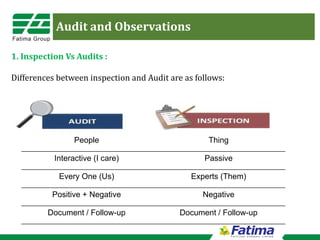
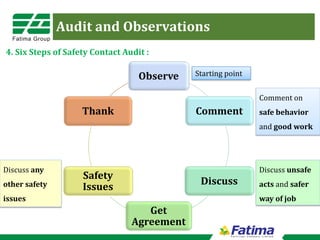
This document discusses audits and observations for safety management. It notes the differences between inspections and audits, and lists some of the key benefits of auditing including preventing injuries, raising safety awareness, and identifying unsafe situations. It provides details on the audit process, recommending audits be conducted monthly by various managers. Results should be analyzed to observe safety performance trends over time. The document also presents two methods for quantifying audit results: a Time Weighted Index that works well for process plants, and an Unsafe Acts Index that is better for labor-intensive locations.