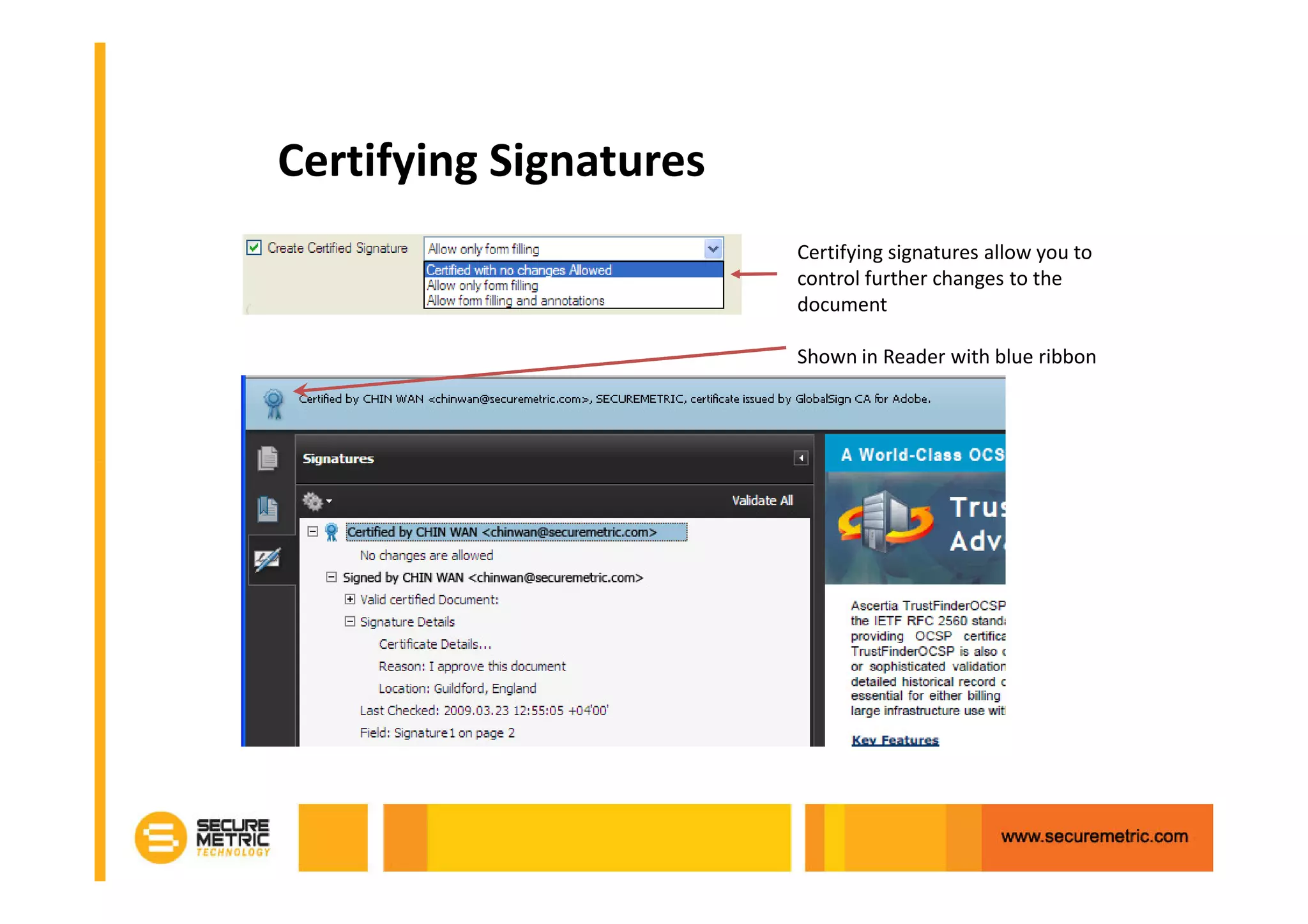
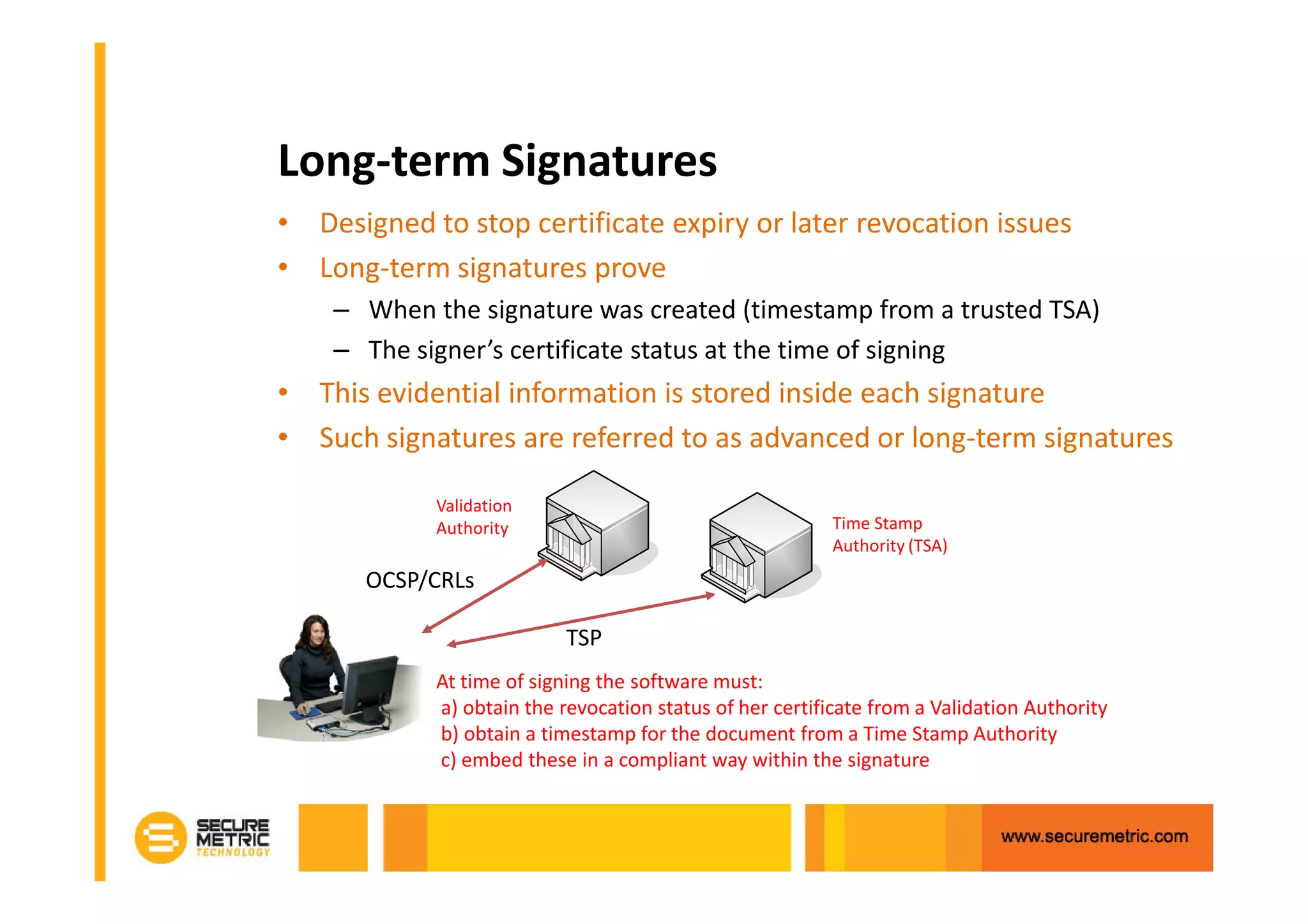
The document discusses the benefits of digitizing paper documents using public key infrastructure (PKI) to reduce business risks and costs. It notes that paper-based processes are inefficient, wasting time and resources on tasks like printing, filing, searching, and recreating lost documents. PKI provides digital signatures for authenticating, protecting integrity, and non-repudiation of electronic documents and transactions. The document examines considerations for PKI solutions, including security services, integration options, data security, and digital signature options for PDF documents.