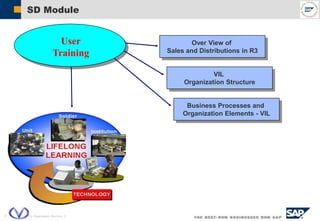
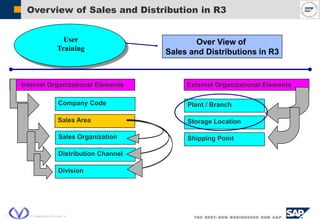
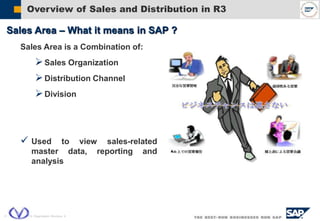
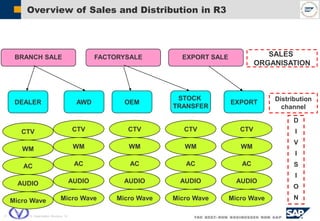
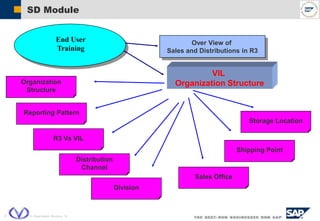
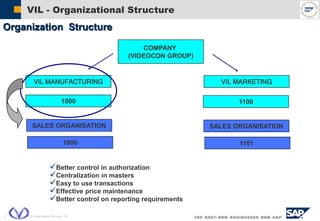
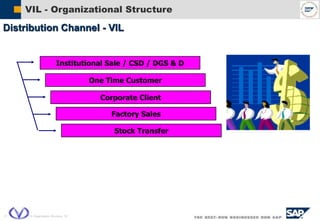
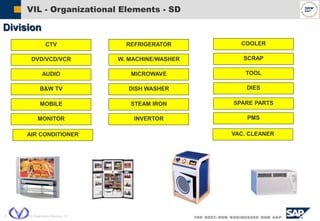
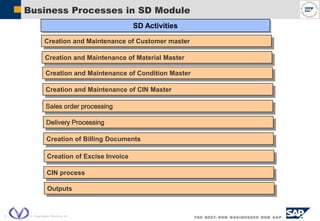
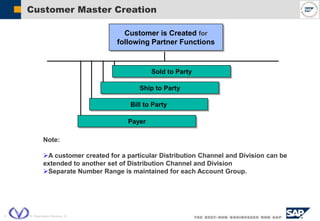
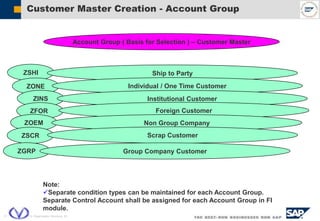
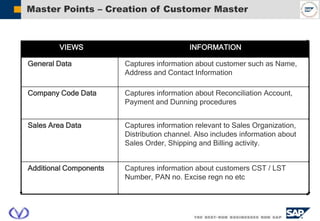
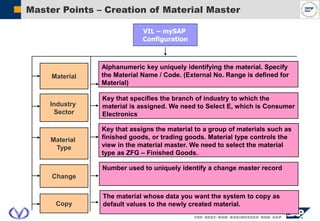
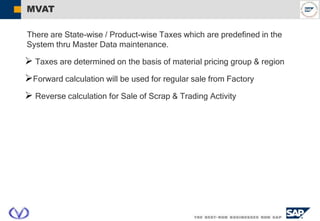
The document outlines the organizational structure and key components of the Sales and Distribution (SD) module within SAP for Videocon Industries Limited. It details internal and external organizational elements such as company codes, sales organizations, distribution channels, and the processes involved in sales order processing, customer master creation, and billing documentation. The training material is aimed at end-users to facilitate an understanding of the SD module's functionalities and business processes.