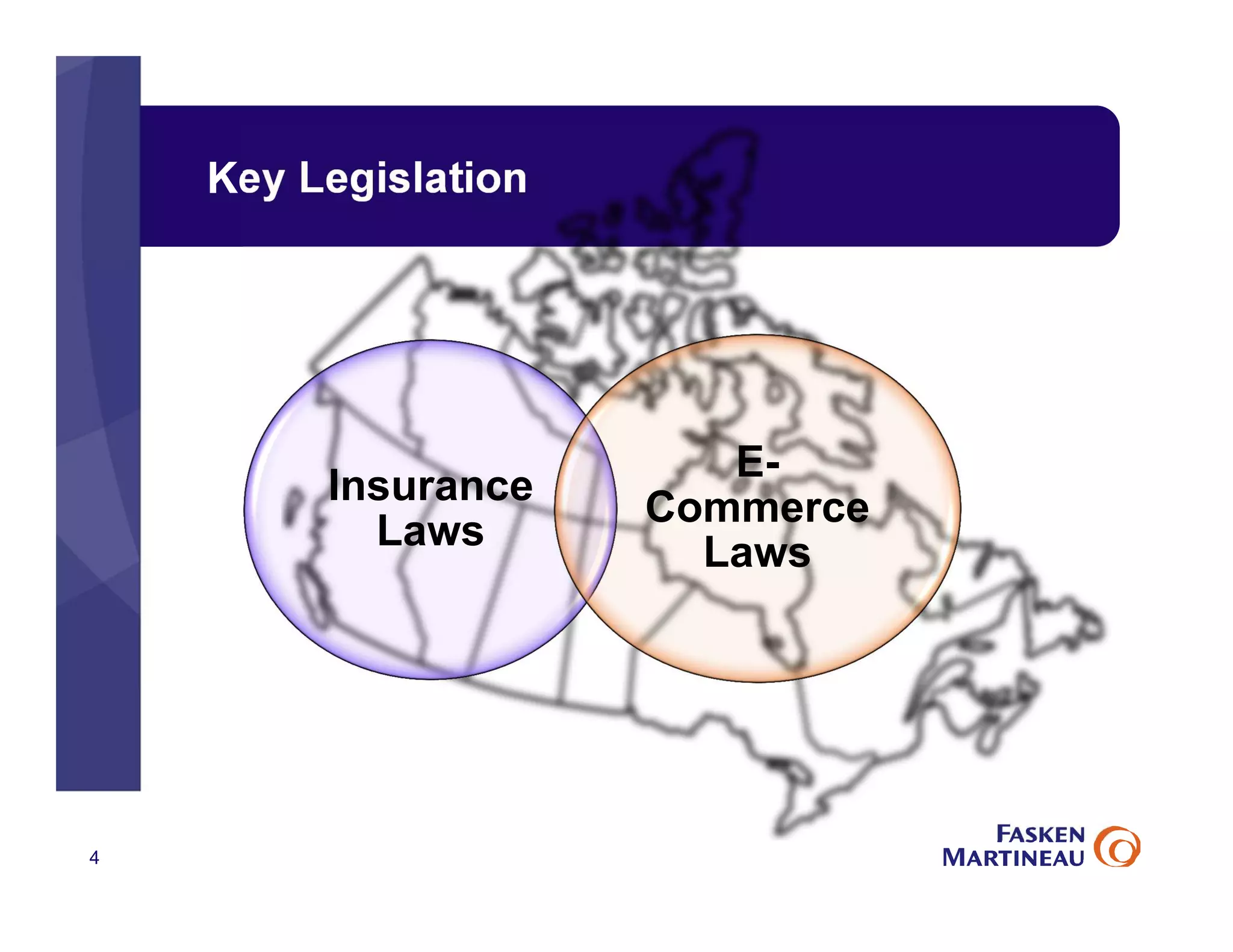
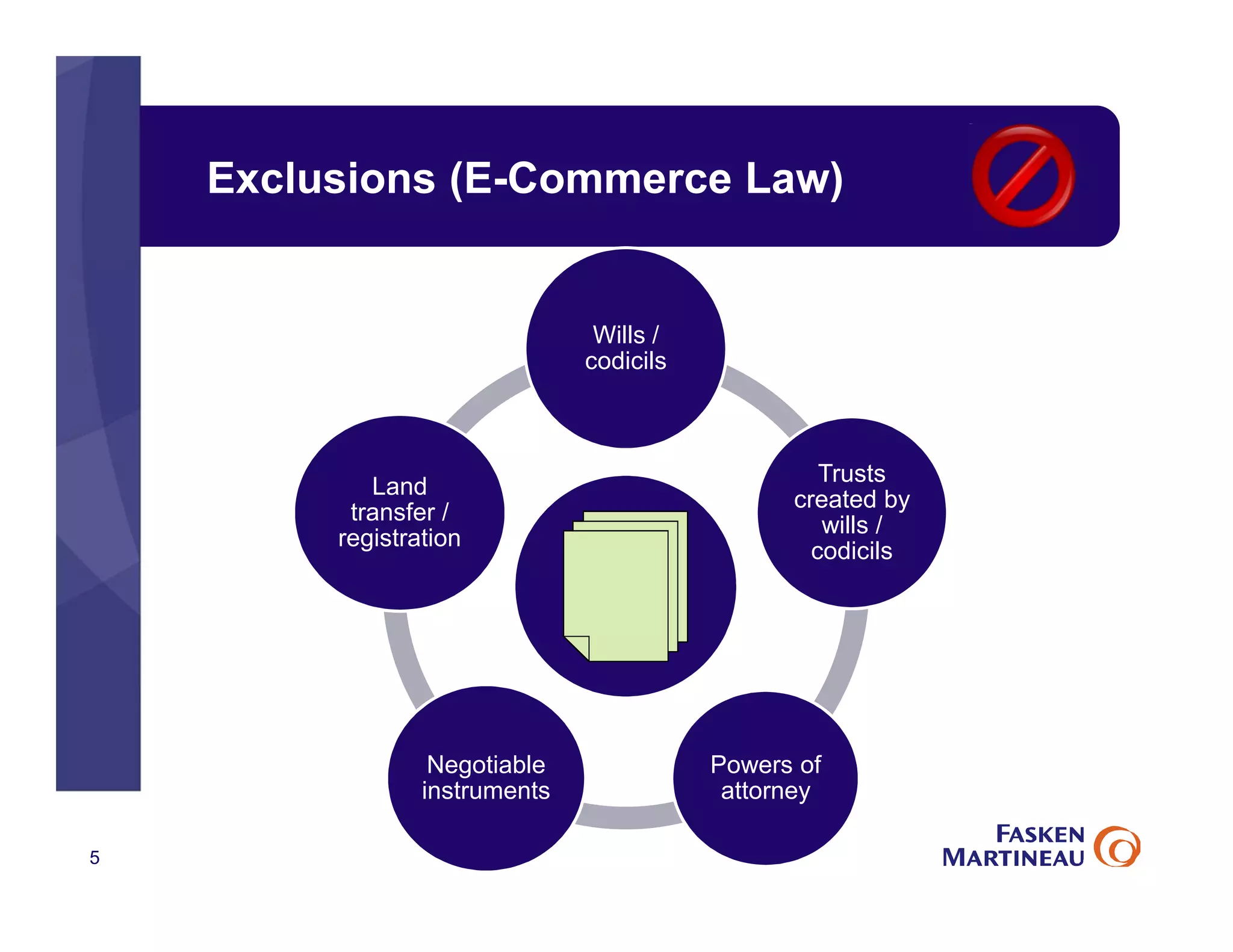
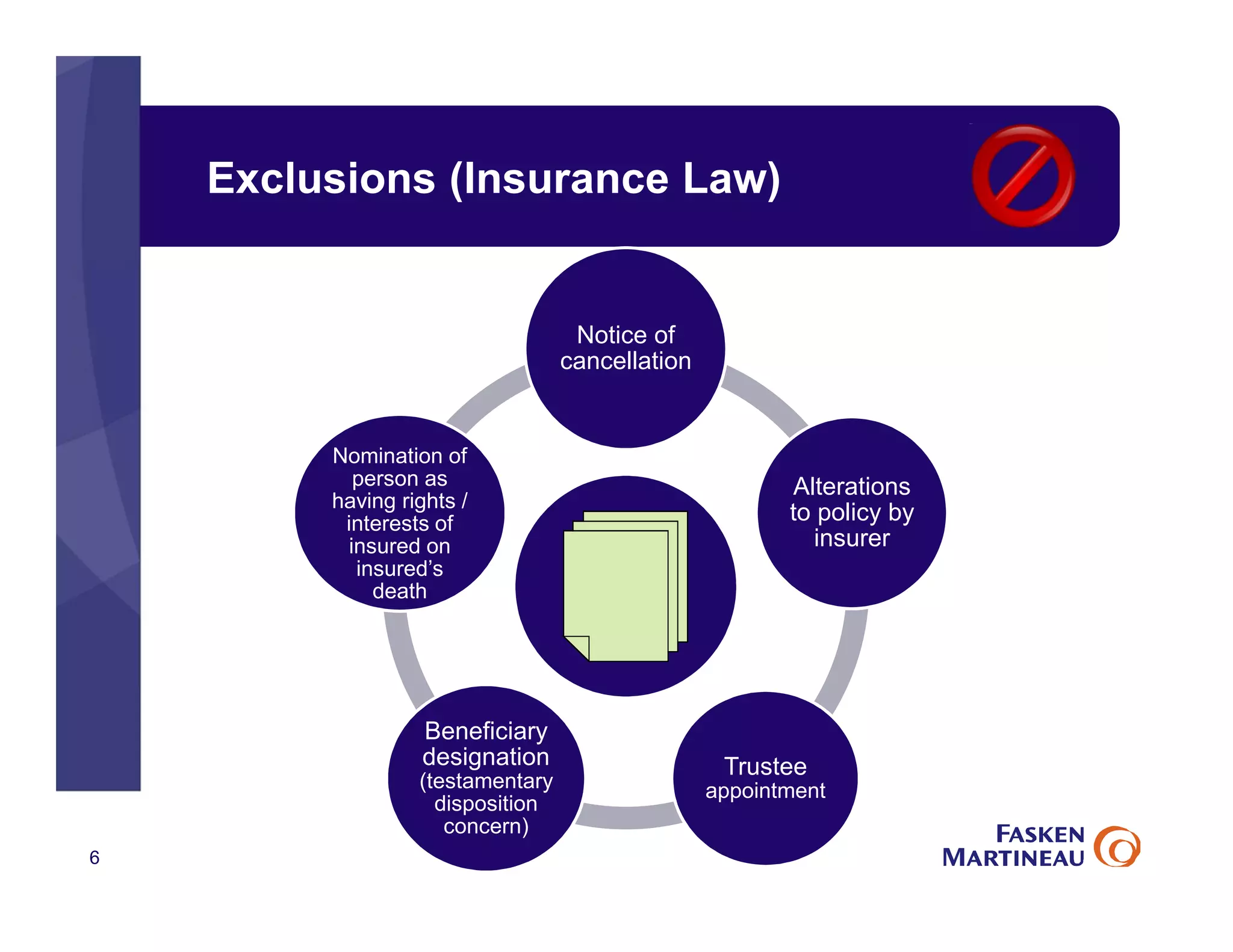
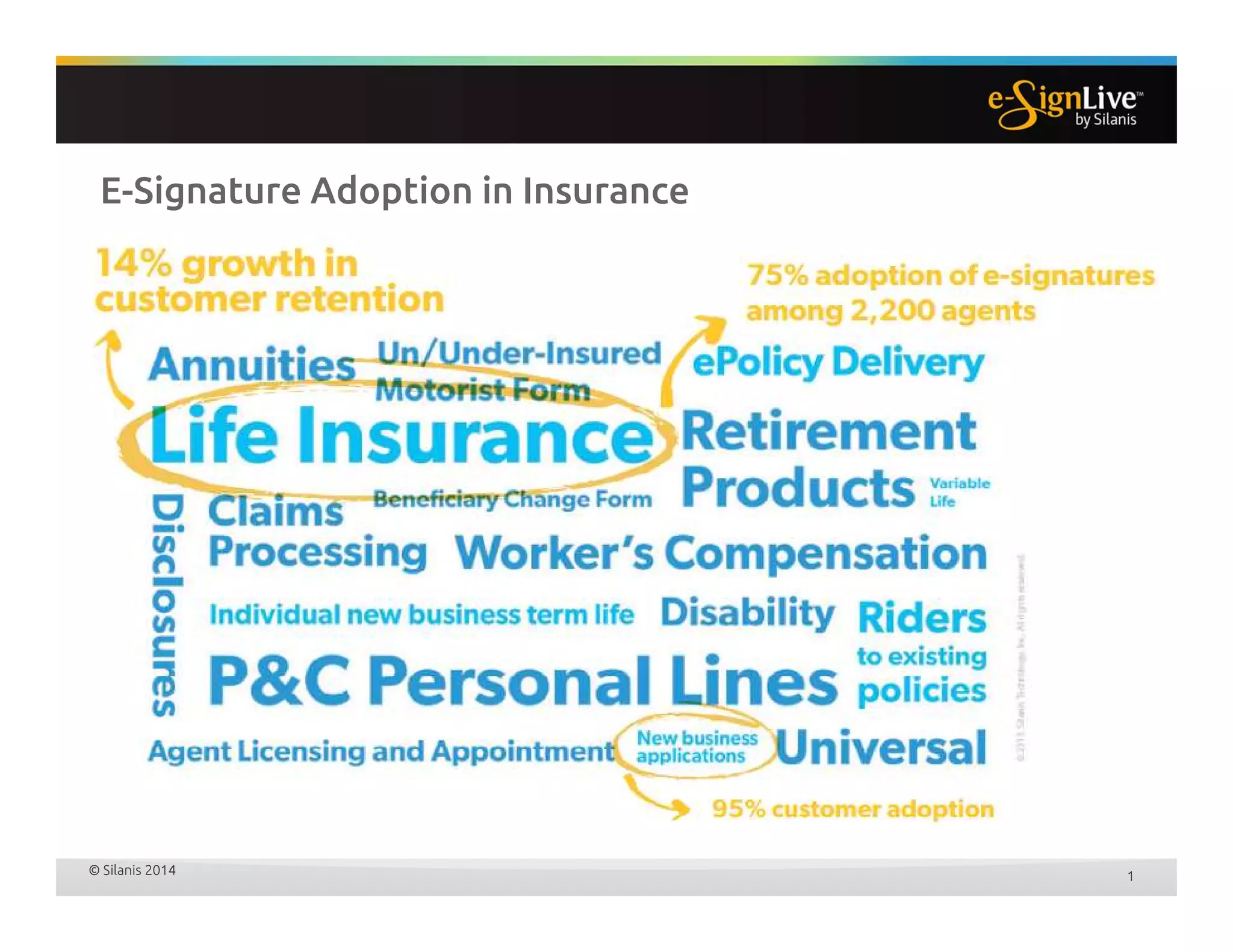
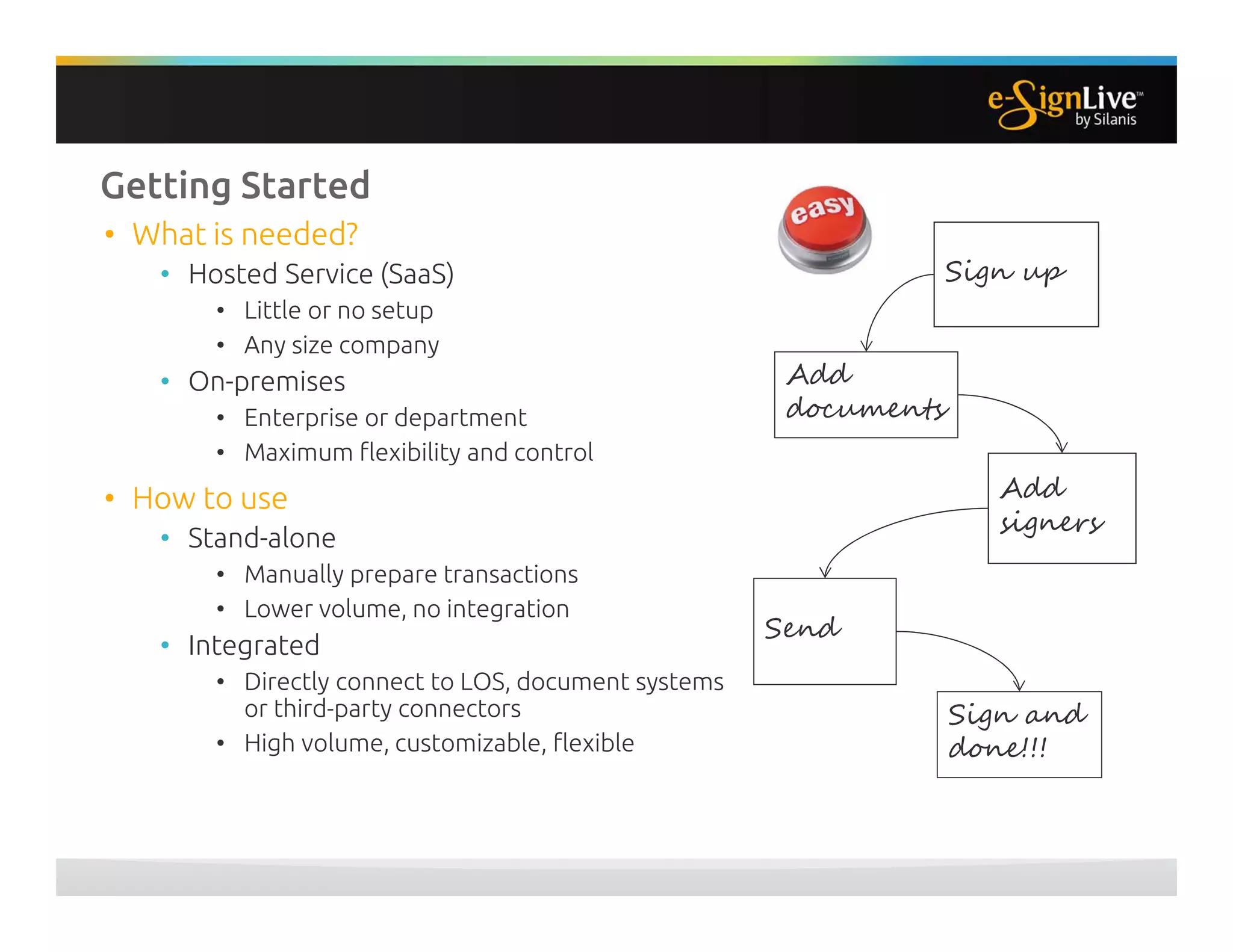
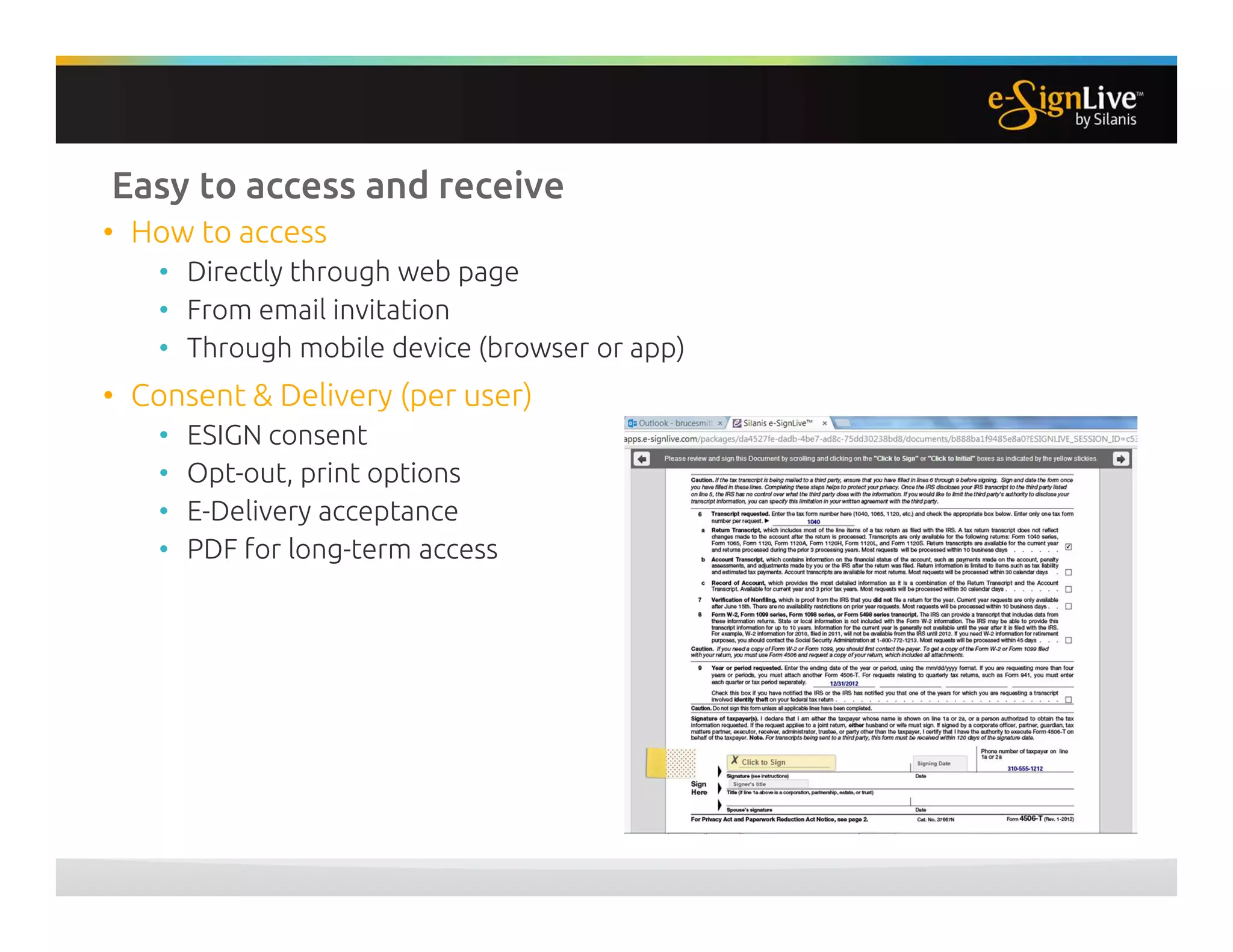
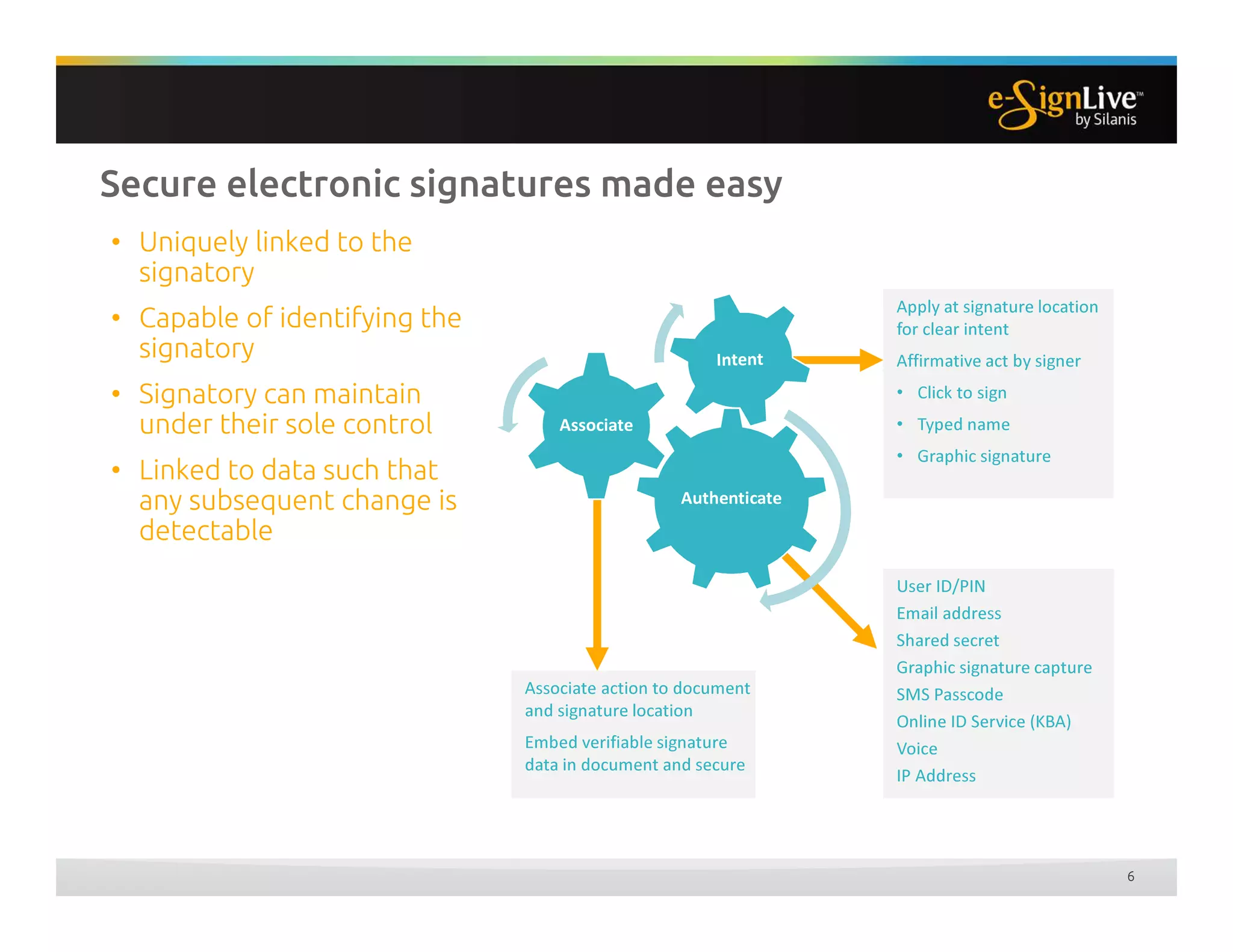
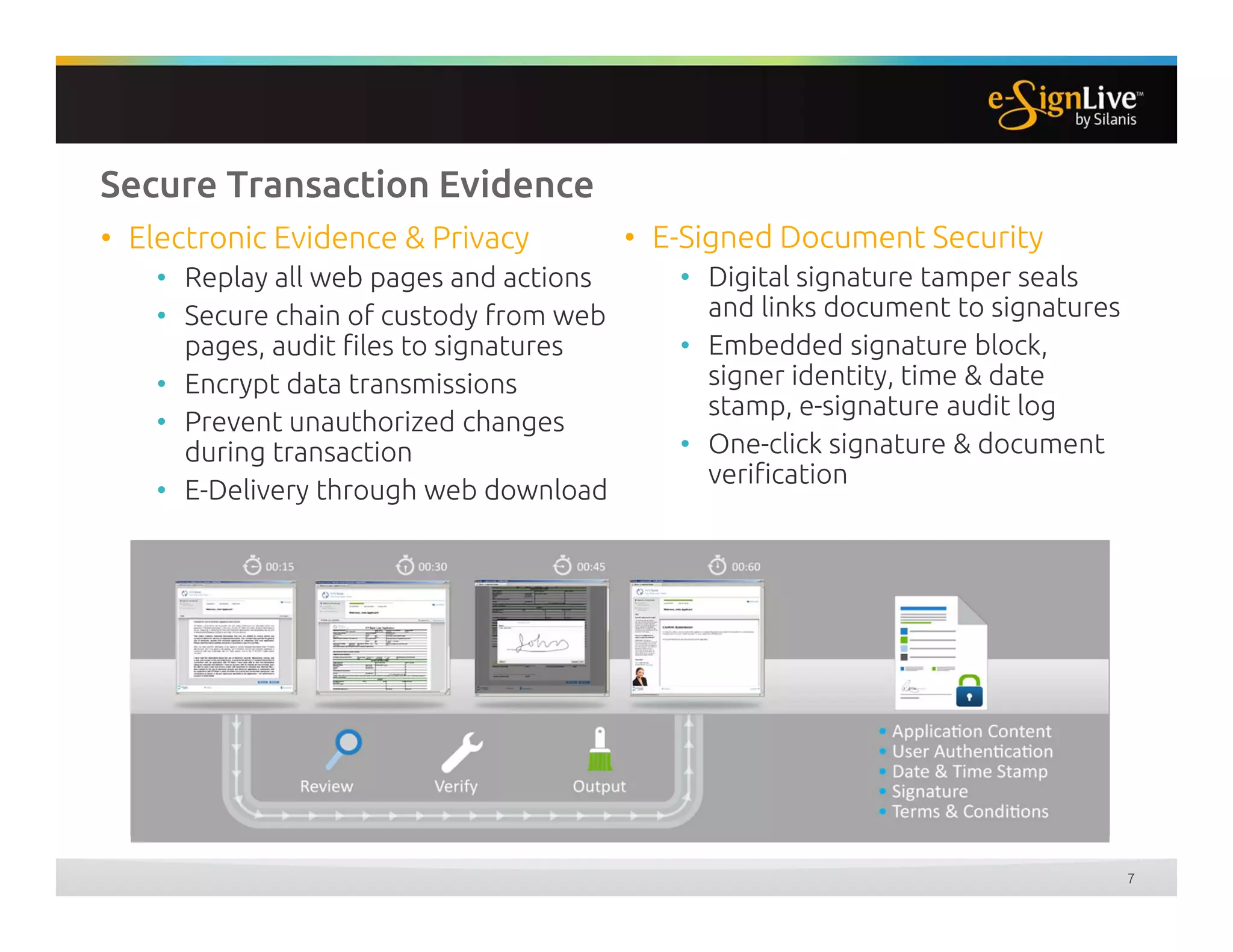
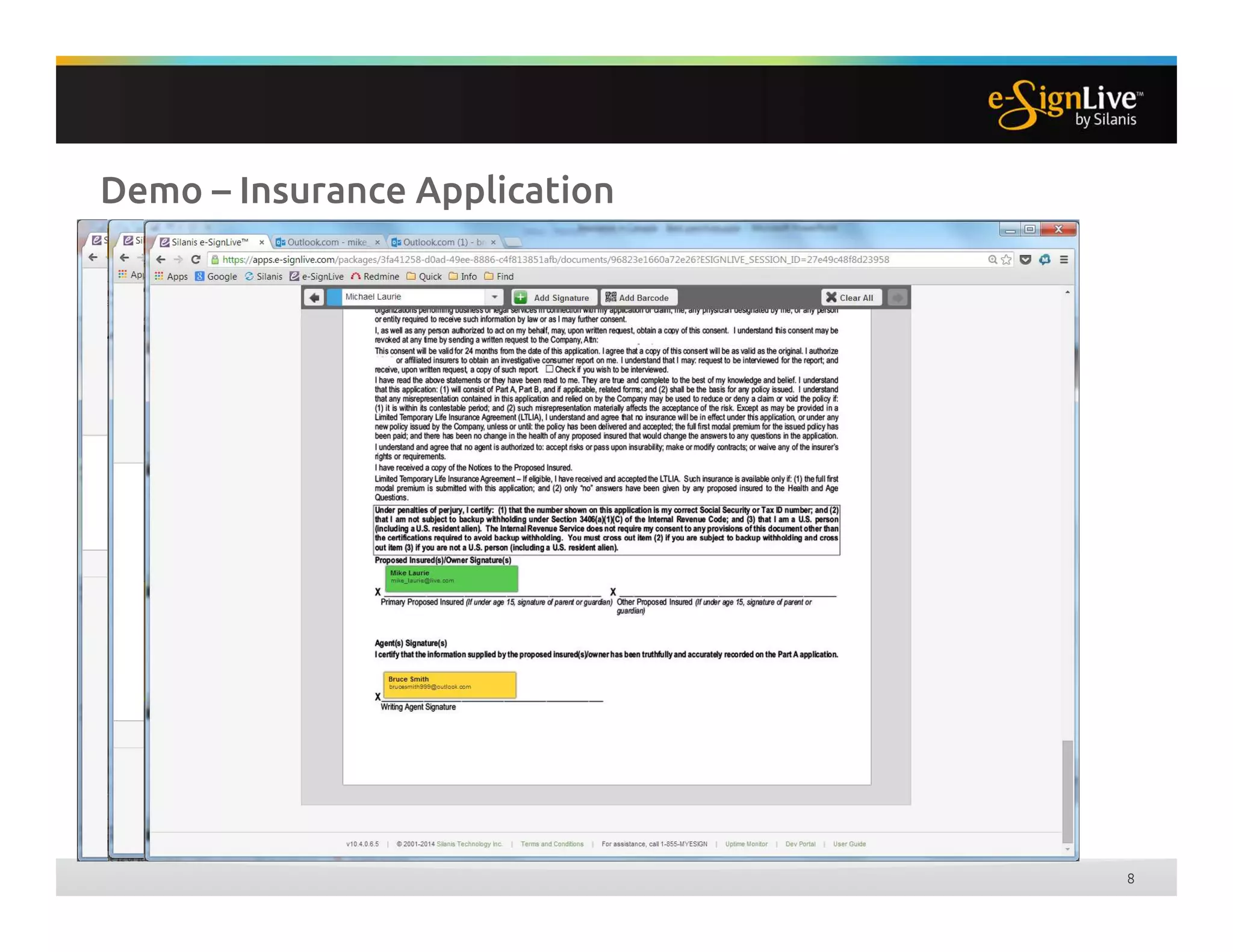
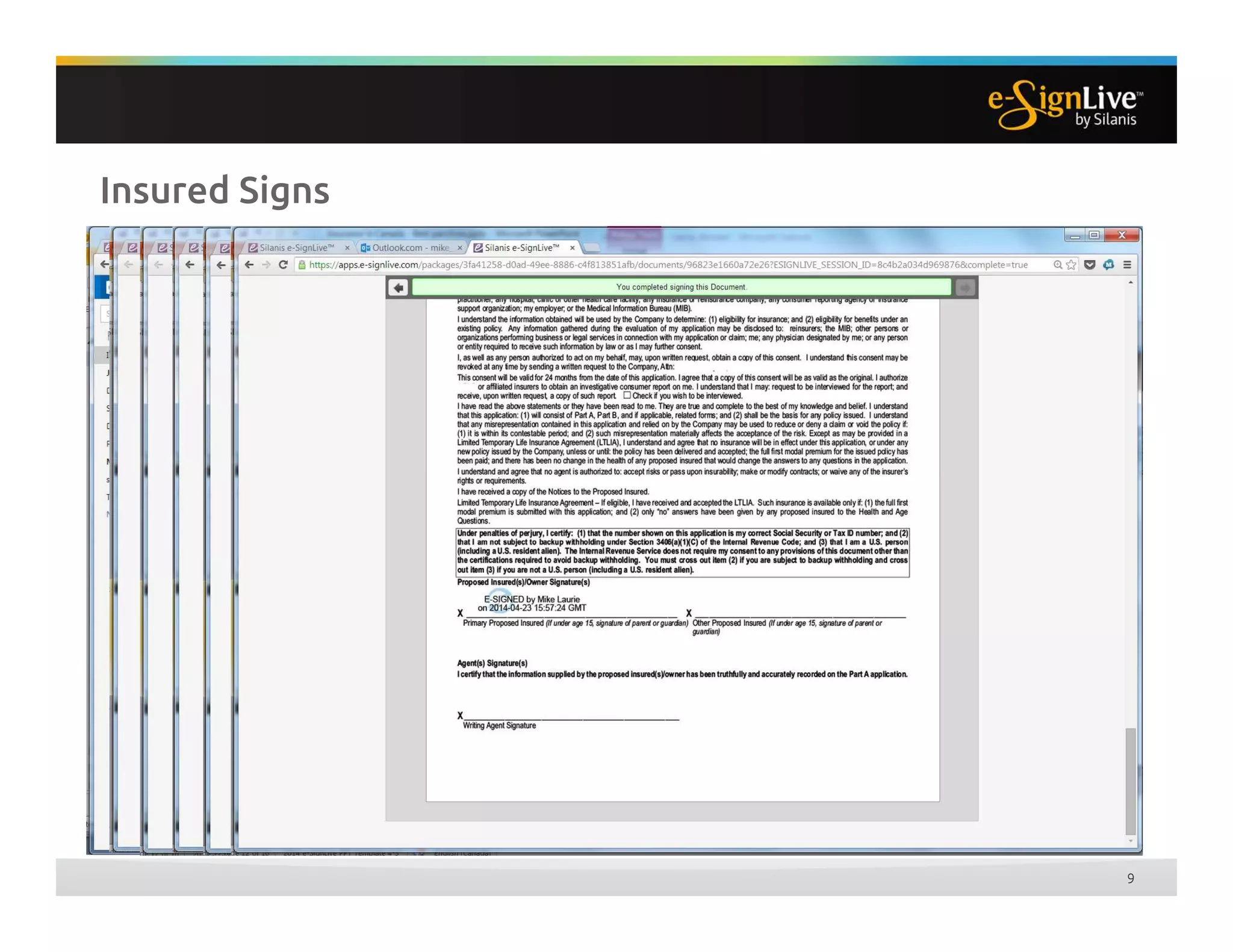
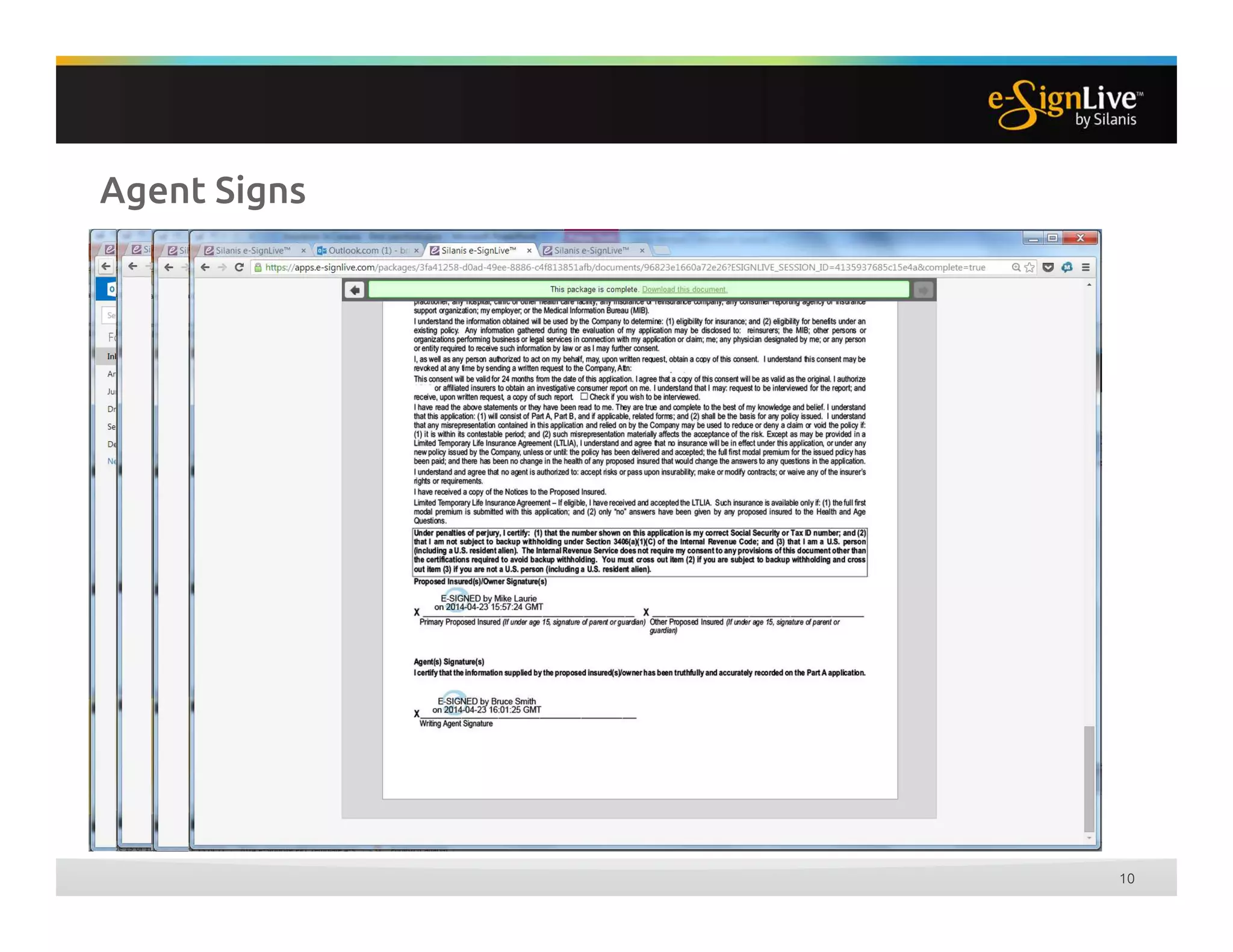
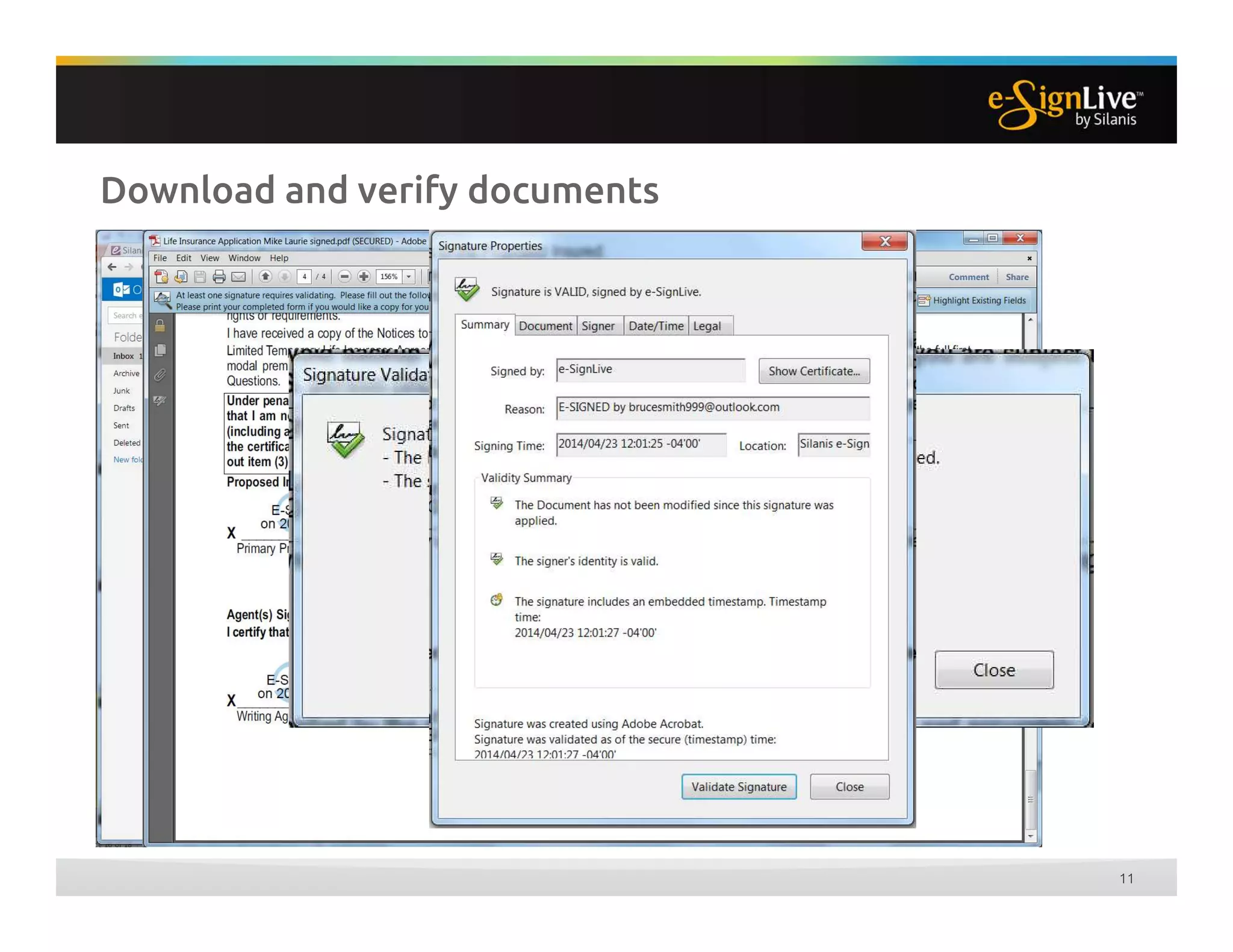
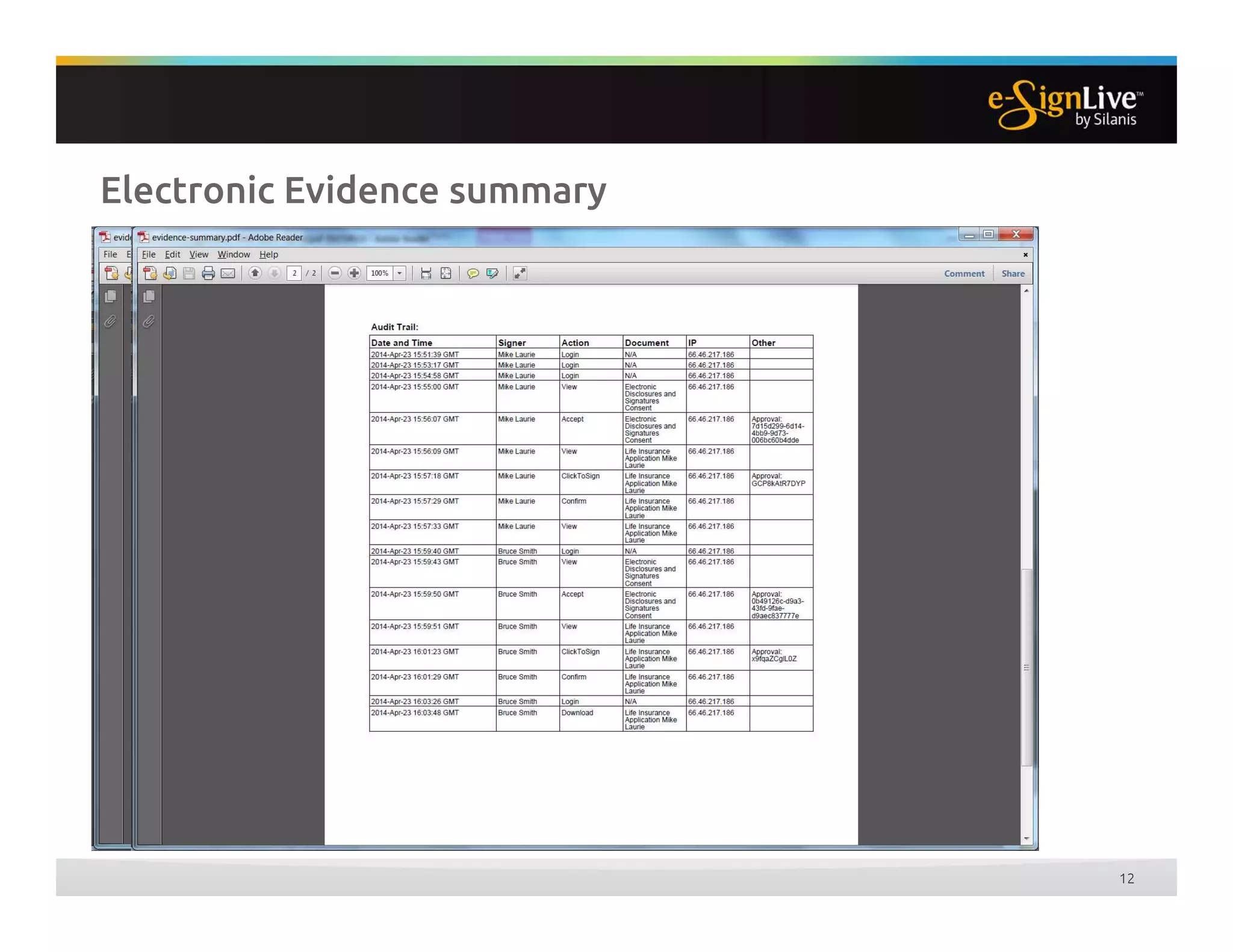
The document discusses legal best practices for using e-signatures in the insurance industry, emphasizing the importance of compliance with e-commerce and insurance laws. It outlines the processes for obtaining consent, ensuring the integrity of electronic signatures, and the retention of e-records. Furthermore, it highlights the benefits of e-signatures, such as improved customer experience and reduced operational costs.