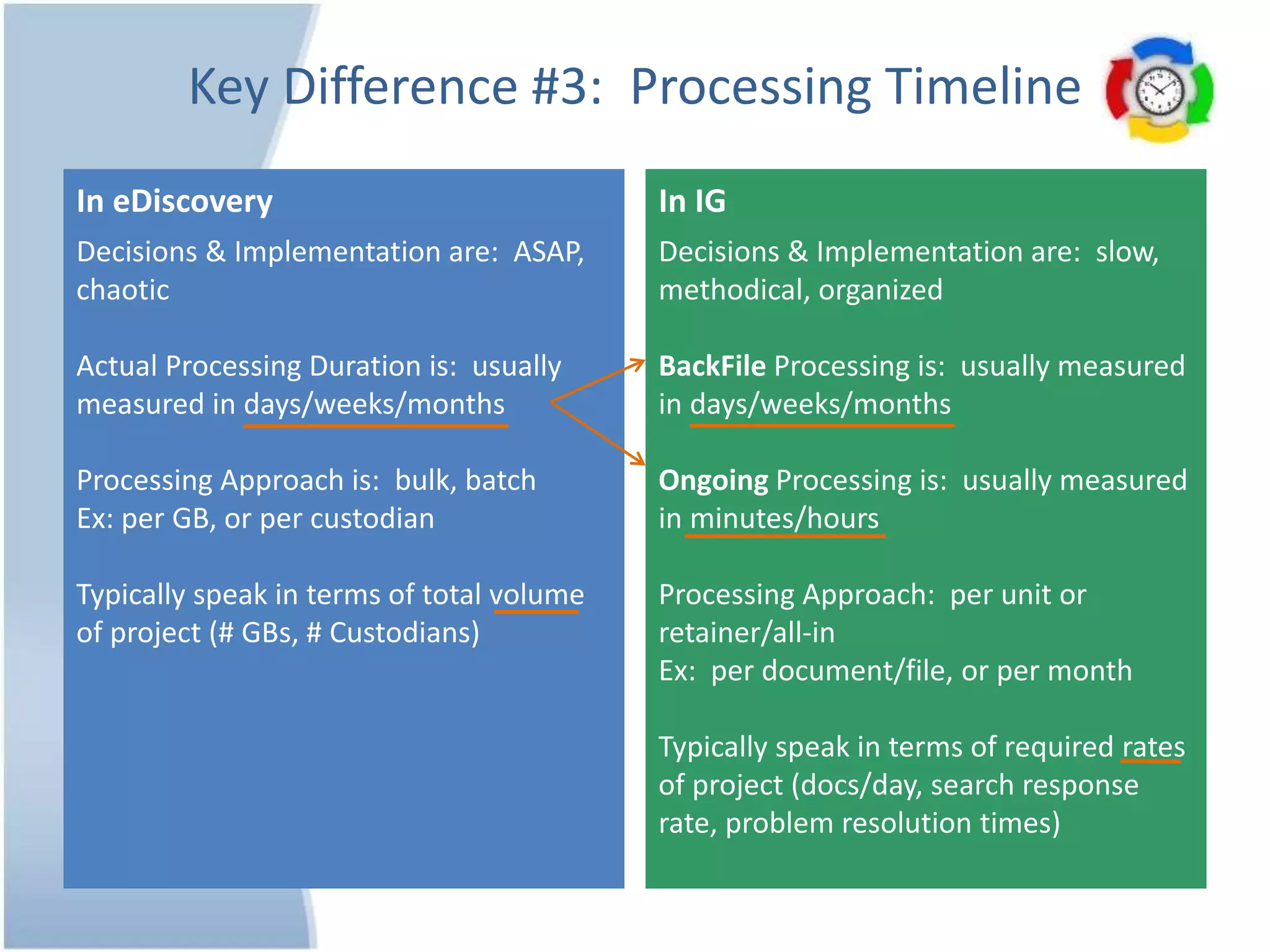
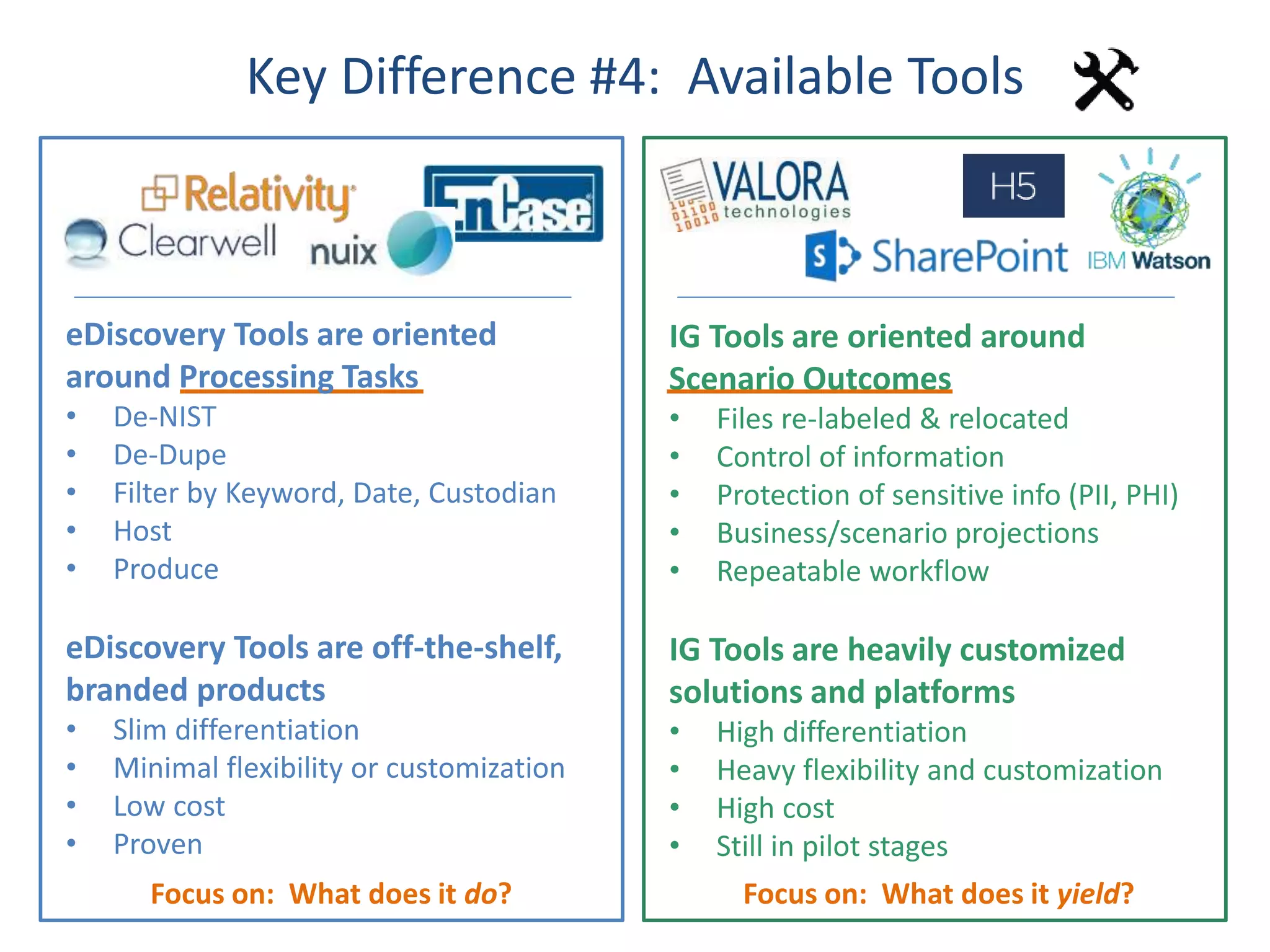
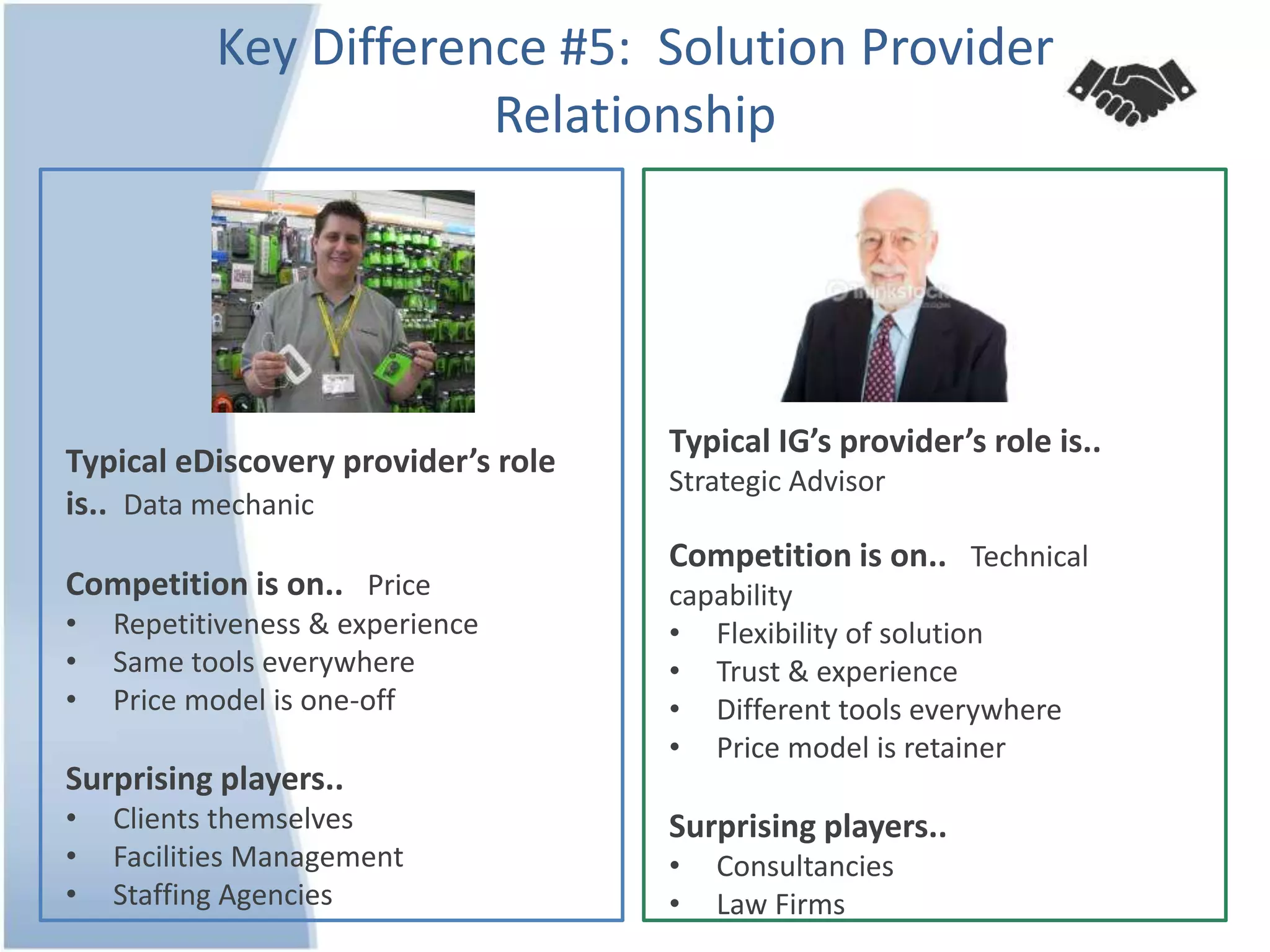
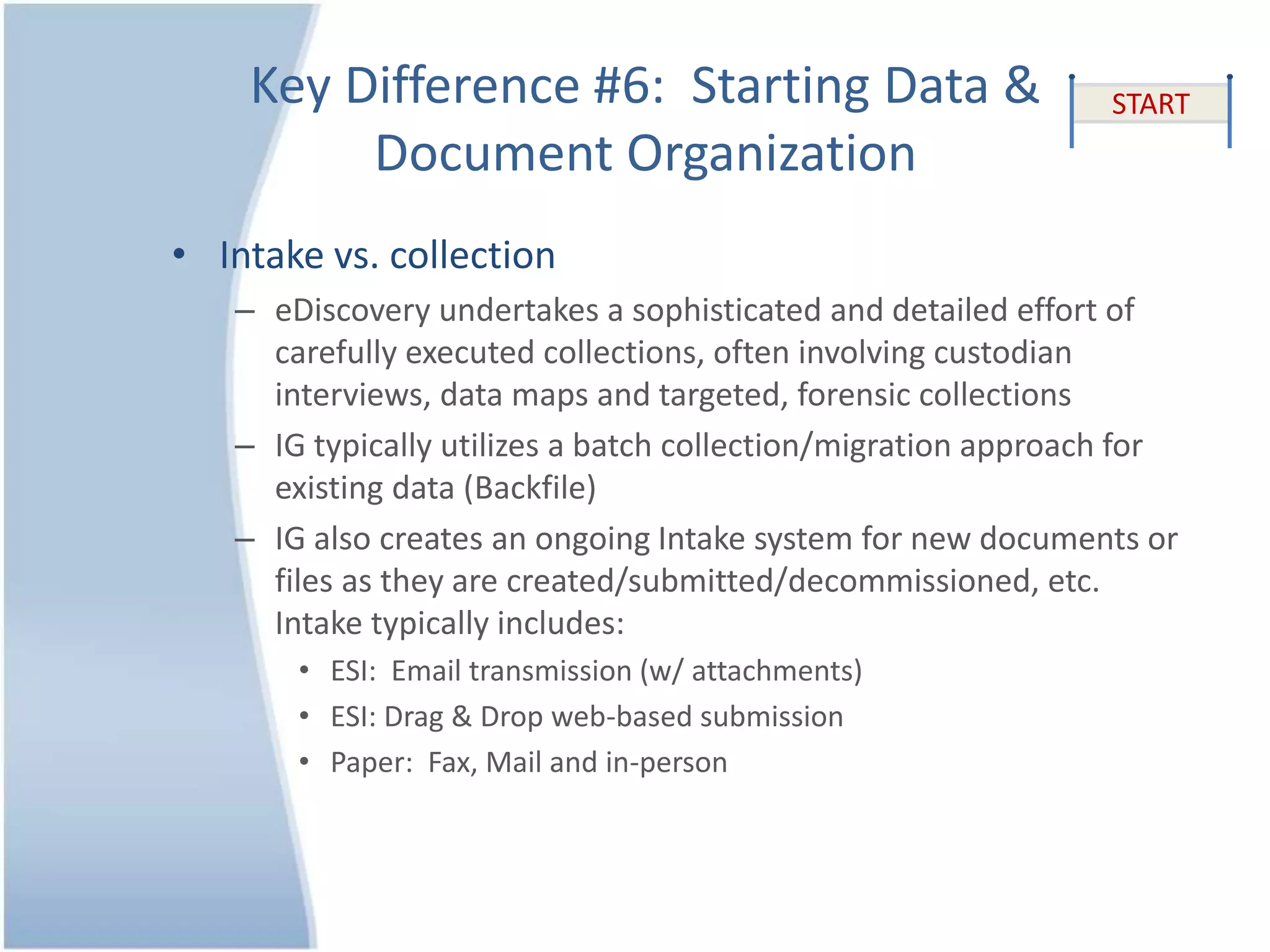
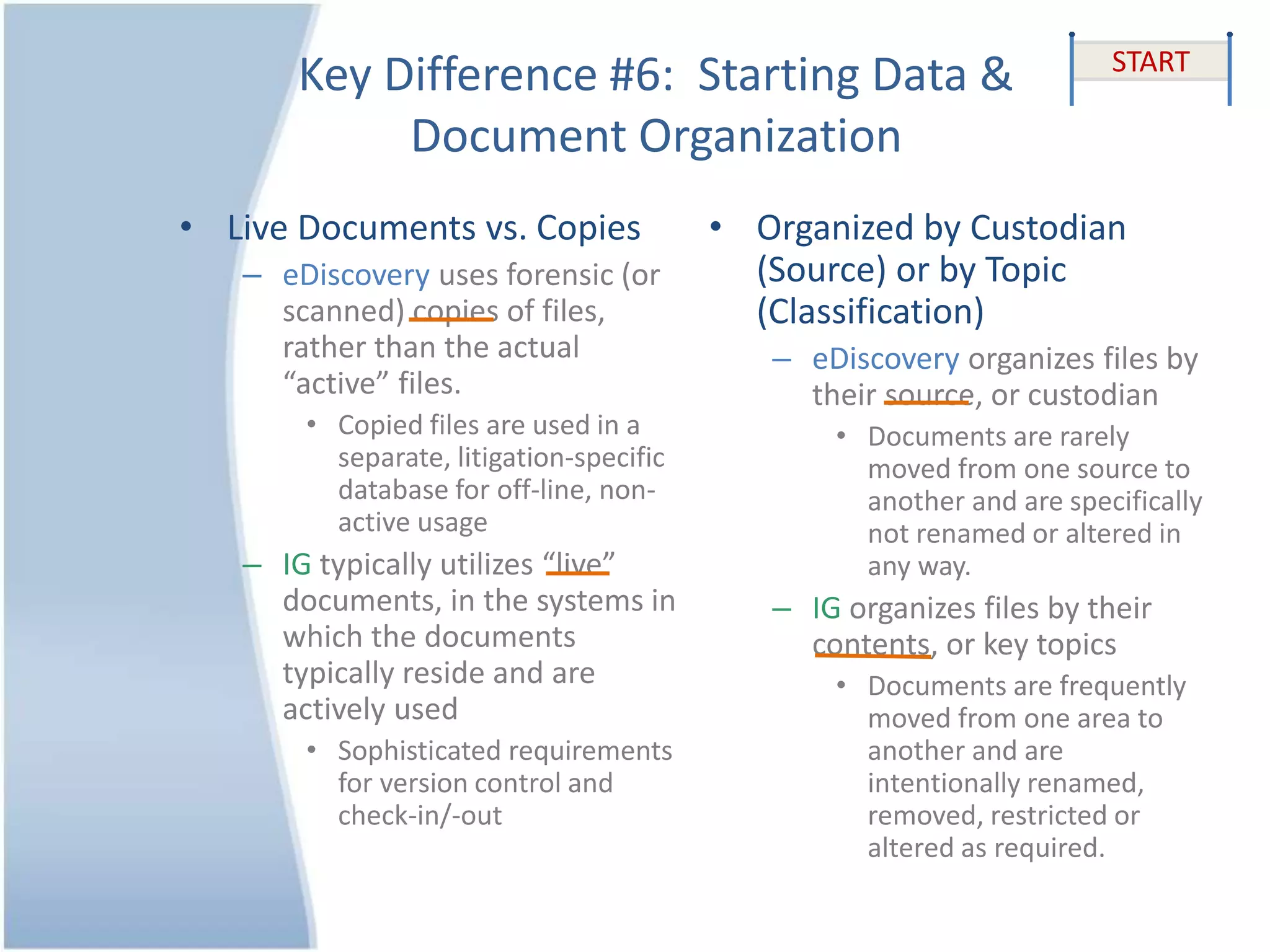
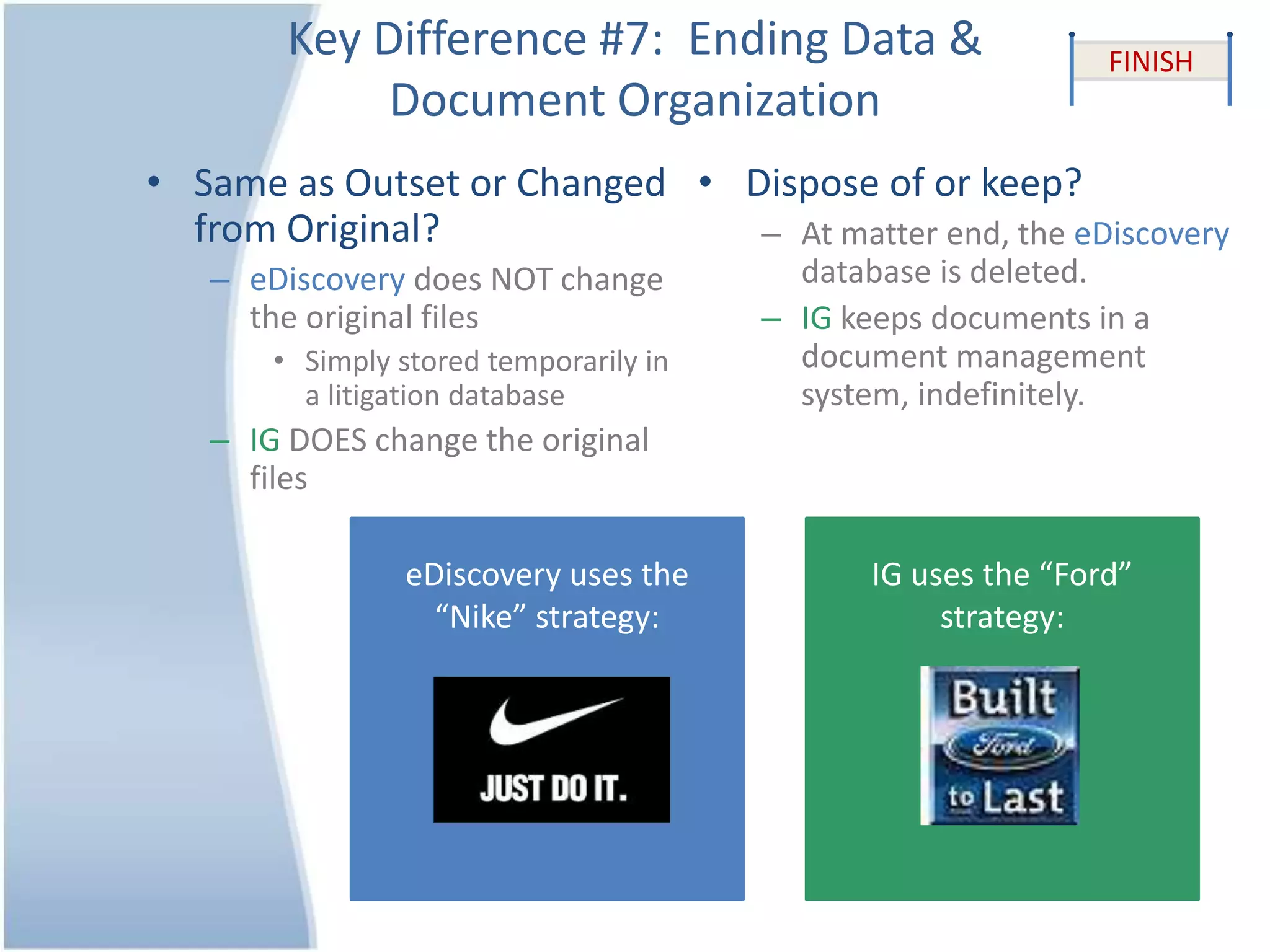
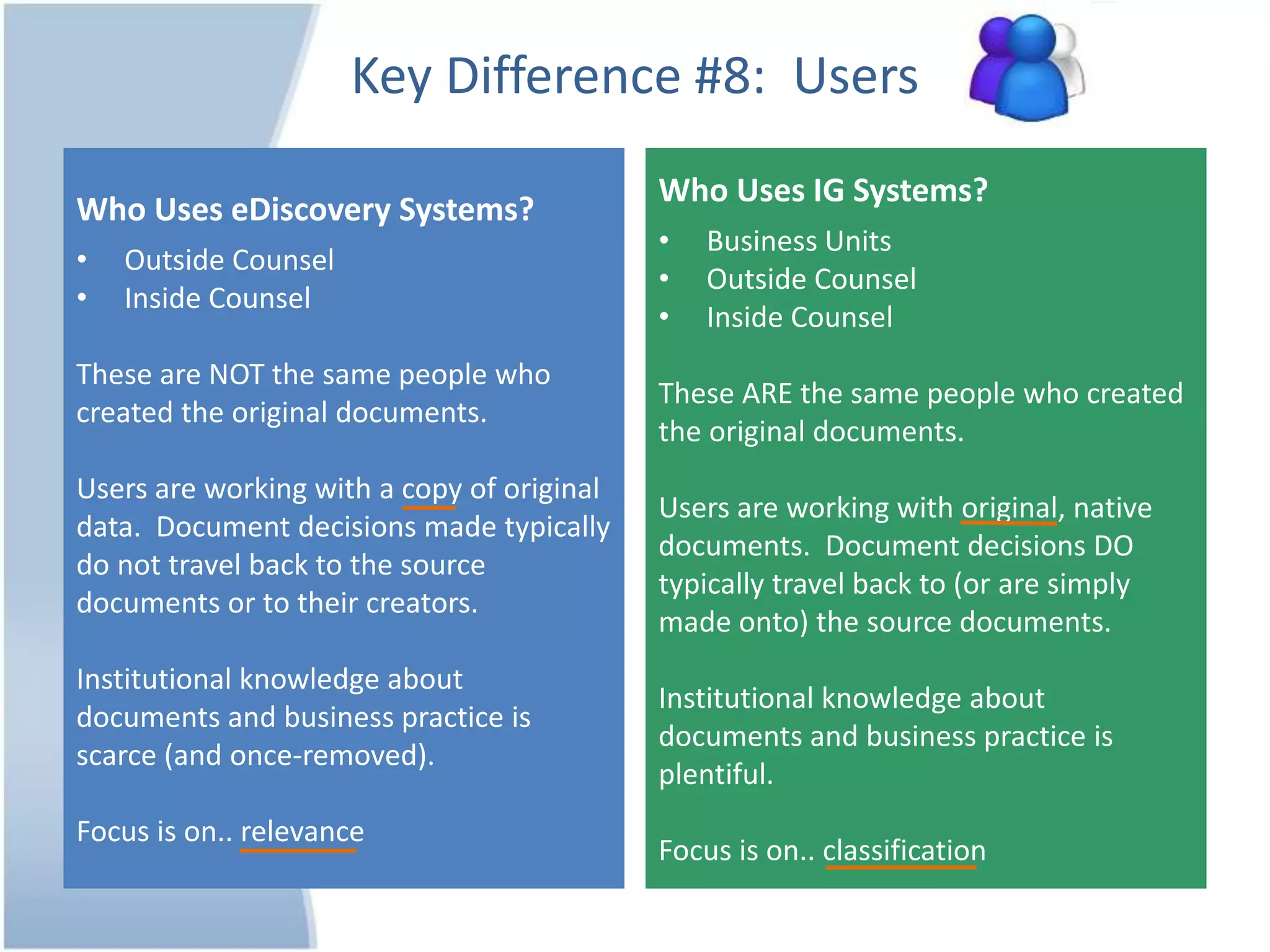
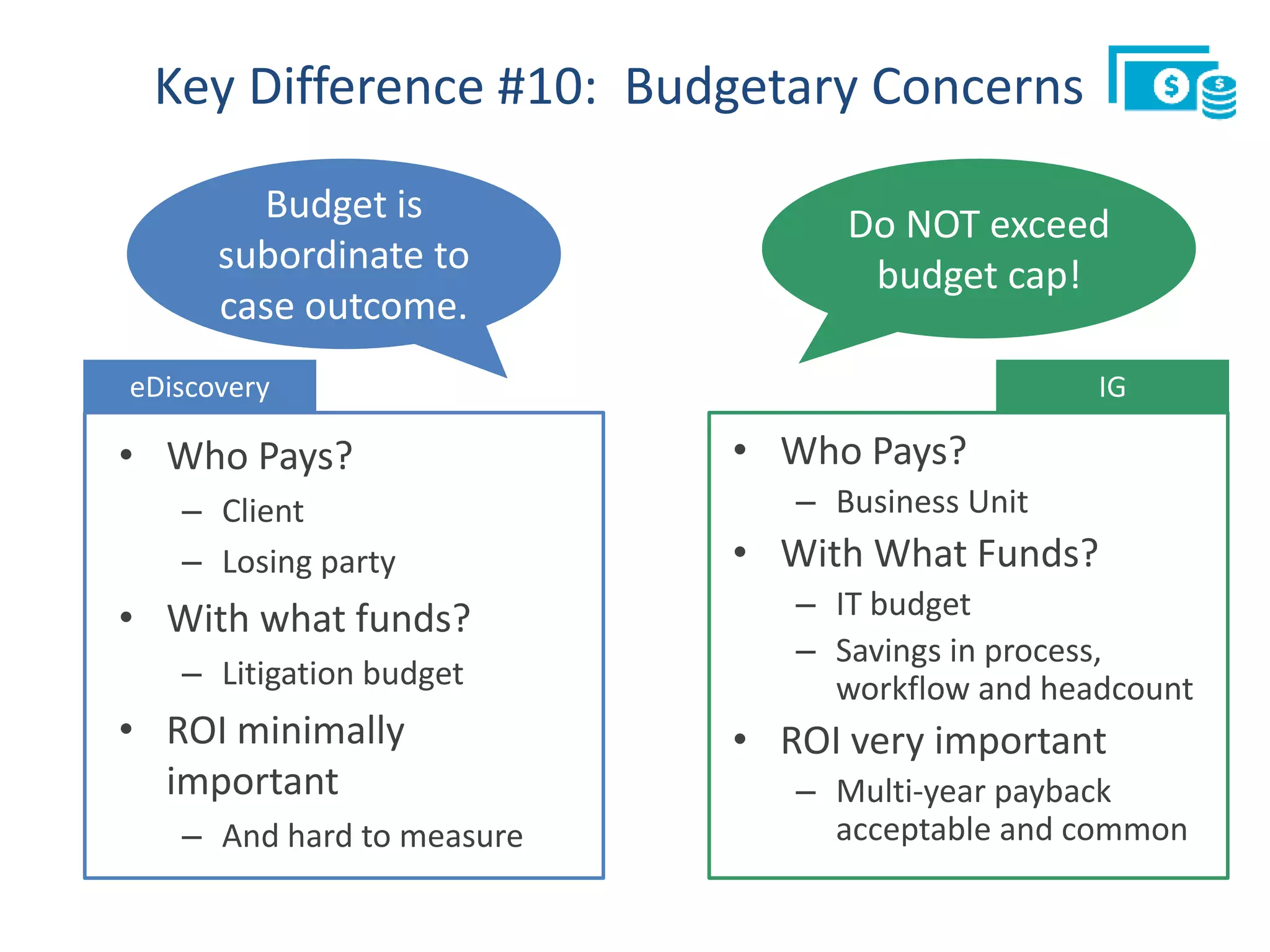
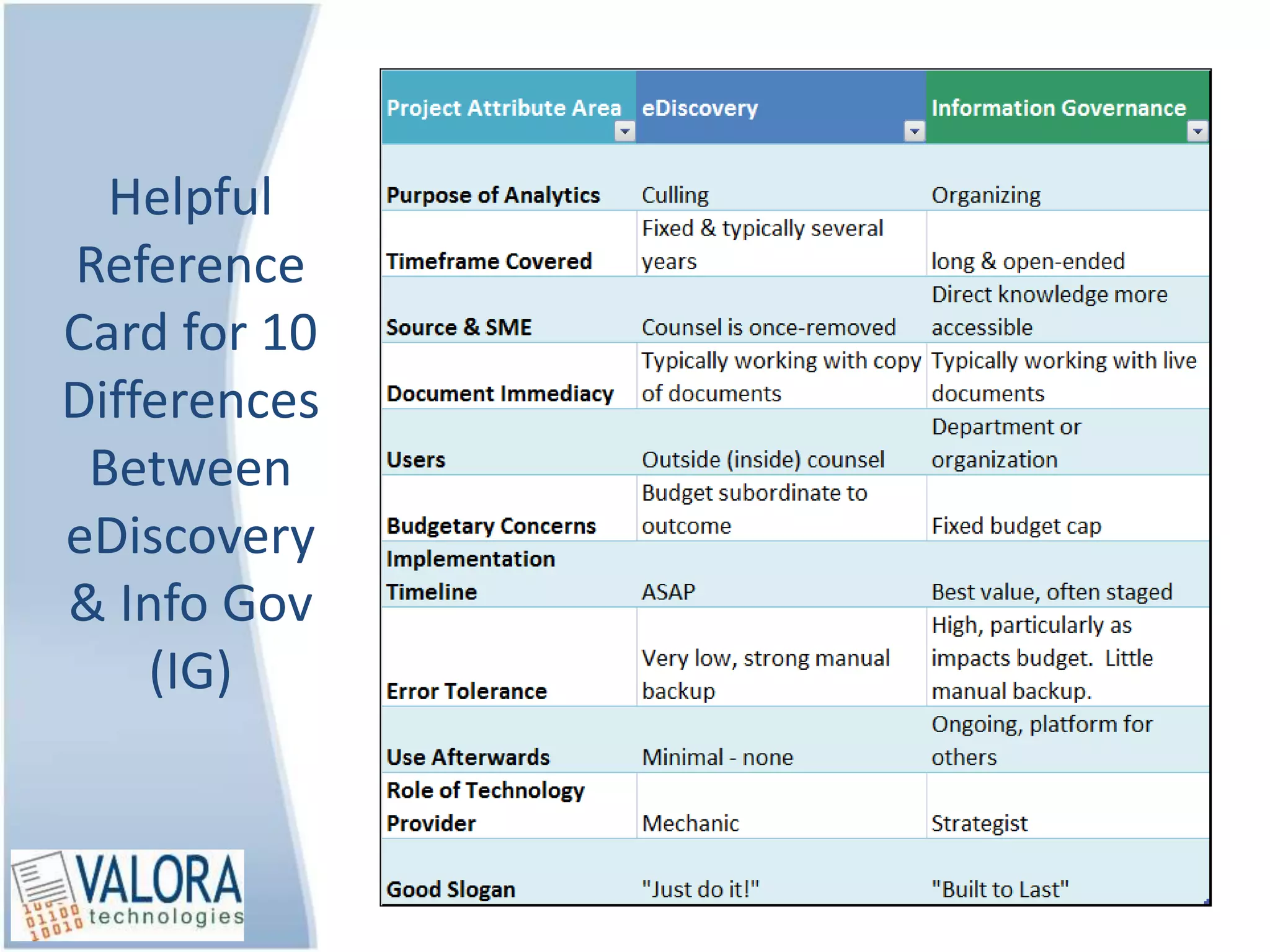
The document outlines 10 key differences between eDiscovery and information governance. Some of the main differences include: eDiscovery's primary goal is to reduce data for review and production in litigation, while IG's goal is to organize data for various uses now and in the future. eDiscovery has a fixed timeframe based on the legal case, while IG has an open-ended timeframe. Solution providers for eDiscovery focus on processing tasks, while IG providers focus on strategic advice and customized solutions.