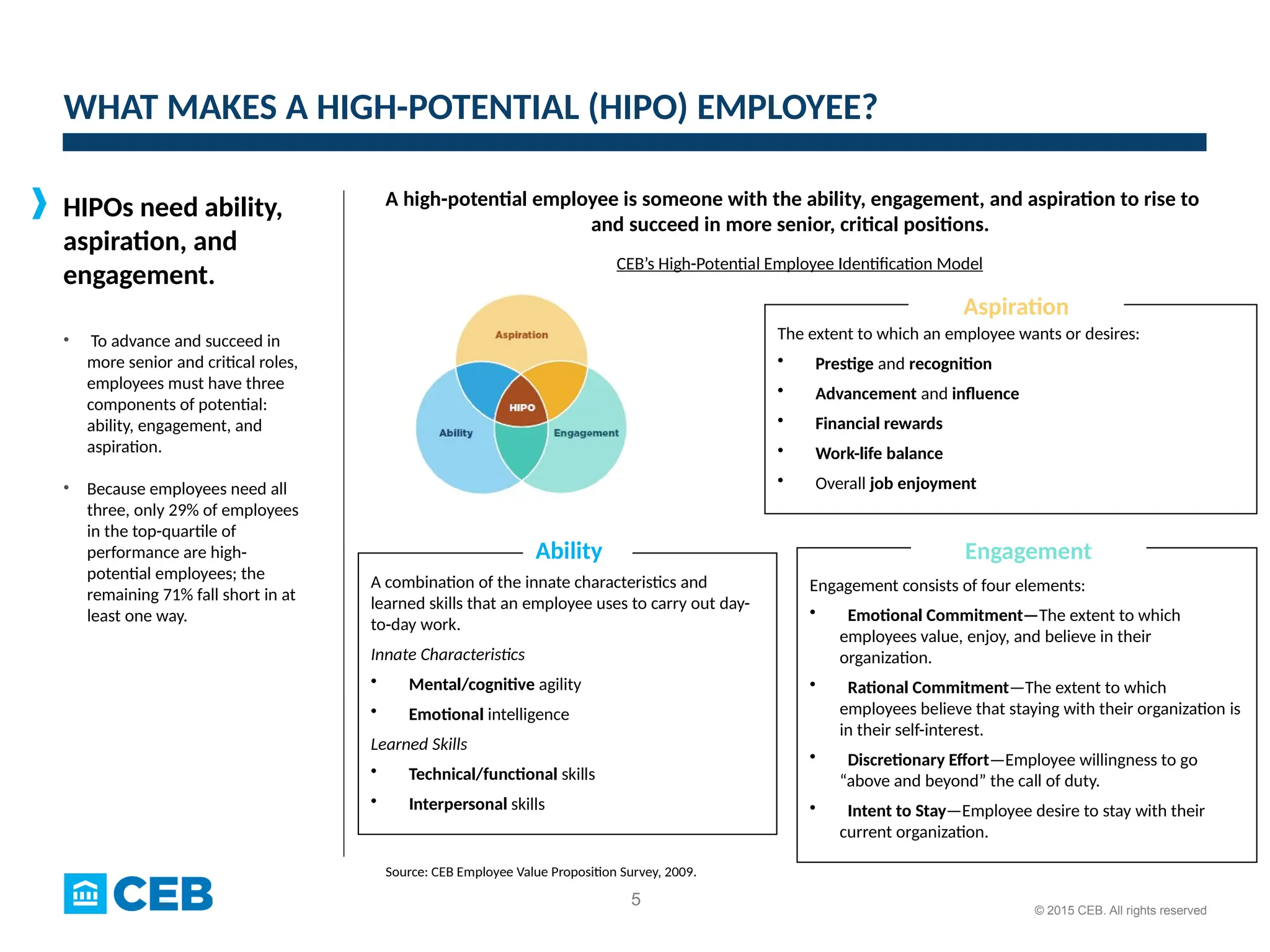
The document outlines a template for a High-Potential (HIPO) rotational program strategy aimed at enhancing employees' skills, engagement, and aspirations. It emphasizes the significance of developing HIPO employees through targeted rotational experiences, which can improve business outcomes, increase job satisfaction, and enhance talent retention. The program includes a structured approach to selecting participants and opportunities, as well as continuous support and evaluation throughout the rotations.











![© 2015 CEB. All rights reserved
13
STRATEGY OF OUR HIPO ROTATIONAL PROGRAM
Skill Gaps and Development Needs Addressed by HIPO Rotational
Program
Capability How the Rotational Experience Will Build the Capability
1. [Insert a capability or skill the rotational program is designed to
build among HIPOs.]
[Describe the experiences associated with a rotational program you
will use to build the capability.]
2. [Insert a capability or skill the rotational program is designed to
build among HIPOs.]
3. [Insert a capability or skill the rotational program is designed to
build among HIPOs.]
4. [Insert a capability or skill the rotational program is designed to
build among HIPOs.]
5. [Insert a capability or skill the rotational program is designed to
build among HIPOs.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1hiporotationalprogramstrategytemplate-241213051853-d9f411c4/75/1-HIPO-Rotational-Program-Strategy-Template-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![© 2015 CEB. All rights reserved
14
STRATEGY OF OUR HIPO ROTATIONAL PROGRAM (CON’T)
HIPO Rotational Program Success Measures
Success Measure Expected Result
1. [Insert success measure you will use to evaluate the effectiveness
of your HIPO Rotational Program.]
[Insert the goal related to this success measure you hope to achieve.]
2. [Insert success measure you will use to evaluate the effectiveness
of your HIPO Rotational Program.]
3. [Insert success measure you will use to evaluate the effectiveness
of your HIPO Rotational Program.]
4. [Insert success measure you will use to evaluate the effectiveness
of your HIPO Rotational Program.]
5. [Insert success measure you will use to evaluate the effectiveness
of your HIPO Rotational Program.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1hiporotationalprogramstrategytemplate-241213051853-d9f411c4/75/1-HIPO-Rotational-Program-Strategy-Template-pptx-14-2048.jpg)

![© 2015 CEB. All rights reserved
16
STRUCTURE OF OUR HIPO ROTATIONAL PROGRAM
HIPO Rotational Program Participant Profile
Level:
Mid-Level
Skills:
• Manage direct reports
• [Insert required skill for
HIPO to participate.]
Experience
• P&L responsibility
• [Insert required
experience for HIPO to
participate.]
Criteria Used to Match Participants:
[Insert criteria you will use to match participants to rotational
experiences.]
Nomination Method for Participation:
[Describe how participants will be nominated for the program.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1hiporotationalprogramstrategytemplate-241213051853-d9f411c4/75/1-HIPO-Rotational-Program-Strategy-Template-pptx-16-2048.jpg)


![© 2015 CEB. All rights reserved
19
STRUCTURE OF OUR HIPO ROTATIONAL PROGRAM (CON’T)
HIPO Management Responsibilities During the Rotational Program
Role Responsibilities Owner
1. Role Builder
Determines the scope and
responsibilities of the HIPO’s role and
how those might change over the
rotation
[Example: HIPO Manager During
Rotation]
2. Day-to-Day Project Manager
Oversees the HIPO’s projects during
the rotation on a day-to-day basis
[Example: HIPO Manager During
Rotation]
3. Feedback Deliverer
Provides formal and informal
feedback to HIPOS during and at the
end of the rotation
[Example: HIPO Manager During
Rotation]
4. Development Planner
Works with HIPOs, HR, and Hiring Managers to
create challenging and attainable learning and
performance goals across rotations [Example: HIPO Development Coach]
5. Reflection Facilitator
Forces HIPOs to reflect on their experiences and
ensure that they are learning during the program [Example: HIPO Development Coach]
6. Feedback Coach
Helps HIPOs to internalize feedback and change
their behavior accordingly during the program [Example: HIPO Development Coach]
7. Learning Accelerator
Works with line managers to customize the scope
and learning components of roles to increase
learning opportunities across rotations
[Example: HIPO Development Coach]
8. Development Advisor
Serves as a mentor in development-planning
meetings and provides informal feedback and
support across the rotation
[Example: Senior Executive]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1hiporotationalprogramstrategytemplate-241213051853-d9f411c4/75/1-HIPO-Rotational-Program-Strategy-Template-pptx-19-2048.jpg)

![© 2015 CEB. All rights reserved
21
HIPO ROTATIONAL PROGRAM COMMUNICATION PLAN
Audience Communication Goals Level of Detail Needed Communication
Delivery Method
Target Date or
Frequency
HIPOs 1. [Goal]
2. [Goal]
• [Level of Detail] • [Communication
channel]
• [Date or Frequency]
HIPOs’ Managers
1. [Goal]
2. [Goal] • [Level of Detail]
• [Communication
channel] • [Date or Frequency]
HR Staff 1. [Goal]
2. [Goal]
• [Level of Detail] • [Communication
channel]
• [Date or Frequency]
Business Unit Leaders 1. [Goal]
2. [Goal]
• [Level of Detail] • [Communication
channel]
• [Date or Frequency]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1hiporotationalprogramstrategytemplate-241213051853-d9f411c4/75/1-HIPO-Rotational-Program-Strategy-Template-pptx-21-2048.jpg)


