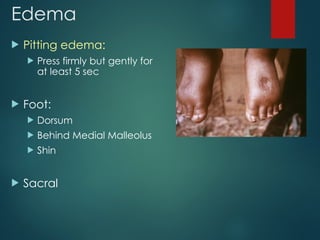
The document outlines the general physical examination (GPE) procedures for assessing a patient's overall health and detecting internal diseases. It details the examination steps, including patient interaction, environment considerations, vital signs assessment, and systematic examination of various body parts. It emphasizes maintaining patient comfort, privacy, and the importance of a structured approach to the examination.