This document provides an overview of the EN1052 Introduction to Telecommunications course, including:
- The course provides 2 credits over 2 lecture hours per week with additional practical work. Assessment is based on a midterm, assignments, and end of semester exam.
- The course objectives are to understand basic communication systems concepts, analog vs. digital principles, computer networks, network topologies, and end user equipment.
- The document outlines the long history of telecommunications milestones from the 1800s to present.
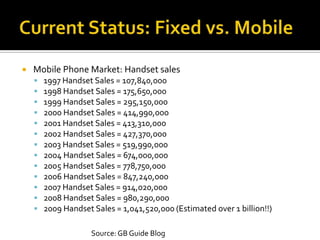
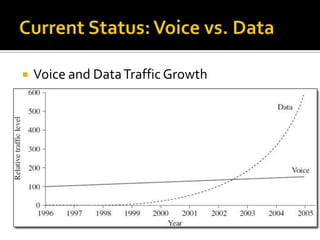
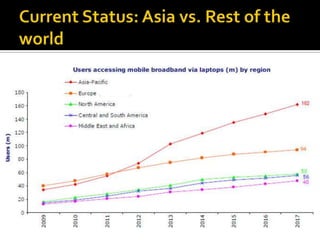
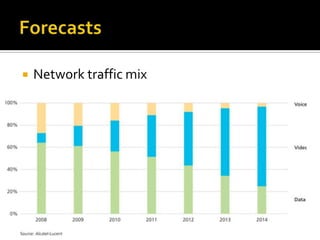
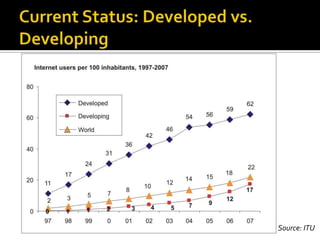
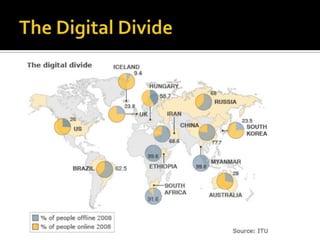
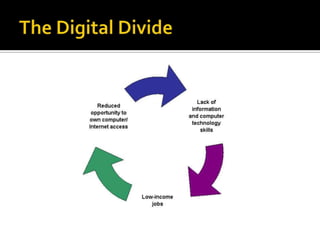
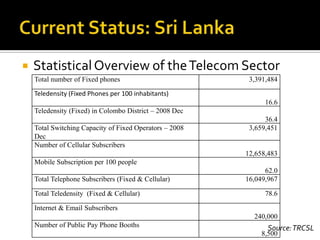
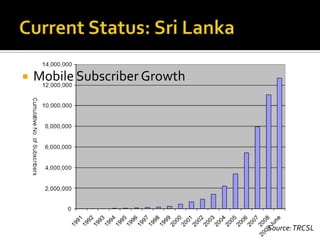
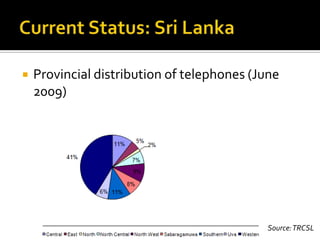
- It reviews the current status of telecommunications including submarine cables, communications satellites, cellular networks, and the digital divide between developed and developing nations.